The rise of voice AI agents is redefining how businesses interact with customers. Gone are the days of static IVRs or rigid scripts. Today, intelligent voice agents can understand natural language, call external tools, maintain context, and respond in real-time with human-like clarity. Combining Teler’s real-time voice infrastructure with OpenAI’s AgentKit orchestration framework, teams can build next-generation voice agents that are reliable, scalable, and compliant.
This blog explores the technical architecture, integration flow, and real-world applications, helping founders, product managers, and engineering leads understand how to leverage this full-stack approach for impactful voice automation tools across industries.
What’s changing in the world of voice AI agents?
In recent years, business communication has moved far beyond simple menu-based IVRs and scripted voice prompts. Instead, a new class of voice AI agents is emerging – systems that understand spoken language, reason about user intent, call external tools, and respond in real time with natural voice. These are next-generation voice agents built for real-time AI communication rather than fixed decision trees.
Why now? Three major shifts make this possible:
- Large language models (LLMs) have matured, enabling reasoning rather than simple responses.
- Speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) pipelines are fast and high-quality.
- Tooling for orchestration, connectors, evaluation and deployment has arrived in frameworks like AgentKit from OpenAI.
For product managers, engineering leads and founders, the opportunity is clear: build voice automation tools that can serve customers 24/7, connect into CRMs/knowledge bases, handle complex queries and deliver human-like voice experiences – all with minimal latency and maximum reliability.
What exactly is OpenAI’s AgentKit – and why does it matter?
If you’re wondering how the orchestration layer of a voice agent comes together, look no further than AgentKit. At its core, AgentKit is a unified toolkit designed for building, deploying and optimizing agents – not just chatbots, but full-workflow systems that can call tools, manage state, and embed into products.
Key components of AgentKit
- Agent Builder: A visual canvas where you drag-and-drop nodes (Start – Tool – Decision – Output), version your flows, preview runs and deploy agents faster.
- Connector Registry: Secure admin panel to register data-source connectors (e.g., Google Drive, SharePoint) and tools that agents will call. This means your voice agent can reach into your CRM, calendar, analytics system securely.
- ChatKit: While built for chat, this embeddable UI toolkit illustrates how AgentKit can surface conversational agents inside apps. The same workflows underpinning chat can power voice.
- Evals & Optimization: Built-in evaluation tools let you grade agent performance (trace grading, dataset creation), optimize prompts, and monitor end-to-end quality.
Why AgentKit is important for voice
Voice agents demand more than static responses. They require: multi-step reasoning, tool-calling, memory/context, branching logic and evaluation. AgentKit simplifies this orchestration, allowing teams to build voice-capable agents faster, enforce governance and scale deployments. As one analysis notes, “Instead of stitching together prompt logic, data connections and front-ends, AgentKit offers a cohesive stack.”
For engineering leads, this means less time spent building glue-code and more focus on business logic and voice experience. For founders and product leaders, it means faster time-to-value and better control of risk and quality when deploying voice automation tools.
What makes voice agents technically different from chat agents?
