The world of voice AI is in a state of hyper-acceleration. The clunky, frustrating “press one for sales” IVR systems that have defined automated telephony for decades are rapidly becoming historical artifacts. We have now entered a new era, powered by the stunning advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), where building voice bots is no longer about scripting rigid, decision-tree-based menus; it is about creating genuinely intelligent, empathetic, and effective conversational partners.
But this is just the beginning. The next five years will see a series of profound technological and strategic shifts that will once again redefine what is possible.
For developers, business leaders, and strategists, understanding these future conversational ai shifts is not just an academic exercise; it is a critical necessity for staying ahead of the curve. The tools we use, the architectures we design, and the user experiences we create are all about to evolve at a breathtaking pace.
From hyper-realistic emotional expression to the rise of the autonomous agent, the telephony innovation roadmap is pointing toward a future where voice bots are not just a feature, but a core pillar of business operations. This article will explore the five most important trends that will define the next five years of building voice bots.
Table of contents
The Rise of Proactive, Goal-Driven Autonomous Agents
Today, the vast majority of voice bots are reactive. They wait for a user to call and ask a question. The future of voice AI is proactive. The next generation of voice agents will be autonomous, goal-driven systems that can initiate conversations, manage complex, multi-step tasks, and make intelligent decisions without human intervention.
What Does “Autonomous Agent” Mean in a Voice Context?
Think of an AI agent that is integrated with a company’s CRM and sales pipeline.
- Today’s Model: A salesperson logs a note to follow up with a lead in two weeks.
- The Future Model: The salesperson simply tells the system, “Have our AI agent follow up with this lead in two weeks to see if they are ready for a demo.” The AI agent then autonomously schedules the call, makes the call at the designated time, has a natural conversation with the lead, answers their questions, and if the lead is qualified, it directly accesses the salesperson’s calendar and books the demo. The human is only involved at the end of the workflow, not at every step.
This shift is enabled by emerging speech ai models that are not just conversationalists but also powerful “reasoning engines” capable of planning and executing tasks.
Also Read: VoIP API: Building Voice Communication into Your Applications
Hyper-Personalization and Emotional Intelligence (Affective Computing)
The next frontier in building voice bots is moving beyond just understanding the words a user is saying to understanding the emotions behind those words. This field, known as affective computing or emotion AI, will be a game-changer for customer experience.
How Will AI Detect and Respond to Emotion?
The voice platform itself will become a sophisticated sensor. By analyzing the raw audio stream of a call in real-time, it can detect subtle acoustic cues in the human voice, pitch, tone, speaking rate, and volume, to determine the caller’s emotional state.
- The Workflow: An AI voice agent is handling a support call. The underlying platform detects rising levels of frustration in the caller’s voice. This “sentiment score” is passed to the LLM as a piece of metadata along with the transcribed text.
- The Empathetic Response: The LLM, now aware of the user’s frustration, can radically change its strategy. It might switch to a more empathetic tone, proactively offer to escalate the call to a human supervisor, or offer a concession like a discount or a credit.
The Shift to Edge-Native Voice Architectures for Ultra-Low Latency
The speed of the conversation is everything. As we demand more complex and real-time interactions from our voice bots, the architectural limitations of a purely centralized cloud model will become a major bottleneck. The telephony innovation roadmap is pointing decisively toward the edge.
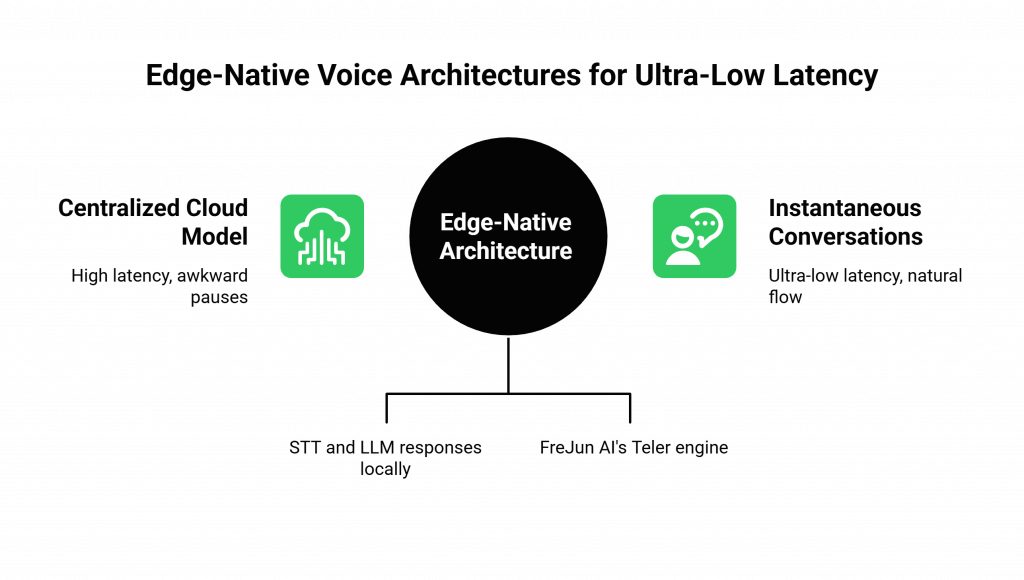
Why is “The Edge” So Important?
