Businesses today are no longer asking if they should connect their CRM with voice AI, but how to do it effectively. With customer interactions shifting toward automation, the ability to integrate top programmable voice AI APIs with low latency is becoming a competitive advantage. A well-designed voice API for developers makes it possible to bridge live conversations with CRM records in real time – reducing manual work, improving data accuracy, and creating seamless customer experiences.
This blog will guide founders, product managers, and engineering leads through the technical path: from mapping CRM schemas to handling speech recognition, latency, and compliance.
Why Connect Voice AI With Your CRM
Customer calls are still one of the most important ways businesses interact with clients. But in most companies, the call data and the CRM system do not talk to each other well. A sales rep or support agent may spend ten minutes on a call, then another five manually writing notes, logging activities, or updating records. This wastes time and creates errors.
By linking an AI-powered voice bot solution directly to a CRM, every part of that process can be automated. Calls are transcribed in real time, customer details are pulled from the CRM instantly, and new records are updated as the conversation happens.
The result is not just efficiency. It also improves the quality of the customer experience, ensures accurate reporting, and gives managers a reliable view of what is really happening on the front line. According to CRM.org, 91% of companies with more than 10 employees already rely on CRM systems, showing how central these platforms are to daily business.
What Does Voice AI and CRM Integration Actually Mean
When we say “connect voice AI to CRM,” we are talking about creating a technical bridge between live voice conversations and structured CRM records. This bridge is made up of a few clear parts:
- Speech-to-Text (STT) turns audio from a call into text, usually within milliseconds.
- A dialogue manager or language model interprets the text, understands intent, and decides what to do next.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) then turns the response into natural audio and plays it back to the caller.
- The CRM connector reads data from the CRM (like customer history) and writes new actions back (like creating a ticket or logging a call).
- The transport layer, which could be telephony or VoIP, ensures low-latency audio streaming so the conversation feels natural.
Unlike traditional IVR menus, this setup allows the AI voicebot to handle free-flowing conversations, adapt in real time, and map spoken actions to actual CRM entities such as contacts, leads, opportunities, or cases.
Why Connecting Voice AI to CRM Systems Is Hard
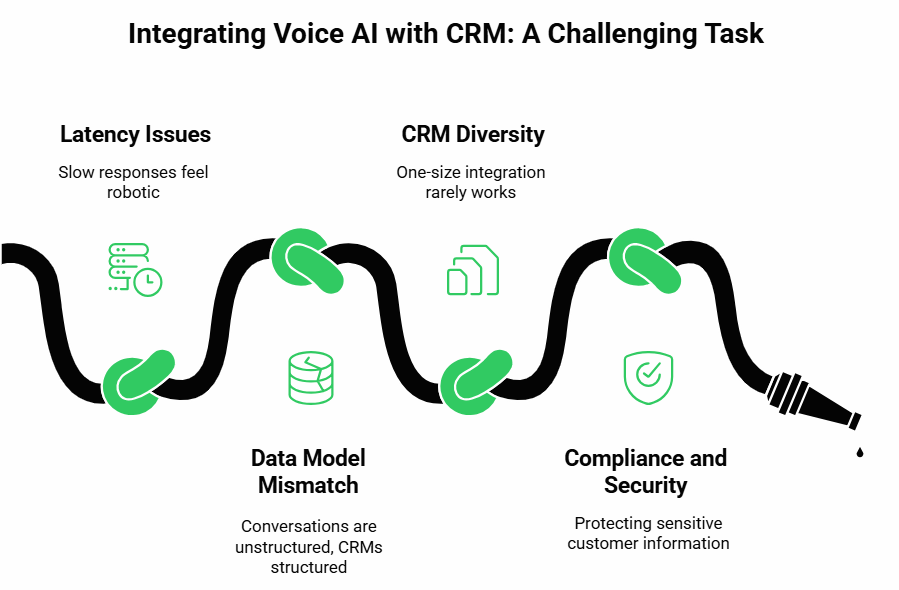
On paper, it looks simple: capture voice, convert it to text, send it to an AI agent, update CRM. In practice, the difficulties are real and often underestimated.
First is latency. A natural conversation has very little tolerance for delay. If the customer finishes a sentence and the response comes two seconds later, the experience feels robotic. This means speech recognition, CRM lookups, and voice playback must all be optimized to work together within a narrow time budget.
Second is the data model mismatch. Conversations are unstructured and fluid. CRMs, by design, are structured systems. A single sentence from a customer like “I want to move my appointment to Thursday at 3” may involve updating a calendar object, changing a ticket status, and creating a note. Mapping natural conversation to structured fields requires careful design.