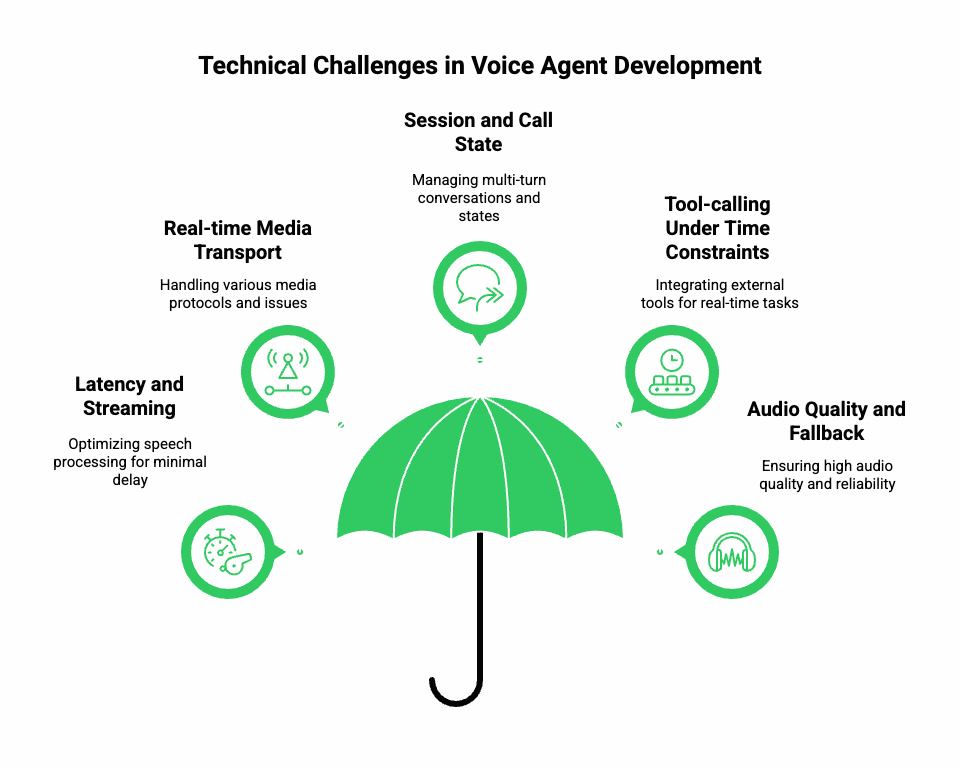
Building a voice agent is fundamentally different – and more challenging – than building a text chatbot. To succeed, you must master real-time media, latency control, session management, and seamless integration of speech components with reasoning logic.
Key technical challenges
- Latency and streaming: In a voice call, every millisecond counts. Users expect near-instant responses. The loop is: user speech – STT – reasoning – TTS – playback. Each stage must be optimized for minimal delay.
- Real-time media transport: Calls may come in via PSTN/VoIP or browser-based web clients. The system must handle codecs, packet loss, jitter, echo cancellation and routing – something typical text bots do not face.
- Session and call state: Unlike chat where you can wait, voice requires high availability and often a multi-turn, multi-agent state (who’s speaking, when to prompt, when to switch context).
- Tool-calling under time constraints: A voice agent might need to query a CRM, schedule an appointment, or verify identity – all while the caller is still listening. The integrations must be synchronous or near-synchronous.
- Audio quality and fallback: STT accuracy depends on good audio; TTS must sound natural and play back reliably. If any link weakens, the user experience degrades.
Because of these, you cannot simply plug an LLM into a voice channel and call it a “voice AI agent”. You must have a robust voice transport layer, real-time streaming, and orchestration logic to make the experience seamless.
This is where a specialized voice infrastructure platform becomes critical. In the next section, we’ll introduce how one such platform supports this layer.
How does FreJun Teler fit into the voice agent ecosystem?
FreJun has a voice platform called Teler, designed to serve as the global voice infrastructure layer for real-time voice agents. It complements AgentKit by managing the media and call transport so your systems can focus fully on reasoning, context and response logic.
What Teler provides
- Real-time media streaming: Inbound and outbound calls (PSTN or VoIP) stream live audio to your backend, and live TTS audio back to the caller.
- SDKs for web, mobile and server-side: So your voice agent logic can be embedded easily and scaled quickly.
- Carrier and VoIP interoperability: Handles bridging traditional telephony and modern web clients.
- Low-latency playback: Ensures the TTS output reaches the caller smoothly and with minimal perceptible delay.
- Call session management, security and reliability: Handles authentication, media encryption, session state and high-availability infrastructure.
Why this matters
By off-loading the heavy lifting of media transport and call infrastructure, Teler allows engineering teams to focus on building the voice logic, integrating with AgentKit and their chosen LLM/TTS/STT stack. In other words: Teler solves the “voice pipe” problem; AgentKit solves the “agent logic” problem. When combined, you have a full stack for next-generation voice agents.
