Voice automation is entering a new era where bots can go beyond conversation to execute complex, multi-step tasks. Models like Kimi K2 bring agentic intelligence, reasoning, planning, and tool use into the voice domain. The challenge is bridging this power with real-world telephony and workflow orchestration.
FreJun provides that bridge, capturing detailed voice requests and returning results via seamless callbacks. This guide shows how to combine Kimi K2’s capabilities with FreJun’s infrastructure to build asynchronous, execution-ready voice agents.
Table of contents
- Beyond Conversation: The Dawn of the Agentic Voice Bot
- What is Kimi K2? A Look Under the Hood
- The Latency Dilemma: Where Power Meets a Practical Barrier
- FreJun: The Asynchronous Voice Infrastructure for Agentic AI
- Tutorial: Building an Asynchronous Kimi K2 Voice Bot
- Real-Time vs. Agentic Voice Bots: A Comparison
- Best Practices for Deploying Your Kimi K2 Voice Bot
- The Strategic Shift from Voice Bots to Voice Agents
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Beyond Conversation: The Dawn of the Agentic Voice Bot
For years, the goal of voice automation has been to create bots that can talk. We’ve built IVRs that route calls and chatbots that answer simple questions. While useful, these systems are fundamentally passive; they respond, but they don’t act. The next frontier isn’t just about conversation; it’s about execution. It is about building voice-driven agents that can understand complex commands, reason through multi-step plans, utilise external tools, and autonomously complete tasks from start to finish.
This is the promise of agentic AI. Models like Moonshot AI’s Kimi K2 are not just language processors; they are reasoning engines designed for autonomous task execution. Imagine a voice bot that can take a command like, “Analyze our latest sales report, identify the top three performing regions, and schedule a meeting with those regional managers,” and then actually do it.
This leap in intelligence, however, introduces a new set of technical challenges. The very complexity that makes these models so powerful also creates a barrier to the real-time, conversational flow we’ve come to expect from voice assistants.
What is Kimi K2? A Look Under the Hood
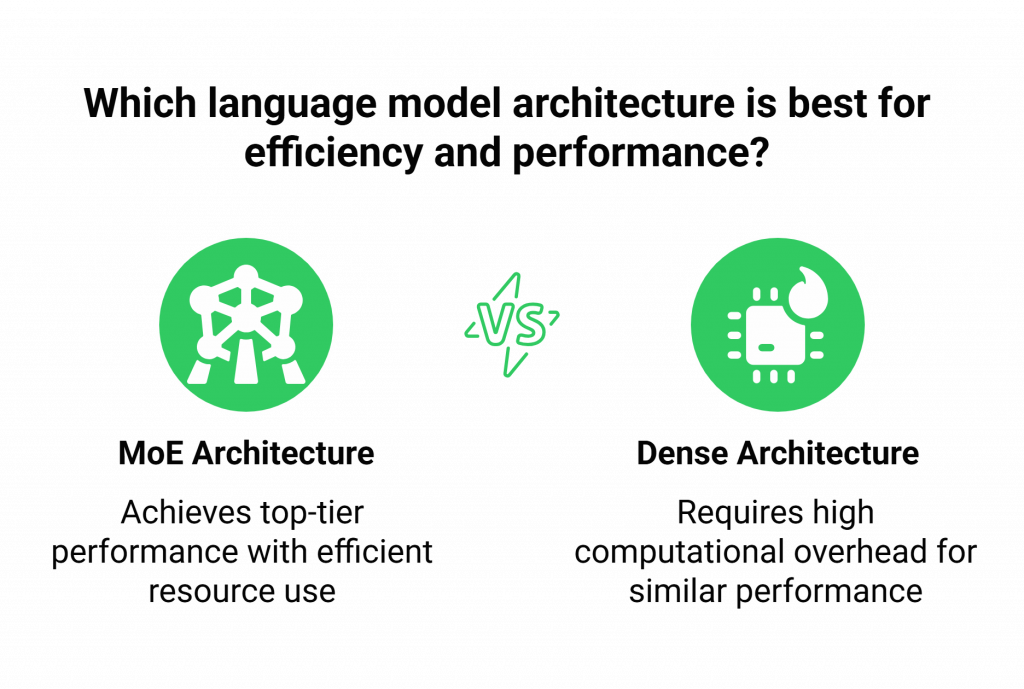
Kimi K2 is a state-of-the-art language model that represents a significant step forward in agentic intelligence. Built on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with a staggering one trillion total parameters, it is designed for efficiency and power. For any given task, it intelligently activates a smaller subset of its “experts” (around 32 billion parameters), delivering top-tier performance without the computational overhead of a dense trillion-parameter model.
