Voice is rapidly becoming the primary interface for AI-driven applications. Whether it’s customer support, sales, or intelligent IVR systems, delivering natural, low-latency conversations is critical. Founders, product managers, and engineering leads must carefully choose the voice infrastructure that supports seamless AI integration, high reliability, and developer control. A modern Voice Chat SDK is more than just a calling library, it’s the backbone of your AI agent’s ability to listen, reason, and respond in real time.
Understanding the essential features helps teams evaluate SDKs effectively, avoid integration pitfalls, and scale voice products that are both technically robust and user-friendly.
Why Choosing The Right Voice Chat SDK Matters Today
Voice is no longer just another interface. Instead, it is becoming the most direct way humans interact with AI systems. As a result, founders, product managers, and engineering leads are now expected to deliver voice experiences that feel fast, reliable, and natural.
However, building voice products is still hard.
While LLMs can reason and generate responses, they cannot talk on their own. Between a user speaking and an AI replying, multiple systems must work together – media streaming, speech recognition, synthesis, call control, and context management. Therefore, the Voice Chat SDK becomes the backbone of the entire experience.
This article answers one key question:
What features should every modern Voice Chat SDK offer to support scalable, AI-driven voice products?
Rather than focusing on surface-level features, this guide breaks down what truly matters for voice quality, performance, and developer control.
What Is A Modern Voice Chat SDK Really Expected To Handle?
Before we list features, it is important to clarify what a Voice Chat SDK actually does today.
Traditionally, voice APIs focused only on calls. However, modern products require much more. A Voice Chat SDK now sits between users, telephony networks, and AI systems. Because of this position, it must handle both real-time media and system coordination.
At a high level, a modern SDK is expected to:
- Capture and stream real-time audio
- Support low-latency, two-way conversations
- Integrate cleanly with STT, LLMs, and TTS systems
- Maintain session and conversational state
- Optimize audio quality across unstable networks
- Expose developer tools for monitoring and control
In other words, the SDK is not the AI. Instead, it is the infrastructure that allows AI to talk.
With this context in mind, let us move step by step through the top ten features.
1. Does The Voice Chat SDK Support Real-Time, Low-Latency Audio Streaming?
Low latency is the foundation of any voice experience. Without it, even the best AI feels broken.
In voice systems, latency accumulates quickly. Audio capture, encoding, transport, decoding, processing, and playback all add delay. Therefore, a Voice Chat SDK must minimize overhead at every stage.
Empirical measurements show that even a 1% packet loss during a call can lead to noticeable audio degradation – highlighting why adaptive stream handling and packet-loss concealment are critical.
What This Feature Requires Technically
- Full-duplex (bi-directional) audio streaming
- Support for streaming protocols such as WebRTC or RTP
- Efficient audio codecs like Opus for speech
- Adaptive jitter buffers to handle network variability
- Packet loss concealment for degraded networks
Why It Matters For AI Voice Products
If round-trip latency becomes too high:
- Conversations feel unnatural
- Users interrupt the system more often
- AI responses arrive too late to stay relevant
Because of this, high-performing teams measure latency continuously and treat it as a core metric of voice SDK performance.
2. Can It Integrate With Any LLM, STT, And TTS Without Lock-In?
Voice agents are not built from a single model. Instead, they are composed of multiple systems working together.
A flexible Voice Chat SDK must allow teams to plug in:
- Any Speech-to-Text engine
- Any Large Language Model
- Any Text-to-Speech provider
Just as importantly, it must do this without controlling the AI logic.
Key Technical Requirements
- Model-agnostic interfaces
- Streaming input and output support
- No hard dependencies on vendor-specific APIs
- Clear separation between voice transport and AI logic
Why This Matters
AI models change fast. Therefore:
- Lock-in increases long-term risk
- Switching providers should not require rewriting call logic
- Teams need freedom to experiment and optimize costs
As a result, the best voice chat SDKs act as neutral carriers, not opinionated AI platforms.
3. How Well Does The SDK Handle Streaming Speech-To-Text In Real Time?
Speech-to-Text is the first link between the user and the AI. If transcription fails, everything else falls apart.
For AI-driven conversations, batch transcription is no longer enough. Instead, systems must work with streaming STT, delivering partial and final results continuously.