Discover how voice bot platforms automate lead qualification effectively, integrating with Teler and AI agents for smarter, faster outreach.
How does the Teler + AgentKit integration work in practice?
To illustrate how Teler integrates with AgentKit and any LLM/TTS/STT stack to build a real-time voice AI agent, here’s a step-by-step architecture and explanation.
High-level architecture flow
- Call initiation
- A user dials in via PSTN or starts a web/VoIP call.
- Teler creates a media session and streams inbound audio to your backend.
- A user dials in via PSTN or starts a web/VoIP call.
- Speech input(STT)
- The audio is streamed either directly to your chosen STT engine or first captured by Teler then forwarded.
- Partial transcripts (real-time) begin flowing to your orchestrator.
- The audio is streamed either directly to your chosen STT engine or first captured by Teler then forwarded.
- AgentKit orchestrator
- Transcripts feed into an AgentKit workflow built via Agent Builder.
- The workflow may do intent detection – state lookup – tool call (CRM, database) – response generation.
- AgentKit uses the Connector Registry to securely access external tools/data.
- The workflow may also trigger guardrails (safety & compliance checks) and log traces for Evals.
- Transcripts feed into an AgentKit workflow built via Agent Builder.
- Response generation (LLM + RAG + tool outputs)
- The agent logic identifies the required content and queries the LLM (plus RAG retrieval if needed) to generate answer text.
- Optionally, tool calls are executed (e.g., scheduling, lookup) and results fed back.
- The agent logic identifies the required content and queries the LLM (plus RAG retrieval if needed) to generate answer text.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS)
- Generated text is sent to your selected TTS engine.
- The audio stream is then routed back via Teler to the caller.
- Generated text is sent to your selected TTS engine.
- Audio playback & call continuation
- Teler plays the TTS audio to the caller with minimal delay.
- When the user speaks again, the cycle repeats.
- Teler plays the TTS audio to the caller with minimal delay.
Integration considerations & best practices
- Streaming latency: Aim for each round trip (speech input – agent response – audio playback) to complete under 700 to 900 ms to maintain a conversational feel.
- Partial result handling: Use incremental STT transcripts to begin processing while speech is ongoing; this reduces latency.
- Fallback logic: If STT fails or TTS pipeline is slow, have fallback prompts or ask the user to wait.
- Tool-call timeout: Since voice callers expect quick responses, tool calls should be optimized (cache common queries, use fast DBs) or fall back to pre-computed answers.
- Session context: Maintain full call context (who is speaking, what has been asked, what tools were called) so multiple turns feel natural. AgentKit’s workflow nodes and state variables help here.
- Media quality monitoring: Teler should provide metrics on jitter, packet loss, latency; your system should monitor these and fallback if quality degrades.
Example mini-pseudocode
# Webhook from Teler: stream begins
def on_audio_frame(frame):
stt_result = stt_engine.process(frame)
if stt_result.partial:
agent_response = agentkit.run_workflow(transcript=stt_result.text, session_id=session_id)
tts_audio = tts_engine.generate(agent_response.text)
teler.playback(session_id, tts_audio)
(This is a simplified view; real implementations involve streaming, buffering, concurrency, and error handling.)
How can engineering teams ensure real-time performance and reliability?
Even the most advanced voice AI agent fails if there’s a perceptible lag, jitter, or dropped response. Real-time performance is the backbone of user trust. When combining Teler AgentKit integration, the focus shifts to optimizing four pillars: latency, throughput, uptime, and monitoring. According to industry research, AI voice-agent deployment has helped organizations reduce human agent headcount by 40-50% while processing 20-30% more calls.
A. Latency management
Every millisecond counts. The complete voice loop – user speech – STT – reasoning – TTS – playback – must remain under one second.