Third is CRM diversity. A modern CRM like HubSpot may have a clean REST API, while an older system may expose only SOAP interfaces with rate limits. A one-size integration rarely works. Middleware layers or custom adapters are often required.
Finally, there are compliance and security demands. Call data often contains personally identifiable information. The system has to encrypt media, protect API credentials, and log access in a way that meets standards such as GDPR or HIPAA.
These challenges make it clear that connecting voice AI to CRM is not just another software integration. It is a systems problem that touches infrastructure, APIs, and compliance all at once.
Core Components You Will Need
A working solution always has five moving parts.
- STT engine – This captures audio from the call and streams text in real time. For voice AI, it must provide partial transcripts and handle domain-specific terms. A survey showed 73% of users cite accuracy as the top barrier in adopting speech recognition, which is why picking the right STT is critical.
- Dialogue and AI layer – This interprets the text, understands intent, and manages conversation flow. It is where the logic for when and how to call the CRM lives.
- CRM connector – This is the technical bridge to the CRM system. It may be a REST API client, a webhook handler, or a middleware layer that adapts old interfaces.
- TTS engine – This generates human-like audio responses. For good user experience, it must support streaming output and barge-in (speaking while still listening).
- Transport layer – This is the telephony or VoIP system that ensures calls can be made or received and audio packets are delivered with minimal delay.
This modular view helps product teams understand that no single vendor usually solves all five. Most successful projects pick best-in-class components for each layer and then stitch them together.
Explore our guide on deploying AI voicebots over existing SIP trunks to scale automation without replacing your core infrastructure.
How To Connect an AI Voicebot to a CRM Step by Step
The process of integration is best done in stages rather than all at once.
Step 1: Define use cases
Start by deciding what business problems the voice AI will solve. Will it qualify leads, reschedule appointments, or handle tier-1 support questions? The CRM fields you need to read or write depend directly on these goals.
Step 2: Map CRM schema
Review the CRM’s object model. Understand how contacts, tickets, deals, or custom fields are structured. This schema mapping is essential to avoid integration failures later.
Step 3: Set up STT, AI, and TTS pipeline
Establish the real-time audio flow. Connect STT to the dialogue manager, ensure responses are generated quickly, and confirm that TTS playback feels natural in a call environment.
Step 4: Build middleware for the CRM
Rather than connecting your AI agent directly to CRM APIs, introduce a middleware service. This service can queue requests, manage retries, handle authentication, and translate between conversational outputs and CRM fields.
Step 5: Test with a narrow workflow
Start with one specific use case, such as “check order status” or “log a new lead”. Run it end-to-end with real calls. Measure latency, transcription accuracy, and CRM write speed.
Step 6: Scale gradually
Once the narrow workflow is reliable, expand to additional cases. Introduce error handling, fallbacks to human agents, and monitoring dashboards.
This step-by-step approach ensures that complexity is introduced gradually and problems are isolated early.
Which CRM Systems Are Commonly Integrated With Voice AI
Different CRM systems require different integration strategies.
- Salesforce – Offers REST and streaming APIs, supports webhooks, and has a mature ecosystem. Good fit for real-time updates.
- HubSpot – Provides modern APIs for contacts, tickets, and deals. Can be extended with custom apps.
- Zoho and Freshworks – API-first CRMs with straightforward authentication. Well suited for smaller deployments.
- Microsoft Dynamics – Often used in large enterprises, requires more configuration and sometimes legacy adapters.
- Legacy or custom CRMs – May expose only SOAP APIs or require CSV-based imports. These often need a middleware service to adapt to modern AI pipelines.
Choosing the right CRM is not just about features, but also about API performance and flexibility. If a CRM cannot handle the required request volume with low latency, the voice AI experience will always suffer.
How to Maintain Conversational Context Inside a CRM
A common failure in AI voicebot projects is treating the CRM as just a note-taking system. Simply dumping transcripts or call summaries into a notes field does not create usable data.
Instead, conversational context should be preserved in a structured way.
- Key actions, like “create ticket”, “update opportunity”, or “reschedule appointment”, must map directly to CRM entities.
- Full transcripts can be stored as attachments or reference logs, but summaries should be extracted into structured fields.
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques can be used to fetch CRM data mid-call, so the voice AI can answer with live context.
- State management ensures the conversation flows logically. If a customer mentions an order number early in the call, that identifier should be carried forward and used when updating CRM records later.
