In our deeply interconnected global marketplace, your next customer is just as likely to be in Tokyo as they are in Texas. The internet has erased geographical borders for commerce, but a far more fundamental barrier remains: language. For decades, providing high-quality, scalable customer support across multiple languages was a logistical and financial nightmare, requiring separate, dedicated human teams for each region. This created a fractured, inconsistent, and incredibly expensive global support strategy. However, a new architectural paradigm, powered by modern voice bot solutions, is finally breaking down this “Tower of Babel.”
The ability to speak a customer’s native language is not a luxury; it is a fundamental prerequisite for earning their trust and their business. This preference is even stronger in the world of customer support, where clarity and understanding are paramount.
The multilingual voicebot solutions of today are not just about translating a script; they are about leveraging a flexible, AI-powered architecture to deliver a truly native and natural conversational experience to every user, on every continent.
Table of contents
- Why Did Traditional Voice Systems Fail at Multilingual Support?
- What is the Architectural Shift That Enables Modern Multilingual Voicebots?
- How Does a Multilingual Call Work in Real-Time? A Step-by-Step Workflow
- What Are the Business Benefits of Deploying Multilingual Voicebot Solutions?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Did Traditional Voice Systems Fail at Multilingual Support?
To appreciate the modern solution, we must first understand why the old model was so fundamentally broken. Traditional Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems were built on a foundation of rigidity.
- They Were Hard-Coded and Static: An IVR was a simple, pre-programmed flowchart. To support a new language, you had to build an entirely new, separate flowchart.
- They Relied on Pre-Recorded Audio: Every single prompt and menu option had to be professionally recorded in every target language. Adding a simple new option, like for a temporary promotion, required a new recording session for every language, a slow and costly process.
- They Created a Fractured User Experience: Businesses set up separate language-specific numbers or clumsy menus, and these systems remained siloed with no shared intelligence or context.
This model was not scalable, not agile, and certainly not intelligent. It was a 20th-century solution that was completely unprepared for the demands of a 21st-century global economy.
Also Read: How Do You Measure Success After Building Voice Bots? Which KPIs Matter?
What is the Architectural Shift That Enables Modern Multilingual Voicebots?
The revolution in multilingual voicebot solutions is not the result of a single, magical “translation” AI. It is the result of a profound architectural shift from a monolithic, vertically integrated model to a decoupled, model-agnostic one.
The “Brain and Senses” Model of a Modern Voicebot
Think of a modern voicebot not as a single piece of software, but as a system with a central “brain” and a set of pluggable “senses.”
- The “Brain” (The LLM): The core intelligence of your voicebot is its Large Language Model (LLM). Modern, state-of-the-art LLMs (like those from OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic) are inherently multilingual. They are trained on vast datasets of global text and can understand and generate responses in dozens of different languages with incredible fluency. You have one, powerful, multilingual brain.
- The “Senses” (The STT and TTS): The “ears” of your bot (the Speech-to-Text engine) and the “mouth” (the Text-to-Speech engine) are the specialized sensory inputs. The key is that these are now interchangeable, pluggable components.
The platform that connects this all together is a modern voice bot solution provider like FreJun AI. Our platform is model-agnostic. We are not the brain or the senses. We are the high-performance “nervous system” that connects them. Our job is to provide the high-quality, low-latency audio stream, and we give you the complete freedom to connect that stream to the absolute best-in-class “ears” and “mouth” for any given language.
How Does a Multilingual Call Work in Real-Time? A Step-by-Step Workflow
This model-agnostic architecture allows for an incredibly powerful and dynamic workflow for handling a multilingual call. Let’s trace the journey of a call from a German-speaking customer.
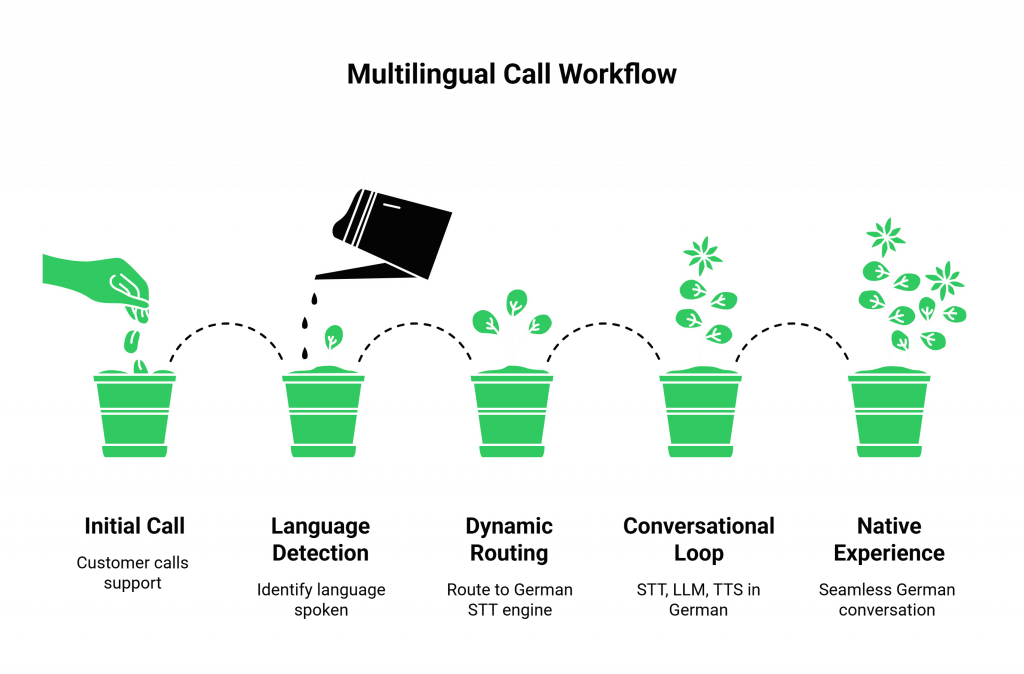
Step 1: Real-Time Language Detection
The first, critical step is to identify the language being spoken. This is the core of language detection voice ai.