Here’s how teams can achieve this benchmark:
- Streaming APIs over batch: Always use streaming STT and TTS pipelines. Teler supports streaming media frames; AgentKit workflows can process incremental transcripts.
- Parallelism and pre-fetching: Pre-fetch tool data likely to be requested (like CRM info) as the STT partials come in.
- Local caching for frequent actions: Keep common lookup results in-memory to avoid repeated network calls.
- Edge deployment: Host latency-critical services (STT/TTS) in the same region as your Teler nodes.
B. Reliability and fault recovery
Downtime in voice calls directly impacts customer satisfaction.
- Session re-hydration: If the connection drops, Teler allows session recovery without losing context.
- Retry queues for tool calls: AgentKit’s connector registry supports safe retries.
- Fallback responses: Pre-recorded or local TTS prompts can handle service degradation gracefully (“Let me check that for you, one moment please”).
- Metrics and alerts: Monitor RTT (round-trip time), packet loss, and STT error rates.
- Auto-scaling: Both Teler and AgentKit are built cloud-native, allowing horizontal scaling during traffic spikes.
C. Monitoring and observability
Voice agents aren’t just about logs – you need traceable context across each call.
- AgentKit Evals integration: Evaluate workflows using trace grading and structured feedback datasets.
- Call analytics in Teler: Capture duration, silence ratio, latency, and interruption rate.
- Cross-trace correlation: Combine Teler call IDs with AgentKit trace IDs for full-session observability.
A sample performance dashboard might look like this:
| Metric | Ideal Range | Description |
| Average latency (ms) | < 900 ms | Total loop time from speech to playback |
| Packet loss (%) | < 1 % | Ensures clean audio streams |
| STT accuracy | > 92 % | Dictates understanding quality |
| Call uptime | > 99.9 % | Infrastructure reliability |
| Workflow success | > 95 % | AgentKit tasks executed without error |
This table forms the baseline for internal SLAs when deploying next-generation voice agents.
Explore the top voice APIs enabling secure, low-latency business communication, perfectly complementing Teler-powered AI voice agents.
How can teams maintain safety, compliance, and governance?
Voice automation introduces new compliance dimensions – call recording, data privacy, consent, and model alignment. OpenAI’s AgentKit includes built-in governance mechanisms, but aligning them with Teler’s telephony layer completes the compliance circle.
Security alignment between Teler and AgentKit
| Layer | Managed by | Responsibility |
| Voice media encryption | Teler | Encrypts audio streams (SRTP, TLS) |
| User data & credentials | AgentKit | Secure connector registry; no plaintext secrets |
| Logging and retention | Both | Configurable trace expiration |
| Access control | AgentKit | Role-based API keys and dataset isolation |
| Consent & notification | Teler | Pre-call disclaimers, recording prompts |
Privacy-first practices
- Mask sensitive inputs: Avoid sending personal identifiers to the LLM context.
- Opt-in call recording: Only record after explicit consent.
- Data minimization: Retain only essential conversation metadata for Evals and improvement.
- Controlled prompt injection: Guardrail unsafe or unverified content within workflows.
By adopting these practices, enterprises can meet both regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA) and customer-trust standards while running real-time AI communication pipelines.
What real-world use cases are emerging with Teler + AgentKit?
