What if your AI agents could do more than just process text in a simulated environment? Imagine an AI that could pick up the phone, collaborate with another AI to solve a problem, and then execute a task in the real world, like booking your dinner reservation or qualifying a sales lead. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the powerful future unlocked by a framework called Camel-AI.
But these brilliant agents are often trapped, unable to speak or listen. The key to unleashing their true potential lies in one transformative technology: VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI.
Camel-AI, which stands for Communicative Agents for “Mind” Exploration of Large Scale Language Model Society, introduces a groundbreaking concept where AI agents role-play and instruct each other to complete complex tasks. This creates a powerful, autonomous system for problem-solving.
However, without a voice, their ability to interact with the world is severely limited. This guide will show you how integrating a voice layer can bridge that gap, turning your text-based agents into powerful, real-world actors.
Table of contents
- What is Camel-AI and Why is it Different?
- Why Does Your AI Agent Need a Voice?
- How To Guide of VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI
- Unlocking New Use Cases with Voice-Enabled Camel-AI
- FreJun AI: The Voice Infrastructure Built for Your AI
- Challenges and Considerations for Your Project
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Camel-AI and Why is it Different?
Before we connect a voice, it’s crucial to understand what makes Camel-AI so special. Unlike single chatbots that simply respond to a user, Camel-AI creates a dynamic partnership between multiple agents.
The Power of Role Playing Agents
The core idea of Camel-AI is a clever technique called “inception prompting.” Here is how it works in simple terms:
- An “AI user” agent is created. Its job is to act like a human and provide instructions.
- An “AI assistant” agent is created. Its job is to follow the instructions and solve the problem.
The AI user tells the AI assistant what to do, and the assistant works on the task, asking for clarification if needed. This setup allows the agents to carry on a conversation and “brainstorm” solutions together, leading to more comprehensive and creative problem solving without constant human intervention.
Beyond Single Agents: Creating a Collaborative AI Society
This framework allows developers to build entire “societies” of AI agents that can collaborate to break down and solve incredibly complex problems. This approach moves us from simple command and response AI to a future where autonomous agents can manage multi-step projects. But to tackle tasks in the real world, this society needs a way to communicate outside its digital sandbox.
Also Read: How To Reduce Call Drop Rates With Voice AI Agents?
Why Does Your AI Agent Need a Voice?
The biggest limitation of a purely text-based multi-agent system is that the real world doesn’t run on text alone. Many essential tasks, from customer support to appointment scheduling, happen over the phone. Without a voice, your sophisticated Camel-AI system can’t call a supplier to check on an order or phone a customer to confirm their shipping address.
This is where a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) API comes in. A VoIP API is a service that allows your application to make and receive phone calls over the internet. Think of it as the perfect bridge that connects the digital intelligence of your Camel-AI agents to the global telephone network. This is the essence of VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI.
How To Guide of VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI
Integrating a voice layer might sound complex, but modern platforms have made it incredibly straightforward for developers. You don’t need a degree in telecommunications. Here’s a simple blueprint for bringing your agent to life.
Step 1: Choosing the Right Voice Infrastructure
The first and most important step is selecting a voice infrastructure platform. This is the “plumbing” that will handle all the complexities of making and receiving calls. When choosing a provider, you should look for:
- Low Latency: The delay in a conversation must be minimal for it to feel natural.
- Real Time Streaming: The platform must be able to send and receive audio data instantly.
- Developer Friendly SDKs: Well documented toolkits that make integration easy.
- Reliability and Scalability: An enterprise grade foundation that can handle high call volumes.
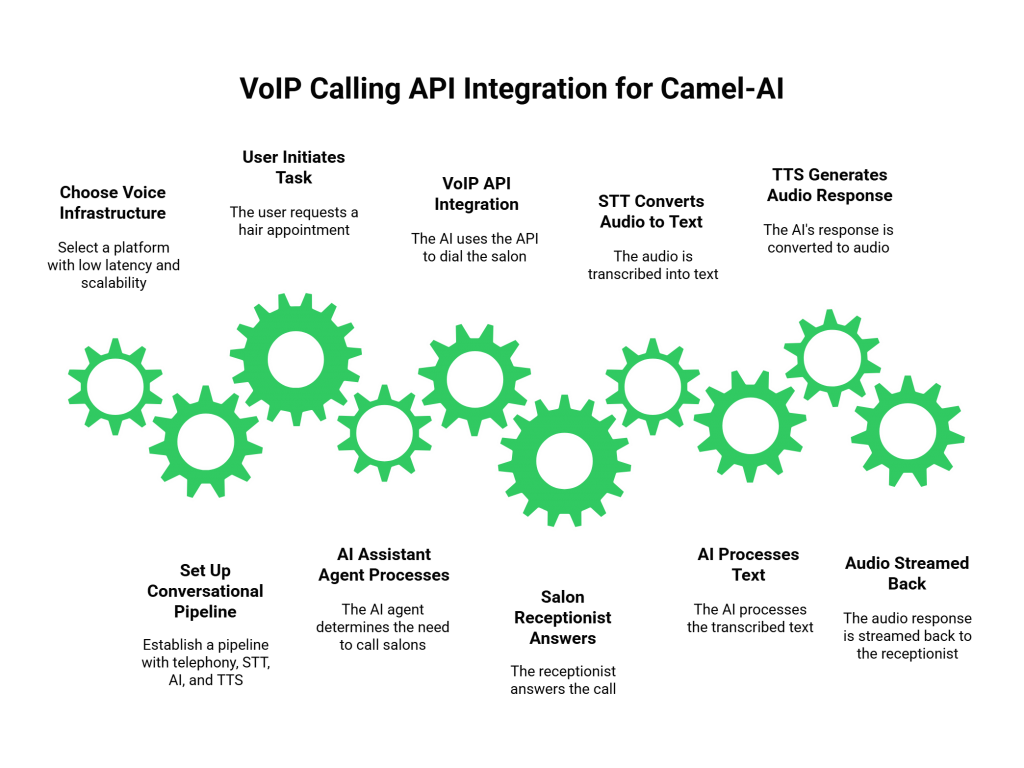
Step 2: Setting Up the Conversational Pipeline
To enable a full conversation, you need a few key components working together in a pipeline:
- Telephony Layer: This is your voice infrastructure provider that manages the phone call itself.
