Call drops remain one of the biggest challenges in customer communication – every disconnected call translates into frustration, revenue loss, and weaker loyalty.
This blog explores how to reduce call drop rates with voice AI agents by addressing both technical and experience-driven causes. We will look at the role of top programmable voice AI APIs with low latency, how voice APIs for developers can be integrated with speech recognition, language models, and synthesis, and why transport reliability is just as critical as conversational intelligence.
For founders, product managers, and engineering leads, this is a practical roadmap to building voice AI that keeps customers connected.
Why Call Drop Rates Hurt Business
Every phone call to a business is an opportunity to build trust or lose it. Yet, contact centers across the world still struggle with high call drop rates and call abandonment rates. Both problems may sound similar, but they are different.
- Call drop rate (DCR) refers to active calls that disconnect suddenly because of a technical fault. These can happen due to network instability, session failures, or misconfigured systems.
- Call abandonment rate (CAR) refers to customers who give up before speaking to an agent or before completing their task.
The impact is serious. A dropped call leaves the impression that the company is unreliable, while an abandoned call shows inefficiency. Together, they damage customer satisfaction, increase repeat call volume, and add operational costs.
This is where voice AI agents, also known as AI voicebots, play a role. By combining speech recognition, real-time processing, and reliable telephony infrastructure, they can reduce both drops and abandonments significantly.
Why Do Calls Drop in Call Centers?
Before diving into solutions, it is important to understand the causes. Call drops can be grouped into two broad categories: technical failures and customer experience failures.
Technical failures happen when the network or telephony infrastructure cannot maintain the connection. In wireless environments under load, VoIP capacity can shrink by up to 20% and end-to-end delay can rise above 100 ms, conditions that increase the likelihood of dropped calls.
Examples include:
- Packet loss or jitter in the VoIP stream
- Codec mismatches between carrier and endpoint
- SIP session timeouts
- Weak mobile coverage or unstable Wi-Fi
Customer experience failures happen when the system makes users wait or frustrates them to the point of hanging up. These are not pure “network drops” but are just as damaging. Examples include:
- Long queue times with no callback option
- Complicated IVR menus that force multiple selections
- Dead air or long silences during transfers
- Asking for the same details repeatedly
When customers face these conditions, they often hang up. In metrics, this is counted as abandonment, but from a user’s perspective, it feels no different from a drop.
Explore our detailed comparison of programmable voice APIs vs cloud telephony to choose the right infrastructure for reliable AI conversations.
Can Voice AI Agents Really Reduce Call Drop Rates?
Yes, but not in the way most people first imagine. Voice AI agents are not magic boxes that fix broken networks. What they do is reduce the conditions that lead to drops and abandonments. They create smoother, faster, and more reliable interactions that keep customers on the line.
A voice AI agent is built on a set of technologies working together:
- Speech-to-Text (STT) transcribes the caller’s speech in real time.
- Large Language Models (LLMs) process the intent, decide the next step, and maintain context.
- Retrieval systems (RAG) connect the AI to live data sources like CRM or knowledge bases.
- Tool calling lets the AI perform actions such as checking account status or updating an order.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) converts the response into natural audio.
- Telephony transport (SIP, VoIP, WebRTC) streams the audio reliably in and out.
Unlike old IVR systems, where callers press keys and navigate rigid menus, AI voicebots listen, understand, and act. This leads to faster resolution, fewer transfers, and a reduction in frustration.
The result: fewer abandonments, lower repeat call volume, and less pressure on networks.