What Strong STT Integration Looks Like
- Partial (interim) transcripts delivered in real time
- Final transcripts with timestamps
- Confidence scores for decision-making
- Support for interruptions and restarts
- Handling of silence and background noise
Why Streaming Transcription Matters
When partial transcripts are available:
- LLMs can start reasoning earlier
- Decisions are made faster
- Overall response latency drops
Additionally, accurate timestamps make it easier to align speech with actions, tools, or follow-up prompts.
4. Does It Support Natural, Low-Latency Text-To-Speech Playback?
Once the AI responds, its output must sound right. Otherwise, trust drops immediately.
A modern Voice Chat SDK must support streamed TTS playback, not just static audio files.
Technical Capabilities To Look For
- Chunked audio streaming for fast start
- Support for SSML controls
- Audio format normalization
- Volume and speed control
- Fallback voices or engines
Why This Is Important
Without streamed playback:
- Users wait longer to hear responses
- Conversations feel mechanical
- Interruptions become harder to handle
Moreover, natural voice pacing helps maintain flow, which is why voice quality optimization is tightly tied to TTS design.
5. Can The SDK Maintain Full Conversational Context Across A Live Call?
Conversational AI only works if context survives.
In voice systems, context loss often happens due to:
- Network drops
- Call transfers
- SDK reconnections
- Backend restarts
Therefore, session management is not optional.
What Good Context Handling Includes
- Stable session identifiers
- Ordered event delivery
- Reconnection and resume logic
- Clear hooks to sync context with backend state
Why This Feature Is Critical
Voice agents often use:
- RAG systems
- Tool calls
- Long multi-turn conversations
If the SDK breaks context, the AI appears confused, even if the model is strong.
As a result, high-quality voice SDKs treat session continuity as a core system concern.
6. Does It Provide Reliable Call Control And Telephony Capabilities?
Even in AI-first products, telephony fundamentals still matter.
Many use cases require:
- Inbound calls
- Outbound calls
- Call transfers
- IVR-style routing
Therefore, a Voice Chat SDK must expose call control primitives cleanly.
Key Capabilities
- SIP and PSTN support
- Call state events (ringing, answered, completed)
- DTMF handling
- Programmable call flows
- Webhook-based call orchestration
Why This Still Matters
AI does not replace telephony. Instead, it enhances it.
Without strong call control features:
- Integrations become fragile
- Edge cases multiply
- Scaling becomes harder than necessary
7. How Does The SDK Optimize Voice Quality Under Real-World Network Conditions?
Even if latency is controlled, voice quality can still break the experience. In real deployments, users speak from mobile networks, noisy environments, and unstable connections. Therefore, a Voice Chat SDK must actively optimize for imperfect conditions.
Voice quality optimization is not a single feature. Instead, it is a combination of continuous adjustments.
Core Technical Elements Of Voice Quality Optimization
- Adaptive jitter buffering to handle packet delays
- Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC)
- Noise suppression and automatic gain control
- Codec negotiation based on network conditions
- Packet loss recovery and concealment
Because voice traffic is real time, dropped packets cannot be retransmitted. As a result, the SDK must make audio sound acceptable even when data is missing.
Why This Matters For Voice SDK Performance
If audio quality degrades:
- Speech-to-text accuracy drops
- AI responses become less relevant
- Users repeat themselves more often
Therefore, strong voice SDK performance depends as much on media engineering as it does on AI quality.
8. Can The SDK Record, Transcribe, And Store Conversations For Analytics And RAG?
Recording is no longer just a compliance feature. Instead, it has become an essential input for learning and improvement.
A modern Voice Chat SDK must support recording at scale, while keeping data secure and searchable.
What Recording Support Should Include
- Configurable live or post-call recording
- Separate audio tracks per speaker
- Timestamped transcripts
- Metadata capture (call ID, duration, outcomes)
Why This Feature Is Critical For AI Voice Systems
Recorded conversations are used for:
- Quality analysis
- Model evaluation
- Training data generation
- RAG pipelines using vector databases
Because of this, the SDK should expose clean hooks to export recordings and transcripts into external systems. Without this flexibility, teams struggle to close the learning loop.