- Explicit Identification: The simplest method. The customer calls a dedicated German phone number. Your application sees which number was dial and instantly learn the language context.
- Automatic Identification: The customer calls a general support number. Your application starts by playing a neutral greeting or a multi-language prompt. The first few seconds of the customer’s speech are captured and sent to a specialized, high-speed “language identification” AI model. This model returns a result: “Language Detected: German.”
Step 2: Dynamic, Intelligent Model Routing
Once your application’s central “brain” knows the language is German, it makes a crucial, real-time decision. Instead of using its default English “senses,” it will now use its specialized German ones.
- It takes the live audio stream of the call, provided by the FreJun AI platform’s real-time media API.
- It routes this stream to your chosen, best-in-class German Speech-to-Text (STT) engine.
Step 3: The Multilingual Conversational Loop
The rest of the conversation follows this intelligent, language-specific path.
- The German STT provides a highly accurate transcription of the user’s German speech.
- This German text is sent to your central, multilingual LLM, which understands it and formulates a response in German.
- Your application takes this German text response and sends it to your chosen, high-quality, native-sounding German Text-to-Speech (TTS) engine.
- The FreJun AI platform plays this perfectly synthesized German audio back to the user.
This entire loop happens in a fraction of a second, providing a seamless and completely native-language experience.
Also Read: How Do You Integrate LLMs When Building Voice Bots For Real-Time Calls?
This table visualizes this dynamic, model-switching workflow.
| Stage of the Call | The Core Task | The Architectural Component Used |
| Call Connection | Establish a high-quality, low-latency call from the user’s location. | The global voice infrastructure of the FreJun AI Teler engine. |
| Language Identification | Determine the language the user is speaking. | A specialized language detection voice ai model integrated into your application. |
| Real-Time Transcription | Convert the user’s live speech into accurate text. | The real-time media API is used to stream the audio to your chosen, German-specific STT engine. |
| Response Generation | Create an intelligent, context-aware response in the correct language. | Your powerful, multilingual LLM and your application’s business logic. |
| Voice Synthesis | Convert the response text into a natural-sounding, native voice. | Your chosen, German-specific TTS engine. |
| Audio Playback | Play the synthesized audio back to the user on the live call. | The FreJun AI platform’s call control API. |
Ready to build a voicebot that can speak the language of all your customers? Sign up for FreJun AI and explore our powerful, model-agnostic voice infrastructure.
What Are the Business Benefits of Deploying Multilingual Voicebot Solutions?
Investing in true multilingual voicebot solutions is not just a technical upgrade; it is a powerful driver of global business growth.
- Expanded Global Market Access: By speaking your customers’ language, you remove a major barrier to entry in new international markets. You make your products and services more accessible and your brand more appealing to a vastly larger audience.
- Dramatically Improved Customer Experience (CX) and Trust: Communicating with a customer in their native language is a profound sign of respect. It shows that you understand and value their culture, which is a massive driver of brand loyalty and trust. A recent study by McKinsey on personalization found that 71% of consumers expect companies to deliver personalized interactions, and language is the most fundamental form of personalization.
- Significant Operational Efficiency: This architecture allows you to consolidate your global voice automation onto a single, unified platform. Instead of managing dozens of separate, country-specific IVR systems, you have one, intelligent “brain” that can serve the entire world. This is dramatically more cost-effective and easier to maintain.
Also Read: Why Should Businesses Invest In Building Voice Bots, Not Just Chatbots?
Conclusion
The world is a rich and diverse tapestry of languages. For a business to succeed on a global scale, it must be able to communicate within that tapestry. The rigid, monolithic systems of the past were completely incapable of this.
Modern voice bot solutions, built on the foundation of a flexible, model-agnostic, and globally distributed voice platform, are the key to unlocking true, scalable multilingual communication.
By providing a powerful “nervous system” that allows a single, intelligent AI “brain” to use the best possible “ears” and “mouth” for any language, this architecture makes it possible to deliver a truly native, natural, and exceptional experience to every customer, no matter what language they speak.
Want to do a deep dive into our model-agnostic architecture and see how you can route a live audio stream to a specialized language model? Schedule a demo with our team at FreJun Teler.
Also Read: IVR Software with CRM Integration: Benefits, Setup & Use Cases
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Their model-agnostic architecture allows integration with the best, most accurate, language-specific AI models for a truly native-sounding conversational experience.
Language detection voice ai analyzes the first few seconds of a caller’s speech to automatically identify their language and route them accordingly.
No. You can use a single, central, multilingual AI “brain” (LLM) and then dynamically plug in the correct “senses” (STT/TTS) for each language.
Yes, by integrating with a high-quality, specialized Text-to-Speech (TTS) provider for each target language, the voice can sound like a native speaker.
With a model-agnostic architecture, it is much simpler. It primarily involves integrating a new set of STT and TTS models for that language.
It is a platform that is not tied to a single AI provider, giving you the freedom to choose and integrate the best AI models.
Low latency is critical for a natural conversation in any language. A globally distributed infrastructure ensures a fast response for users everywhere.