- Speech to Text (STT): A service that instantly converts the human’s spoken words into text for your AI to understand.
- Camel-AI Framework: This is the “brain” where your AI user and assistant agents process the text and decide on the best response.
- Text to Speech (TTS): A service that converts your AI’s text response back into natural sounding audio.
Also Read: How To Connect Voice AI To CRM Systems Effectively?
The Technical Workflow in Action
Let’s walk through a real world example. Imagine the Camel-AI user agent gives the assistant agent a task: “Find and book a hair appointment for me for this Friday afternoon.”
- The AI assistant agent determines it needs to call local salons.
- It uses a VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI, powered by a platform like FreJun AI, to dial the first salon.
- The salon receptionist answers, “Good morning, Style Cuts, how can I help?”
- The voice platform streams this audio in real time to an STT service, which transcribes it to text.
- This text is fed into the Camel-AI assistant agent.
- The agent processes the text and formulates its response: “Hello, I would like to schedule a haircut for this Friday afternoon. Do you have any availability?”
- This text is sent to a TTS service, which generates a lifelike audio clip.
- The voice platform streams this audio back to the receptionist with almost no delay.
Unlocking New Use Cases with Voice-Enabled Camel-AI
Once you have a successful VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI, you can build a new generation of autonomous agents capable of performing incredible tasks:
- Proactive Customer Support: Agents that can call a customer back to resolve a support ticket, guiding them through complex troubleshooting steps.
- Intelligent Sales Development: AI agents that can perform initial outreach calls to a list of leads, ask qualifying questions, and even schedule a demo with a human salesperson.
- Automated Concierge Services: Agents that can call to make dinner reservations, book travel, or schedule home repair services on your behalf.
- Dynamic Market Research: Agents that can conduct phone surveys that go beyond a simple script, asking intelligent follow up questions based on the person’s responses.
FreJun AI: The Voice Infrastructure Built for Your AI
To make this all possible, you need a rock solid foundation. FreJun AI provides the essential voice infrastructure designed specifically for AI applications like Camel-AI. Our core philosophy is simple: we handle the complex voice and telephony layer so you can focus on building your AI. FreJun is model agnostic, meaning you can bring your own STT, LLM, and TTS services and plug them into our platform.
Our entire architecture is optimized for the ultra low latency required for natural, real time conversations. With our developer first SDKs and enterprise grade reliability, FreJun AI provides the perfect “plumbing” to connect your Camel-AI’s brain to a real human voice.
Also Read: How To Integrate Voice Into Existing IVR Systems?
Challenges and Considerations for Your Project
As you embark on this journey, there are a few technical challenges to keep in mind:
- Managing Latency: Even a one second delay can make a conversation feel unnatural and frustrating. This is why choosing a low latency voice infrastructure is non negotiable.
- Handling Interruptions: In human conversations, people often talk over each other. Your system needs to be able to detect when the human is speaking and gracefully pause the AI’s response.
- Ensuring Natural Sound: The quality of your chosen STT and TTS services will have a huge impact on the user experience.
Conclusion
The Camel-AI framework represents a major leap forward in creating autonomous, collaborative AI systems. However, these agents unlock their true power only when they move beyond text and interact through the most natural medium: voice. A robust VoIP Calling API Integration for Camel-AI is the critical component that makes this transformation possible.
By combining a powerful multi agent framework with a reliable, low latency voice infrastructure, developers can now build a new class of smart agents that can solve real world problems, one phone call at a time.
Also Read: How Real Estate Agents Thrive Using a Robust Business Phone System in the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Camel-AI is an advanced framework where multiple AI agents work together to solve problems. Typically, one “user” AI gives instructions to an “assistant” AI, which then carries out the task, creating a more autonomous problem solving process.
Not at all. Modern voice infrastructure platforms like FreJun AI are designed for developers. They provide simple SDKs and APIs that handle all the complex telephony, allowing you to make and receive calls with just a few lines of code.
You need four main components for this setup. A voice infrastructure provider like FreJun AI handles the call. A Speech-to-Text (STT) service converts human speech into text. The Camel-AI framework works as the brain. A Text-to-Speech (TTS) service generates the agent’s voice.
Latency is the delay between when someone speaks and when the other party hears and can respond. High latency leads to awkward pauses and makes the conversation feel unnatural and robotic. For a believable AI agent, ultra-low latency is essential.
Since Camel-AI agents run on large language models, they don’t stick to rigid scripts, they adapt naturally to each conversation. They can understand context and respond dynamically to unexpected questions. They can also adapt to changes, making conversations feel more human.