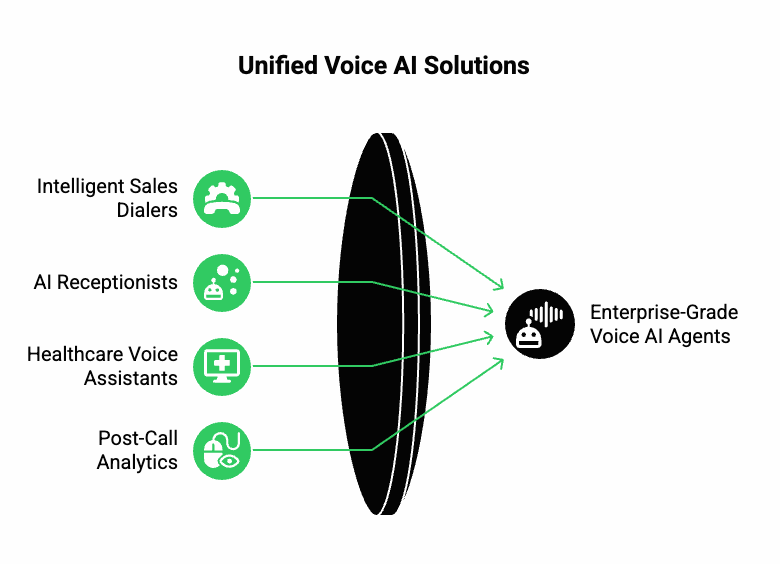
The combined stack is enabling new categories of voice automation tools across multiple industries. Here are some examples:
1. Intelligent Sales Dialers
Teler handles outbound call routing and caller ID masking, while AgentKit automates lead qualification.
Flow: Call initiation – dynamic CRM lookup – LLM-driven qualification – next-step scheduling – CRM update.
Result: Sales teams gain a 50 % reduction in missed leads.
2. AI Receptionists for Service Businesses
Small and mid-size companies use Teler’s inbound call routing to connect to an AgentKit-powered receptionist that answers queries, takes appointments, or escalates calls.
Result: Human agents handle only complex calls, improving response rates and operational efficiency.
3. Healthcare Voice Assistants
Patients can call to check lab results or book appointments securely. AgentKit enforces workflow compliance, and Teler ensures encrypted, reliable voice connections.
Result: Reduced administrative overhead and improved patient accessibility.
4. Post-Call Analytics
Teler records structured call metadata; AgentKit Evals assess conversational outcomes (sentiment, accuracy, compliance).
Result: Organizations gain measurable KPIs for continuous improvement.
These use cases show that the integration is not limited to one industry – it’s a foundational layer for enterprise-grade voice AI agents.
How do Teler and AgentKit compare with other voice automation approaches?
Most “voice bot” solutions today are built on narrow platforms that either:
- Focus purely on telephony (robust calling, weak reasoning), or
- Focus purely on AI logic (strong LLM, weak real-time audio).
| Capability | Teler + AgentKit | Typical Telephony Platform | Typical LLM Platform |
| Real-time audio streaming | Low-latency STT/TTS bridge | Yes | No |
| Multi-tool orchestration | Connector registry | Limited | Partial |
| Evaluation & grading | Built-in Evals | No | Limited |
| Deployment flexibility | API & SDK support | Limited | Limited |
| Regulatory compliance | End-to-end controls | Partial | No voice compliance |
| LLM independence | Any LLM (GPT-4o, Claude, Gemini) | Vendor-locked | Yes |
This integrated approach lets teams choose their preferred LLM, STT, and TTS stack while retaining consistent call quality and orchestration. The result is a platform that combines the strengths of both layers – real-time voice performance and intelligent reasoning.
What’s the roadmap for next-generation voice AI agents?
As voice AI agents mature, three technology tracks are converging:
- Autonomous workflow orchestration
- Agents that can reason across multi-step tool chains.
- Built using AgentKit’s visual workflow builder.
- Agents that can reason across multi-step tool chains.
- Dynamic speech synthesis
- Emotionally adaptive TTS voices responding to user tone.
- Real-time rendering via low-latency audio APIs in Teler.
- Emotionally adaptive TTS voices responding to user tone.
- Context-rich multi-agent systems
- Voice agents cooperating with chat or text agents for unified omnichannel support.
- Shared context memory managed within AgentKit.
- Voice agents cooperating with chat or text agents for unified omnichannel support.
In the near term, teams will deploy modular, event-driven agents that can handle inbound/outbound calls, summarize interactions, and trigger automation across CRMs, support desks, and billing systems.
As Teler and AgentKit continue evolving, they will become the backbone for real-time AI communication infrastructure.
How can founders and product teams start building today?