This disciplined approach prevents the CRM from becoming a dumping ground and instead turns it into a dynamic partner in live conversations.
Best Practices for Low-Latency Voice AI Integration
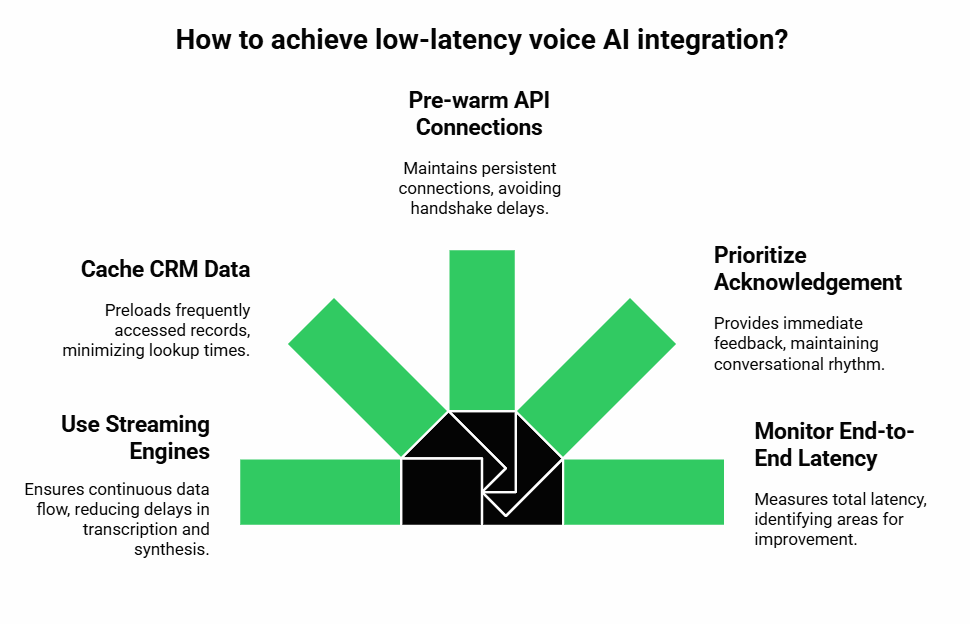
People often ask, how do you avoid awkward pauses in AI-driven conversations? The answer lies in system design.
- Use streaming engines – Both STT and TTS should operate in streaming mode. Batch transcription or synthesis introduces delay that breaks natural flow.
- Cache CRM data – Frequently accessed records, like open tickets for a known customer, can be preloaded to reduce lookup times.
- Pre-warm API connections – Persistent HTTP connections or gRPC channels to the CRM prevent extra handshake time.
- Prioritize acknowledgement – Always send a quick “got it” response to the caller while background CRM writes complete. This maintains conversational rhythm.
- Monitor end-to-end latency – Measure not just STT or TTS, but the total path from spoken word to CRM update to spoken response.
Low latency is not just about technology. It is about designing the system to mask unavoidable delays and keep the interaction feeling natural.
How Does Teler Solve the Hard Parts
Many companies try to build their own telephony bridges or rely on legacy call platforms, only to find that latency and reliability are constant blockers. This is where FreJun Teler comes in.
Teler is designed as a global voice infrastructure for AI agents. Its role is not to replace your AI or your CRM but to act as the transport layer that makes real-time conversations possible.
Key aspects include:
- Real-time media streaming: Audio is streamed in both directions with extremely low delay, so conversations flow naturally.
- Model-agnostic design: You can use any LLM, STT, or TTS provider. Teler does not lock you in, it ensures the pipeline works reliably.
- Developer-first SDKs: Teams can integrate Teler with their backend logic and CRM middleware in days, not months.
- Enterprise reliability: Calls are routed on geo-distributed infrastructure, with built-in redundancy and encryption.
This makes Teler different from competitors. Most platforms that offer calling are optimized for dialer campaigns or contact centers. Teler, on the other hand, is optimized for AI-first workflows, where the AI agent is in control and the call platform is the enabler.
For a founder or engineering lead, this distinction matters. It means you can design your own AI logic, connect it directly to CRM systems, and rely on Teler to handle the hardest part – streaming high-quality voice in real time.
What Are Common Use Cases for Voice AI + CRM Integration
Once the voice AI is linked to the CRM, the number of applications expands quickly. The following are the most common scenarios.
Automated Lead Qualification
An AI voicebot can make outbound calls to new leads, ask qualifying questions, and log results directly into the CRM. Reps only need to follow up with leads that meet defined criteria.