9. Does It Meet Enterprise-Grade Security And Reliability Standards?
Voice data is sensitive. As a result, security cannot be added later.
A production-ready Voice Chat SDK must be designed with security and reliability from the start.
Key Security Requirements
- Encryption for audio in transit (TLS, SRTP)
- Secure storage for recordings
- Access controls and role-based permissions
- API authentication and request signing
- Audit logs for compliance use cases
Reliability Expectations At Scale
- High availability architecture
- Graceful handling of partial failures
- Geographic redundancy
- No single point of failure
If the voice layer goes down, the entire AI system becomes unreachable. Therefore, reliability is not optional – it directly impacts business continuity.
10. Are The Developer Tools And Observability Features Production-Ready?
Finally, even the most advanced voice features fail without strong developer tooling.
A modern Voice Chat SDK must make it easy to:
- Build
- Debug
- Monitor
- Operate
Developer Tools That Matter
- Client SDKs (Web, Mobile)
- Server SDKs (Node, Python, etc.)
- Webhooks for call and media events
- Clear API documentation
- Sample applications and reference flows
Observability Capabilities
- Call logs and transcripts
- Latency and jitter metrics
- Error tracking
- Media quality scores
Because voice systems are complex, visibility matters. Without proper observability, teams
Where Does FreJun Teler Fit In A Modern Voice Chat SDK Stack?
At this point, the requirements of a modern Voice Chat SDK should be clear.
However, many platforms still focus only on calling. They provide dial tone, but not the infrastructure needed for AI-driven conversations.
This is where FreJun Teler fits in technically.
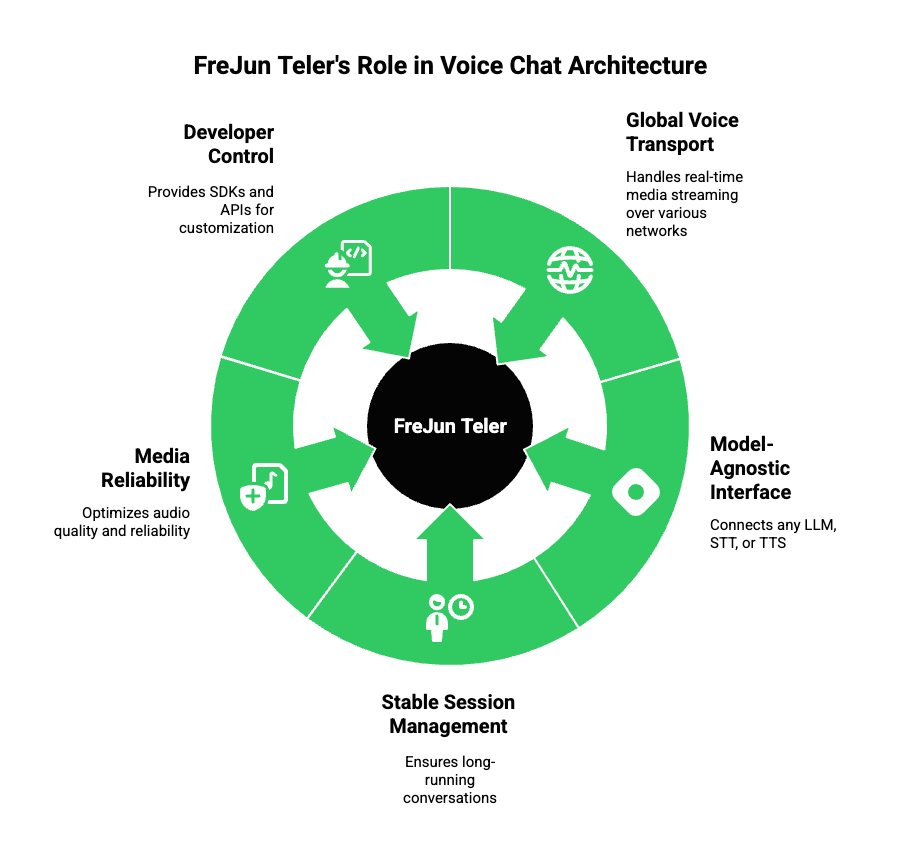
FreJun Teler’s Role In The Architecture
FreJun Teler acts as the global voice transport layer for AI agents and LLMs. Instead of replacing your AI logic, it focuses on handling the hardest parts of voice infrastructure.