Here’s a concise implementation roadmap to deploy your own next-generation voice agent:
Step-by-step deployment checklist
- Select your LLM provider
- Compatible with AgentKit (e.g., OpenAI GPT-4o, Anthropic Claude 3).
- Compatible with AgentKit (e.g., OpenAI GPT-4o, Anthropic Claude 3).
- Integrate Teler voice layer
- Configure inbound/outbound numbers, WebRTC clients, or SIP endpoints.
- Configure inbound/outbound numbers, WebRTC clients, or SIP endpoints.
- Set up STT and TTS
- Pick providers (Whisper, Deepgram, Play.ht, ElevenLabs) based on latency and cost.
- Pick providers (Whisper, Deepgram, Play.ht, ElevenLabs) based on latency and cost.
- Build AgentKit workflow
- Design agent logic: intent recognition, tool calls, fallback prompts.
- Design agent logic: intent recognition, tool calls, fallback prompts.
- Configure data connectors
- Securely connect CRM, scheduling, or database tools via Connector Registry.
- Securely connect CRM, scheduling, or database tools via Connector Registry.
- Deploy and test
- Run controlled user sessions; measure latency, accuracy, satisfaction.
- Run controlled user sessions; measure latency, accuracy, satisfaction.
- Optimize and evaluate
- Use AgentKit Evals + Teler analytics to refine performance iteratively.
- Use AgentKit Evals + Teler analytics to refine performance iteratively.
- Scale and monitor
- Enable auto-scaling and continuous logging for 24/7 operations.
- Enable auto-scaling and continuous logging for 24/7 operations.
This structured roadmap helps teams go from idea to deployment within weeks, not months – a major edge in fast-moving markets.
Conclusion
By integrating Teler’s real-time, low-latency voice infrastructure with OpenAI’s AgentKit orchestration, teams gain a full-stack platform to build intelligent, reliable, and secure voice AI agents. This combination eliminates the complexity of stitching together fragmented APIs, allowing founders, product managers, and engineering leads to focus on creating value-driven, human-like conversations.
Teler ensures carrier-grade connectivity and seamless media streaming, while AgentKit provides intelligent reasoning, context management, and tool orchestration. Together, they empower the development of next-generation voice agents that are scalable, compliant, and enterprise-ready.
Schedule a demo with FreJun Teler today and accelerate your journey to real-time AI communication.
FAQs –
- What is a voice AI agent?
A voice AI agent is a real-time system using STT, TTS, LLMs, and orchestration for automated human-like conversations. - How does Teler support voice AI agents?
Teler provides low-latency streaming, carrier-grade connectivity, session management, and SDKs for seamless real-time voice AI integration. - What is OpenAI AgentKit used for?
AgentKit orchestrates AI workflows, manages context, enables tool calls, and evaluates agent performance in multi-step conversational flows. - Can I use any LLM with Teler?
Yes, Teler is model-agnostic, allowing integration with GPT-4o, Claude, Gemini, or any preferred AI backend. - Why is low latency important in voice AI?
Sub-second latency ensures natural conversations, reduces interruptions, and maintains user engagement in real-time voice interactions. - How do Teler and AgentKit work together?
Teler handles media transport; AgentKit orchestrates reasoning and workflows. Together, they form a full-stack voice agent solution. - What tools can AI agents call?
Agents can call CRMs, databases, scheduling systems, analytics platforms, or custom APIs via AgentKit connectors. - Are Teler-powered agents enterprise-ready?
Yes, Teler offers carrier-grade reliability, security protocols, low latency, and scalable infrastructure suitable for enterprise deployments. - Can I deploy AI voice agents in multiple industries?
Absolutely – from customer service, healthcare, finance to outbound campaigns, Teler + AgentKit support versatile, real-time applications.
How do I start building a voice AI agent?
Choose LLM, integrate Teler for voice, set up STT/TTS, design AgentKit workflow, test, optimize, and scale efficiently.
