Meta’s Llama 3 delivers state-of-the-art reasoning and conversational ability, unlocking the potential for hyper-intelligent voice automation. But creating a phone-ready AI agent means solving a far harder problem than text chat, real-time telephony. That’s where FreJun’s voice infrastructure changes the equation.
Table of contents
- The Next Leap in Business Communication: The AI-Powered Voice
- What is a Llama 3 Voice Bot and How Does it Work?
- The Hidden Hurdle: Why is Telephony the Hardest Part?
- FreJun: The Voice Infrastructure for Your Llama 3 Voice Bot
- How to Build a Production-Ready Llama 3 Voice Bot?
- DIY Telephony vs. FreJun: A Strategic Comparison
- Best Practices for a Flawless Voice Bot Experience
- Stop Building Plumbing, Start Building Intelligence
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
By handling low-latency audio streaming, global connectivity, and call reliability, FreJun allows developers to focus on Llama 3’s intelligence. This guide shows how to combine both, building a production-ready voice bot capable of natural, responsive conversations at scale.
The Next Leap in Business Communication: The AI-Powered Voice
The ability to automate conversations is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a strategic necessity. Businesses are constantly seeking ways to scale their customer interactions, from support calls to sales outreach, without exponentially increasing headcount. While chatbots have handled text-based queries for years, the true game-changer is mastering real-time voice communication.
The release of Meta’s Llama 3, a state-of-the-art open-source language model, has provided the “brain” for a new generation of hyper-intelligent conversational agents. Its advanced reasoning and natural language capabilities are precisely what’s needed to handle dynamic, human-like conversations.
However, possessing a powerful AI model is only one piece of the puzzle. The most significant challenge isn’t what the bot will say, but how it will listen and speak over a live telephone call, a challenge that trips up even the most skilled development teams.
What is a Llama 3 Voice Bot and How Does it Work?
A Llama 3 voice bot is an AI-driven conversational system that uses Meta’s advanced language model to engage in natural, spoken interactions. It can automate a vast range of business processes, including 24/7 customer support, outbound sales qualification, appointment scheduling, and personalized reminders.

The magic of a voice bot lies in its ability to seamlessly orchestrate several technologies in near real-time. The core workflow is a sophisticated digital relay race:
- Voice Input: The user speaks into their phone.
- Speech-to-Text (ASR): An Automatic Speech Recognition engine, like OpenAI Whisper or Google Speech-to-Text, instantly transcribes the spoken words into digital text.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The transcribed text is sent to the Llama 3 model, which analyzes the input to understand the user’s intent, context, and sentiment.
- Response Generation: Leveraging its vast knowledge and reasoning skills, Llama 3 formulates a relevant and coherent response in text format.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): The system sends the text response to a TTS engine, such as Amazon Polly or Microsoft Azure TTS, which converts it into natural-sounding, human-like audio.
- Voice Output: The system sends the text response to a TTS engine, such as Amazon Polly or Microsoft Azure TTS, which converts it into natural-sounding, human-like audio.
This entire cycle must happen in a fraction of a second to maintain a fluid, natural conversation. Any significant delay, and the illusion of a real conversation is shattered.
Also Read: How to Build AI Voice Agents Using MiniMax-Text-01?
The Hidden Hurdle: Why is Telephony the Hardest Part?
While setting up the AI components (ASR, Llama 3, TTS) is relatively straightforward with modern APIs, connecting them to a live phone call is a fundamentally different and more complex challenge. This is the domain of real-time voice infrastructure, a world of protocols, carriers, and network conditions that are notoriously difficult to manage.
Attempting to build this layer yourself means wrestling with:
- Latency: The biggest killer of conversational flow. You must engineer a system that minimizes delay at every step—from audio capture to AI processing to audio playback.
- Jitter and Packet Loss: Public telephone networks are imperfect. Your system must be resilient enough to handle inconsistent data delivery without degrading audio quality.
- Scalability: A solution that works for one call might crumble under the pressure of hundreds or thousands of simultaneous conversations. Scaling voice infrastructure is a non-trivial engineering feat.
- Integration Complexity: Stitching together a VoIP provider, your ASR/LLM/TTS stack, and your business logic into a cohesive, reliable system is a massive undertaking.
This is the hidden hurdle where most voice bot projects stumble. They invest heavily in AI, only to be bottlenecked by the underlying plumbing.
FreJun: The Voice Infrastructure for Your Llama 3 Voice Bot
FreJun is the specialized solution to this complex problem. We are not an LLM provider. Instead, we provide the robust, developer-first voice infrastructure that handles all the complex telephony, so you can focus exclusively on your AI. Our platform is the critical transport layer designed for speed and clarity, turning your text-based Llama 3 model into a powerful, production-ready voice agent.