How Voice AI Agents Reduce Call Abandonment
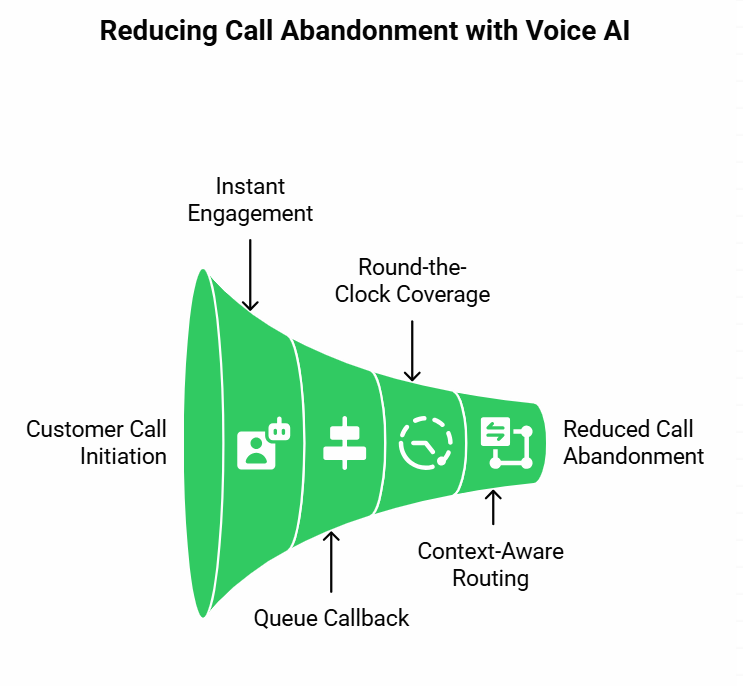
Call abandonment is often the first bottleneck to solve, because it inflates queues and worsens customer perception. Voice AI agents provide several advantages here.
Instant engagement
Instead of long rings or static hold music, callers are greeted by an intelligent system that responds right away. A voice AI agent can capture intent within seconds, which reduces the risk of a caller dropping out at the start.
Queue callback
If human agents are overloaded, the AI can schedule a callback at the customer’s convenience. This prevents frustration from long wait times.
Round-the-clock coverage
Unlike human staff, AI voicebots are always available. Customers calling after hours can still complete common tasks like account lookup, booking changes, or payment processing.
Context-aware routing
AI systems can connect to CRM data and past interactions. That means if a customer has already provided details online, the agent does not need to ask again. This speeds up the journey and reduces the chance of hang-ups.
By addressing abandonment in these ways, voice AI agents indirectly reduce drop rates. A shorter queue and smoother experience lower the load on infrastructure and improve stability.
How Voice AI Agents Reduce Actual Call Drops
While abandonment is more about user patience, call drops are about system design. Here too, voice AI agents help by ensuring that the conversation loop runs with minimal delay.
The most important factor is latency. In natural conversation, people expect a response in less than a second. If an AI takes longer, the user hears silence and may hang up.
To avoid this, the processing pipeline must be engineered for speed. A well-structured loop looks like this:
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD) detects when the caller has finished speaking.
- Streaming STT transcribes the words as they are spoken, not after the full sentence.
- The LLM begins generating tokens as soon as it receives partial text.
- Streaming TTS converts those tokens into audio in small chunks.
- Transport layer plays audio back to the caller with jitter buffering to ensure stability.
Each part of this loop has its own timing budget. The goal is to keep the entire chain – speech to response – within 700 milliseconds. Anything above that introduces unnatural pauses and increases the risk of drop-offs. Humans start noticing audio delays as low as 100 ms, and delays beyond a quarter-second break conversational flow.
Reliability also comes from the telephony layer itself. Session border controllers, SIP keep-alives, codec negotiation, and failover routing are all part of ensuring the call does not terminate prematurely. A properly engineered voice AI setup pays attention to these factors, not just the AI logic.
What Metrics Show Success
Founders, product managers, and engineering leads need to track the right metrics to know if voice AI agents are actually reducing call drops. These go beyond the usual contact center KPIs. Across the industry, an abandonment rate below 5% is considered healthy, while anything above 7% suggests structural problems in queue handling.
- Call Abandonment Rate (CAR): Number of calls abandoned before resolution, divided by total incoming calls.
- Call Drop Rate (DCR): Percentage of connected calls that ended due to technical issues.
- Time to First Audio (TTFA): How long it takes for the system to respond after a caller stops speaking.