Specifically, Teler provides:
- Real-time, low-latency media streaming over PSTN, SIP, and VoIP
- A model-agnostic interface to connect any LLM, STT, or TTS
- Stable session management for long-running conversations
- Media-level reliability and quality optimization
- SDKs and APIs designed for developer control
Because of this design, your application maintains full ownership of:
- Dialogue state
- Prompting strategy
- RAG pipelines
- Tool calling logic
Teler simply ensures that audio moves quickly and reliably between humans and machines.
This separation is important. It allows teams to iterate on AI without reworking voice infrastructure.
How Would You Implement A Complete AI Voice Agent Using A Modern Voice Chat SDK?
For many teams, implementation clarity matters as much as features.
Below is a simplified flow that shows how modern voice agents are typically built.
High-Level Voice Agent Flow
- A user places or receives a call
- The Voice Chat SDK streams live audio
- Audio is forwarded to Speech-to-Text
- Partial transcripts are sent to an LLM
- The LLM reasons, fetches context via RAG, or calls tools
- The response text is sent to Text-to-Speech
- Audio is streamed back to the user in real time
Why This Architecture Scales
- Voice infrastructure and AI logic remain decoupled
- Each component can be upgraded independently
- Latency is controlled at the transport layer
- Failures can be isolated and recovered
When these responsibilities are clearly separated, teams move faster and ship more reliable voice products.
How Do You Evaluate The Best Voice Chat SDK For Your Product?
After understanding the features, the next step is evaluation.
Here is a simple checklist founders and engineering leads can use during a proof of concept.
Quick Evaluation Checklist
- Does it support real-time bi-directional streaming?
- Can it integrate with any LLM, STT, and TTS?
- How does it optimize voice quality under poor networks?
- Does it handle call control and telephony cleanly?
- Are recordings and transcripts RAG-ready?
- Is security built in by default?
- Are developer tools and metrics strong enough for production?
If an SDK struggles in any of these areas, scaling will be difficult.
Final Thoughts
AI-powered voice products are no longer experimental; they are becoming essential business tools that drive engagement and efficiency. The difference between a proof-of-concept demo and a production-ready system often comes down to the infrastructure choices. A modern Voice Chat SDK must provide low-latency streaming, model-agnostic integration, reliable real-world performance, and full developer control.
When these foundations are in place, AI voice agents can scale seamlessly across multiple use cases and geographies, delivering consistent, human-like interactions. Choosing the right infrastructure early prevents costly rework later.
FreJun Teler simplifies this journey, enabling any AI or LLM to talk over real-time, reliable voice channels.
Schedule a demo today to experience a scalable voice infrastructure.
FAQs –
- What is a Voice Chat SDK?
A Voice Chat SDK enables real-time audio streaming, integrating with AI models to build scalable, interactive voice applications. - Why is low latency important in voice apps?
Low latency ensures natural, fluid conversations, preventing interruptions and improving user satisfaction during AI-driven interactions. - Can I use any AI or LLM with a voice SDK?
Yes, modern SDKs are model-agnostic, allowing seamless integration with any LLM, STT, or TTS system. - How does a voice SDK handle real-world network conditions?
It uses jitter buffers, packet-loss concealment, echo cancellation, and adaptive codecs to maintain consistent audio quality. - Do voice SDKs record calls for analysis?
Yes, they provide transcription, metadata capture, and recordings for analytics, RAG pipelines, and quality improvement. - What is the role of developer tools in a voice SDK?
They allow monitoring, debugging, and managing sessions, ensuring faster development and reliable deployment of voice applications. - Can I scale voice apps globally with a SDK?
Absolutely, SDKs with resilient infrastructure support global deployments with low-latency performance across geographies. - How is security maintained in a voice SDK?
Through encrypted streams, secure storage, API authentication, role-based access, and compliance with enterprise-grade standards. - What differentiates Teler from regular voice SDKs?
Teler provides robust, model-agnostic real-time voice infrastructure for AI agents, handling complex streaming and session management.
How quickly can I deploy AI voice agents with Teler?
With Teler’s SDK and APIs, you can launch real-time voice agents in days, not months, with enterprise reliability.