With FreJun, you bring your AI stack. Our model-agnostic API allows you to connect any ASR, LLM, and TTS service you choose. We manage the real-time media streaming, ensuring every word is captured from the caller and every response is delivered back with minimal delay. Your application maintains full control over the dialogue state, while our platform ensures the connection is stable, clear, and ready to scale.
Also Read: Virtual Number Implementation for B2B Operations with WhatsApp Business in Brazil
How to Build a Production-Ready Llama 3 Voice Bot?
Here’s a practical, step-by-step guide to architecting your voice bot, with a focus on building a scalable and reliable solution.
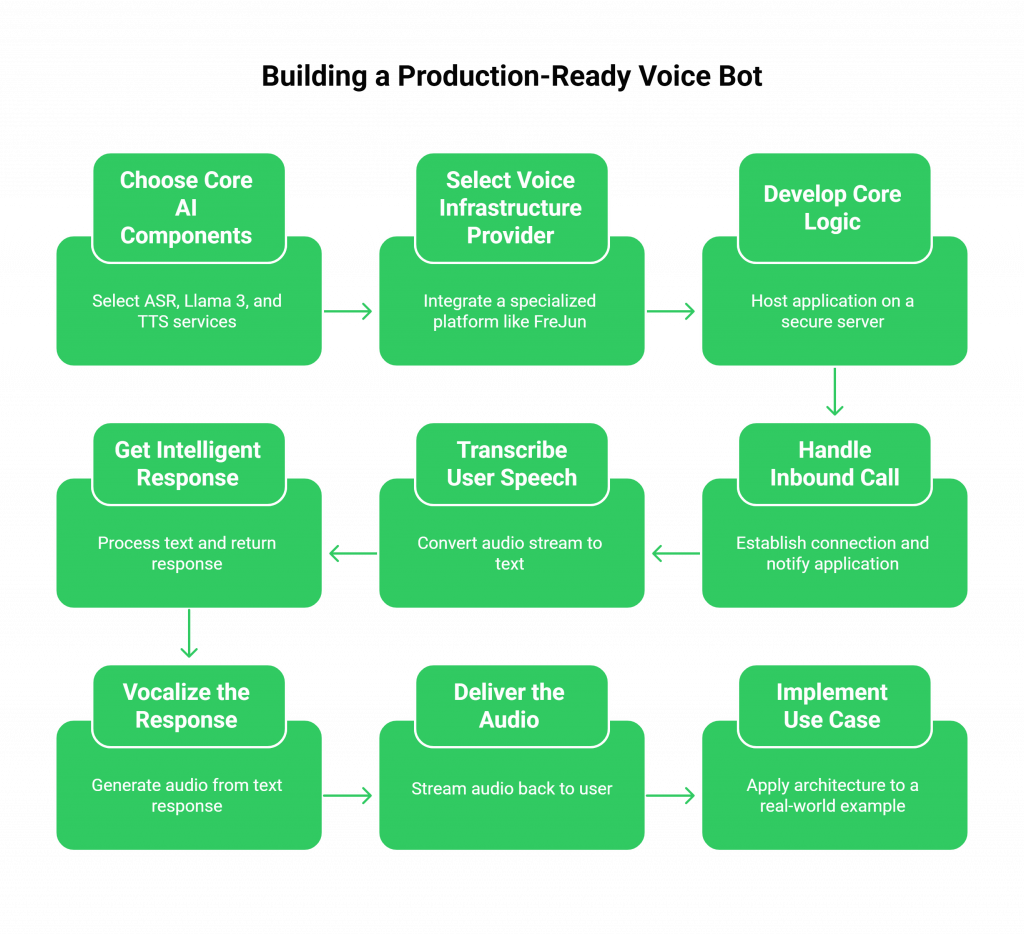
Step 1: Choose Your Core AI Components
First, assemble the “brain” and “voice” of your bot. These services will be called by your central application logic.
- ASR Service: Select a high-accuracy transcription service like Google Speech-to-Text or OpenAI Whisper.
- Llama 3 Instance: Decide how you will access Llama 3. You can use a managed API or deploy a fine-tuned instance on your own secure server for more control.
- TTS Service: Choose a provider known for low-latency, natural-sounding voices, such as Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure TTS, or Google Cloud TTS.
Step 2: Select Your Voice Infrastructure Provider
This is the most critical decision that will impact your project’s speed, cost, and reliability. Instead of building from scratch, you integrate a specialized platform like FreJun. Our API becomes the central nervous system for your bot’s communication.
Step 3: Develop Your Bot’s Core Logic
Host your application on a secure, low-latency server. This application will orchestrate the entire conversation by making API calls.