- Dead-air duration: Total silence during a call, often a sign of latency or pipeline failure.
- Warm transfer success rate: Percentage of calls handed over to humans without forcing customers to repeat information.
- First Call Resolution (FCR): Number of calls solved in one attempt without escalation.
By correlating these metrics, teams can see where problems originate. For example, if TTFA is consistently above one second, it likely correlates with higher abandonment. If DCR spikes in certain regions, the cause may be telephony routing or carrier issues.
How To Implement a Voice AI Agent Step by Step
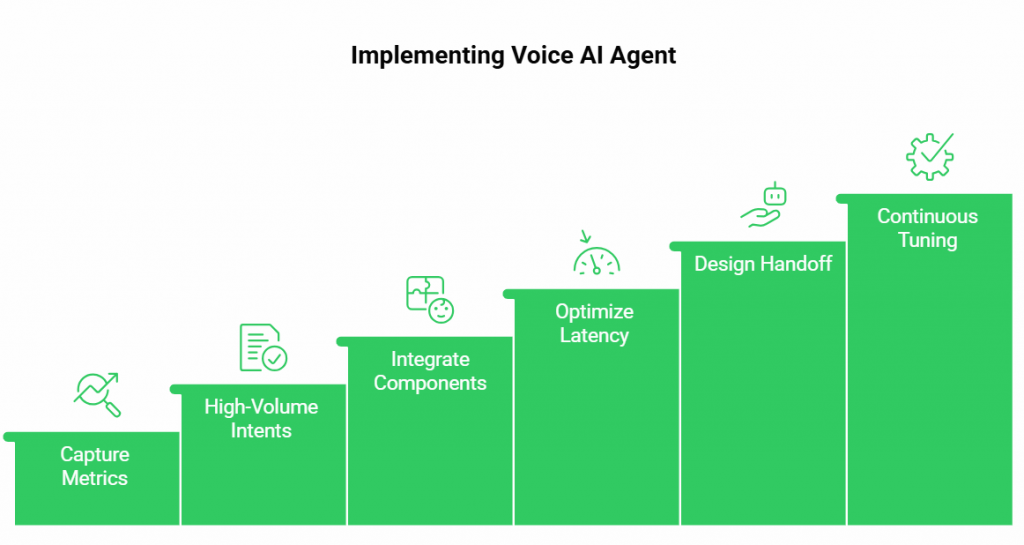
Reducing call drop rates with AI is not only about plugging in a model; it is about building an architecture that balances reliability, speed, and customer experience. The following step-by-step approach gives a roadmap for teams.
Step 1: Capture Baseline Metrics
Before making any changes, track your current Call Abandonment Rate (CAR), Call Drop Rate (DCR), and latency metrics. This baseline becomes the benchmark to measure improvements after AI deployment.
Step 2: Start With High-Volume Intents
Most call centers see repetitive queries – order status, billing, appointment booking. These are ideal for the first deployment because they are easy to automate and relieve pressure on human agents.
Step 3: Integrate Speech and Language Components
Choose Speech-to-Text (STT), a Language Model (LLM), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems that support streaming. Streaming reduces dead air and makes conversations feel natural.
Step 4: Optimize Latency Budgets
Map the entire conversation loop and measure delays at each stage. Keep time to first audio below 700 milliseconds by:
- Using streaming transcription instead of batch processing
- Running LLM inference in low-latency modes
- Using chunked audio output from TTS
- Pinning media paths closer to user regions
Step 5: Design for Handoff and Fallback
Not all calls can be resolved by AI. Build in smooth transfers to human agents, and always carry context forward so customers are not asked to repeat details. Also, design fallback options such as DTMF menus or SMS links in case of voice pipeline issues.
Step 6: Continuous Tuning
Voice AI is not a one-time setup. Monitor call logs for abandoned intents, high dead-air counts, and repeated queries. Feed this data back into the system to improve intent recognition and expand coverage.
Learn practical techniques to lower latency in voice AI conversations and deliver seamless, human-like responses without customer frustration.