“The edge” refers to a computing architecture where the processing happens at a location physically closer to the end-user, rather than in a distant, centralized data center.
- The Latency Problem: In a centralized model, a call from a user in Tokyo might have to travel all the way to a server in Virginia and back. This physical distance adds hundreds of milliseconds of latency, creating that awkward pause in the conversation.
- The Edge Solution: In an edge-native architecture, the Tokyo user’s call is handled by a server in Tokyo. The most time-sensitive parts of the AI workflow, like the initial Speech-to-Text (STT) processing and even some simple LLM responses, happen locally. This drastically reduces the round-trip time, making the conversation feel instantaneous.
This is a core part of the FreJun AI architectural philosophy. Our globally distributed Teler engine is an edge-native platform, designed to provide the ultra-low-latency foundation that the future of voice AI will be built on.
Ready to build on a platform that is designed for the future of AI? Sign up for FreJun AI.
Also Read: Voice Call API: Automating and Scaling Customer Communication
The Rise of Multimodal and Omnichannel Voice Experiences
Voice will no longer be an isolated channel. The future of building voice bots is about creating seamless, multimodal experiences where a conversation can start in one channel and move fluidly to another, with the full context of the interaction intact.
What is a Multimodal Conversation?
Imagine a customer is on a voice call with an AI agent to troubleshoot a piece of hardware. The AI says, “I see you’re having trouble with the setup. I’m sending a video tutorial to your phone right now. Can you take a look?”
The customer can watch the video while still on the line with the AI, who can then answer any follow-up questions. This blending of voice, video, and text in a single, unified session will become the new standard for a great customer experience.
This table summarizes these key future trends.
| Trend | What It Is | The Impact on Building Voice Bots |
| Proactive, Autonomous Agents | AI that can initiate and execute complex, goal-driven tasks. | A shift from reactive, inbound bots to proactive, outbound agents that manage entire workflows. |
| Emotional Intelligence | AI that can understand and respond to the user’s emotional state. | A move from purely transactional bots to more empathetic and human-like conversational partners. |
| Edge-Native Architectures | Processing the AI workflow at a location closer to the user. | A relentless focus on minimizing latency to enable truly real-time, natural-sounding conversations. |
| Multimodal & Omnichannel | Blending voice with other channels like text and video in a single, unified session. | A move away from building a “voice bot” to building a single AI “brain” that can communicate across all channels. |
A Hyper-Specialization of AI Models
The era of a single, monolithic LLM trying to do everything is coming to an end. The future of emerging speech ai models is specialization.
- The “Mixture of Experts” Model: The AI voice architecture 2025 will likely involve a sophisticated routing system where a single voice agent uses multiple, smaller, specialized AI models during a single conversation. A small, incredibly fast model might handle the initial greeting and simple Q&A. A model specifically trained on empathetic language might be called upon when a user is upset. A model with deep technical knowledge might be used for a complex support query.
- The “Model-Agnostic” Imperative: This trend makes a model-agnostic voice infrastructure an absolute necessity. Businesses must have the freedom to choose the best-in-class specialized model for each part of the conversational task. A platform that locks you into a single, proprietary LLM will be a major competitive disadvantage.
This trend in enterprise adoption patterns will favor platforms that provide maximum flexibility and control, allowing businesses to assemble their own “dream team” of AI models.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Voice Calling SDK for Your Product
Conclusion
The journey of building voice bots is just beginning. The technology is moving beyond the simple automation of repetitive tasks and is entering a new, more profound phase of intelligence, empathy, and autonomy. The next five years will be defined by a relentless push for more natural, more proactive, and more deeply integrated conversational experiences.
The companies that will win in this new era will be those that embrace the future conversational ai shifts, the move to the edge, the fusion of multiple channels, and the hyper-specialization of AI. For developers and business leaders, the message is clear: the time to start building on a flexible, scalable, and future-ready voice platform is now.
Want to have a strategic discussion about your company’s telephony innovation roadmap and how our platform can help you prepare for these future trends? Schedule a demo for FreJun Teler.
Also Read: How to Select the Best Cloud Telephony Solution for Your Industry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The single biggest trend is the move from reactive to proactive, autonomous agents. The future of voice AI will be defined by bots that can independently initiate and execute complex, multi-step tasks based on a given goal, rather than just responding to inbound queries.
The key trend is specialization: voice agents will use multiple smaller expert models for tasks like empathy or technical knowledge.
The telephony innovation roadmap focuses on moving intelligence to the network edge. It builds a global infrastructure that processes time-sensitive AI conversation parts closer to the user, minimizing latency.
Enterprise adoption is shifting from small IVR projects to unified conversational AI platforms deployed across channels and business units.
The key shift is integrating emotional intelligence, enabling voice bots to sense caller emotions and respond with empathy and personalization.
A multimodal conversation blends multiple communication types in one session. For example, a voice bot can send a diagram or video to a user while the call is ongoing, creating a richer, more effective interaction.
AI evolves rapidly. A model-agnostic platform like FreJun AI lets you use the best models from any provider, future-proofing your investment.