AI Receptionist and Inbound Triage
Instead of waiting for a human to pick up, incoming calls can be answered by an AI agent that greets the caller, looks up their record in the CRM, and either resolves simple issues or routes the call to the right human.
Proactive Outbound Campaigns
Appointment reminders, subscription renewals, and payment follow-ups can be handled automatically. Every call attempt and outcome is logged back into the CRM for visibility.
Customer Service Automation
Tier-1 support requests, like password resets or order status queries, can be handled without human intervention. The CRM is updated with resolution details, freeing agents for complex issues.
Feedback and Survey Logging
Voice surveys can be conducted at scale, with results automatically tied to customer profiles in the CRM.
Each of these use cases is only possible when the voice AI can fetch data from the CRM during a call and write back actions immediately after.
How Do You Ensure Security and Compliance
Voice data is sensitive. Without proper safeguards, integration can create risks. Here are the essential practices:
- Encrypt everything: Audio streams must be encrypted in transit, and CRM API calls must use secure channels like TLS.
- Role-based access: Not every agent or AI process should have full CRM permissions. Use scoped API keys and granular roles.
- Data minimization: Only the fields required for the conversation should be exposed to the AI agent.
- Audit logging: Every action taken by the AI should be logged with timestamps and identifiers. This helps with accountability.
- Regulatory compliance: For industries like healthcare or finance, ensure that both the voice platform and the CRM integration meet HIPAA, GDPR, or SOC 2 requirements.
Security is not optional. In many cases, a deal with a large client depends entirely on being able to demonstrate compliance.
Learn best practices to secure voice AI and VoIP communications, ensuring encrypted conversations and compliance across customer-facing integrations.
What Mistakes to Avoid in Voice AI + CRM Integration
Many projects fail not because of technology but because of design mistakes. The most common include:
- Dumping transcripts into notes: This creates noise in the CRM and does not enable analytics. Always extract structured actions.
- Ignoring CRM rate limits: A flood of API requests during calls can cause throttling. Middleware should handle retries and batching where needed.
- Overlooking latency: Even a well-trained AI will sound robotic if the infrastructure introduces delays. Choose components that support streaming.
- Skipping human fallback: No AI system can resolve every case. Customers should always have a way to reach a human.
- Not involving CRM admins early: Integrations often break when custom CRM fields or workflows are ignored during design.
Avoiding these mistakes saves months of rework and ensures smoother adoption.
The Future of Voice AI and CRM Integration
Looking ahead, we can expect a few important shifts.
- Predictive insights: Instead of only logging interactions, integrated systems will analyze conversations to predict churn risk or upsell potential.
- Context-aware outreach: Voice AI agents will proactively call customers based on CRM triggers, such as inactivity or approaching renewal dates.
- Multimodal CRM assistants: Agents will combine voice, chat, and screen sharing, with all channels updating the same CRM record.
- AI-first CRM design: Rather than adding AI as a layer on top, new CRMs may be designed around AI agents as the primary interface.
For product leaders, this means planning integrations with flexibility in mind. Choosing a transport layer like Teler ensures the system can evolve as new AI models and CRM features emerge.
Conclusion
Integrating voice AI directly with CRM systems is more than a technology upgrade—it is a way to turn every customer call into structured, actionable insight. By addressing latency, context mapping, and compliance, companies can automate manual tasks, improve accuracy, and scale customer interactions without losing personalization. The path is clear: start small, design modularly, and expand with best practices in place.
FreJun Teler delivers the critical foundation for this journey. With its low-latency, model-agnostic voice infrastructure, Teler ensures any LLM, STT, or TTS engine connects seamlessly with CRM workflows. Founders, product managers, and engineering leads can focus on building intelligent experiences while Teler handles the hardest layer.
Ready to get started? Schedule a demo with Teler.
FAQs –
1: How do AI voicebots update CRM records automatically?
They capture speech, process intent, and use CRM APIs to log actions like new leads, tickets, or follow-ups instantly.
2: What latency is acceptable for real-time voice AI in CRM integration?
Anything under 500 milliseconds feels natural; using streaming STT, TTS, and optimized CRM APIs keeps conversations smooth without awkward pauses.
3: Can AI voicebots integrate with legacy CRMs lacking modern APIs?
Yes, through middleware adapters or connectors that translate conversational intent into batch imports, SOAP calls, or custom database updates.
4: How does Frejun Teler support CRM and AI voicebot integration?
Teler provides low-latency, model-agnostic voice infrastructure that bridges STT, LLMs, TTS, and CRM APIs for seamless real-time automation.