Where FreJun Teler Fits In
Up to this point, the focus has been on what needs to be done. The next question is how to make it work reliably in real-world telephony networks.
This is where FreJun Teler provides the missing piece: the voice transport layer.
Instead of building and maintaining your own telephony infrastructure, Teler offers:
- Global voice connectivity across PSTN, VoIP, and cloud telephony networks
- Real-time media streaming optimized for low latency, keeping time-to-first-audio under target thresholds
- Developer-first SDKs to integrate with any STT, LLM, and TTS provider of your choice
- Resilient infrastructure with jitter buffers, SIP keep-alives, and carrier failover to minimize true technical drops
- Barge-in and endpointing support so customers can interrupt the bot naturally without breaking the session
- Secure transport with encryption and compliance-ready handling of sensitive data
For founders and product managers, this flexibility avoids vendor lock-in. For engineering leads, it provides confidence that the drop rate problem is being addressed at the infrastructure level as well as the AI logic level.
Building the Architecture with Any LLM, Any STT, Any TTS
When integrating a voice AI agent, the architecture usually follows a pattern:
- Inbound Call
- Customer dials in
- Call is routed through SIP trunk or WebRTC into Teler
- Teler streams audio to your backend
- Customer dials in
- Processing Pipeline
- Audio passes through STT for real-time transcription
- Partial transcriptions are streamed to the LLM
- The LLM decides response and can trigger tools (CRM lookup, payment API)
- Output text is sent to TTS in small chunks
- Audio passes through STT for real-time transcription
- Response Playback
- Teler streams audio chunks back to the caller
- Jitter buffers smooth playback
- Endpointing allows the user to interrupt naturally
- Teler streams audio chunks back to the caller
- Handoff if Needed
- If AI confidence is low, the call is transferred to a human agent
- Context (transcript, intent, account info) is passed along
- If AI confidence is low, the call is transferred to a human agent
This flow ensures that both abandonment and drop conditions are minimized.
What Metrics Prove Success
For technical teams and decision-makers, measuring impact is essential. The most important metrics after deployment include:
- Call Abandonment Rate (CAR): should decrease once AI reduces queue times
- Call Drop Rate (DCR): should improve as Teler handles network reliability
- Time to First Audio (TTFA): target under 700 ms
- Dead-air duration: lower silence indicates healthy streaming
- Warm transfer success rate: higher indicates smoother handoff design
- First Call Resolution (FCR): improved resolution shows better intent handling
Tracking these metrics over weeks provides proof that investment in voice AI is directly reducing call drop issues.
Conclusion
Call drops are more than technical failures – they represent lost opportunities and weakened customer trust. Reducing them requires more than just stronger networks; it requires smarter conversations. Voice AI agents engineered for low latency, seamless handoffs, and contextual intelligence address both abandonment and technical drop issues at scale. The winning formula combines real-time transcription, intelligent dialogue logic, backend integrations, and above all, a resilient voice transport layer.
This is where FreJun Teler makes the difference. By handling the complex global voice infrastructure, Teler allows you to plug in any LLM, STT, or TTS and focus on delivering meaningful conversations.
For founders, product managers, and engineering leads ready to cut drop rates and elevate CX, schedule a demo with Teler today.
FAQs –
Q1. How do voice AI agents reduce call abandonment in call centers?
Voice AI agents answer instantly, shorten wait times, provide callbacks, and resolve simple queries – reducing frustration that usually causes abandonment.
Q2. Why is latency important in preventing dropped calls with AI voicebots?
High latency creates dead air; keeping speech-to-response under 700ms ensures natural conversation flow and reduces user hang-ups.
Q3. What makes FreJun Teler different from other voice APIs for developers?
FreJun Teler provides low-latency global voice infrastructure, integrates with any LLM, STT, TTS, and ensures reliable, drop-resistant call transport.
Q4. Can AI voicebots fully replace IVRs in call centers?
Yes, AI voicebots handle natural conversations, reduce menu complexity, and integrate with backend tools, replacing outdated IVR systems effectively.