- Handle the Inbound Call: When a customer calls your FreJun-provided number, FreJun establishes the connection and notifies your application via a webhook, immediately opening a bi-directional audio stream.
- Transcribe User Speech: Your application takes the incoming audio stream from FreJun and forwards it to your chosen ASR service.
- Get an Intelligent Response: The transcribed text is sent to your Llama 3 voice bot API. Llama 3 processes the text and returns its response.
- Vocalize the Response: The text response is sent to your TTS service, which generates the audio.
- Deliver the Audio: Your application streams the final audio back to the FreJun API, which plays it to the user in real-time.
Step 4: Implement a Use Case
Let’s apply this architecture to a real-world example.
- Initiate the Call: Your application triggers an outbound call via the FreJun API to a customer.
- Deliver the Message: Once the customer answers, your bot plays a pre-generated message using your TTS service: “Hello, this is an automated reminder of your appointment with Dr. Smith tomorrow at 10 AM. Can you still make it?”
- Listen and Process: The bot listens for the response. The ASR transcribes it (“Yes, I’ll be there”). Llama 3 understands the affirmative intent.
- Confirm and Log: The bot responds, “Great, we’ll see you then. Thank you!” and automatically logs the confirmation in your CRM or scheduling system via another API call.
This entire interaction is handled in seconds, without any human intervention.
Also Read: Virtual Phone Providers for Enterprise Operations in Norway
DIY Telephony vs. FreJun: A Strategic Comparison
| Feature | Building It Yourself (DIY) | Using FreJun’s Infrastructure |
| Primary Focus | Divided between AI logic, telephony protocols, and infrastructure management. | 100% focused on building and refining your Llama 3 voice bot AI. |
| Time to Market | Months of development and testing to build a stable, scalable voice layer. | Launch a production-ready voice agent in days, not months. |
| Latency | A constant engineering battle. Optimizing the stack for low latency is complex and costly. | Engineered for low latency. Our entire platform is optimized for real-time conversational AI. |
| Scalability | Requires significant investment in new hardware, software, and network capacity to handle load. | Seamlessly scales from one to thousands of concurrent calls on our geographically distributed infrastructure. |
| Reliability & Uptime | Reliant on your own infrastructure’s resilience. Single points of failure are common. | Guaranteed uptime and reliability, backed by an enterprise-grade platform. |
| Support & Expertise | You are solely responsible for troubleshooting every issue, from dropped calls to audio artifacts. | Dedicated integration support from our team of voice experts to ensure your success. |
Best Practices for a Flawless Voice Bot Experience
- Train for Your Domain: For best results, fine-tune your Llama 3 model with industry-specific data and conversation examples to improve its accuracy and contextual understanding.
- Design for Failure: Plan for scenarios where the bot doesn’t understand. Implement graceful fallbacks, such as asking the user to rephrase their request or offering a seamless handover to a human agent.
- Address Noise and Accents: Use high-quality speech enhancement and noise reduction technologies to improve ASR accuracy. Ensure your chosen ASR service has been trained on diverse accents.
- Ensure Compliance: Be fully aware of and compliant with all local and international laws regarding call recording, data privacy, and automated dialing.
- Test Rigorously: Before going live, thoroughly test your entire workflow for latency, audio quality, and response accuracy across a wide range of scenarios.
Stop Building Plumbing, Start Building Intelligence
The opportunity to create a sophisticated Llama 3 voice bot is here. The models are powerful enough, and the business need for scalable communication has never been greater. The strategic choice you face is not whether to build a voice bot, but how.
By choosing to build your voice infrastructure, you are choosing to become a telecom company. By partnering with FreJun, you are choosing to be an AI company. We handle the immense complexity of global, real-time voice communication, providing a reliable and performant foundation upon which you can build the next generation of voice automation.
This allows you to innovate faster, reduce operational overhead, and deliver a superior customer experience from day one.
Get Started with FreJun AI Today!
Also Read: How to Build AI Voice Agents Using o3-Pro?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A complete Llama 3 voice bot requires four key components: a telephony or VoIP provider like FreJun to handle the calls, a Speech-to-Text (ASR) service for transcription, the Llama 3 model for intelligence, and a Text-to-Speech (TTS) service to generate the voice response.
To combat background noise, use ASR services with built-in noise suppression. To handle regional accents, select an ASR model that has been trained on a diverse dataset covering a wide range of accents and dialects.
Low latency is essential for maintaining a natural conversational flow. Long pauses between a user speaking and the bot responding make the interaction feel robotic and frustrating, leading to a poor customer experience and abandoned calls.
Yes, depending on the training data of the Llama 3 model and the language capabilities of your integrated ASR and TTS services. The entire pipeline must support the desired languages.