Here’s what makes Kimi K2 a game-changer for building an advanced voice bot:
- Agentic Intelligence from the Ground Up: Unlike models retrofitted for tool use, Kimi K2 was designed for it. It excels at reasoning, planning, and using tools (like APIs) to execute tasks autonomously.
- Massive Context Window: With a context window of up to 128,000 tokens, it can process and understand long-form inputs and maintain context through complex, multi-step workflows.
- Flexible Integration: It is available through APIs that are compatible with the OpenAI and Anthropic ecosystems, making it relatively straightforward for development teams to integrate into their existing stacks. You can get started in as little as ten lines of code via platforms like Together AI.
- Top-Tier Performance: Benchmarks show Kimi K2 achieving elite performance in difficult reasoning, coding, and tool-use challenges, proving its capability to handle complex business logic.
This combination of features makes it the ideal candidate for a Kimi K2 voice bot that can perform complex, value-added tasks, moving far beyond simple question-and-answer interactions.
Also Read: MiniCPM Voice Bot Tutorial
The Latency Dilemma: Where Power Meets a Practical Barrier
With great power comes a critical trade-off: processing time. The sophisticated reasoning and decision-making that Kimi K2 performs take longer than the simple response generation of a smaller conversational model. The research is clear: latency constraints make Kimi K2 less suited for strictly real-time, turn-by-turn voice conversations where sub-second responses are critical to maintain a natural flow.
If a user asks a question and has to wait several seconds for the model to think, plan, and respond, the experience becomes frustrating and unworkable. This latency issue presents a major hurdle. How can you leverage the incredible task-automation power of a model like Kimi K2 through a voice interface if it’s too slow for a normal conversation?
The answer is to change the interaction paradigm. Instead of building a real-time conversationalist, you build an asynchronous task-taker.
FreJun: The Asynchronous Voice Infrastructure for Agentic AI
This is where FreJun’s robust and flexible voice infrastructure becomes essential. FreJun is not an LLM. We provide the critical communication layer that allows you to design and implement sophisticated voice workflows, both real-time and asynchronous. For a Kimi K2 voice bot, our platform serves as the perfect bridge, managing the voice interactions at the beginning and end of a task.
Here’s how FreJun enables asynchronous voice automation:
- Reliable Voice Capture: Our API captures the user’s initial command with crystal clarity, ensuring every detail of their complex request is passed to your ASR and then to Kimi K2.
- Workflow Orchestration: FreJun’s APIs can be used by the Kimi K2 agent as a “tool.” Once the agent has completed its task, it can use the FreJun API to trigger an outbound call back to the user to deliver the results.
- Call Management: We handle all the underlying telephony, placing calls, managing connections, and ensuring high-quality audio, so your agent can focus purely on task execution.
- Status Updates: You can design workflows where the bot provides an initial acknowledgment (“I’ve received your request to analyze the report and will call you back with a summary in five minutes”) before getting to work. FreJun handles the playback of this initial response seamlessly.
FreJun provides the “voice and ears” for your agent, allowing it to communicate with the outside world without you having to build a complex, multi-faceted telephony system from scratch.
Also Read: Virtual Number Solutions for Professional Operations with WhatsApp Integration in Australia
Tutorial: Building an Asynchronous Kimi K2 Voice Bot
Let’s walk through the conceptual steps to build a voice agent that can take a complex request, work on it in the background, and deliver the result over a phone call.
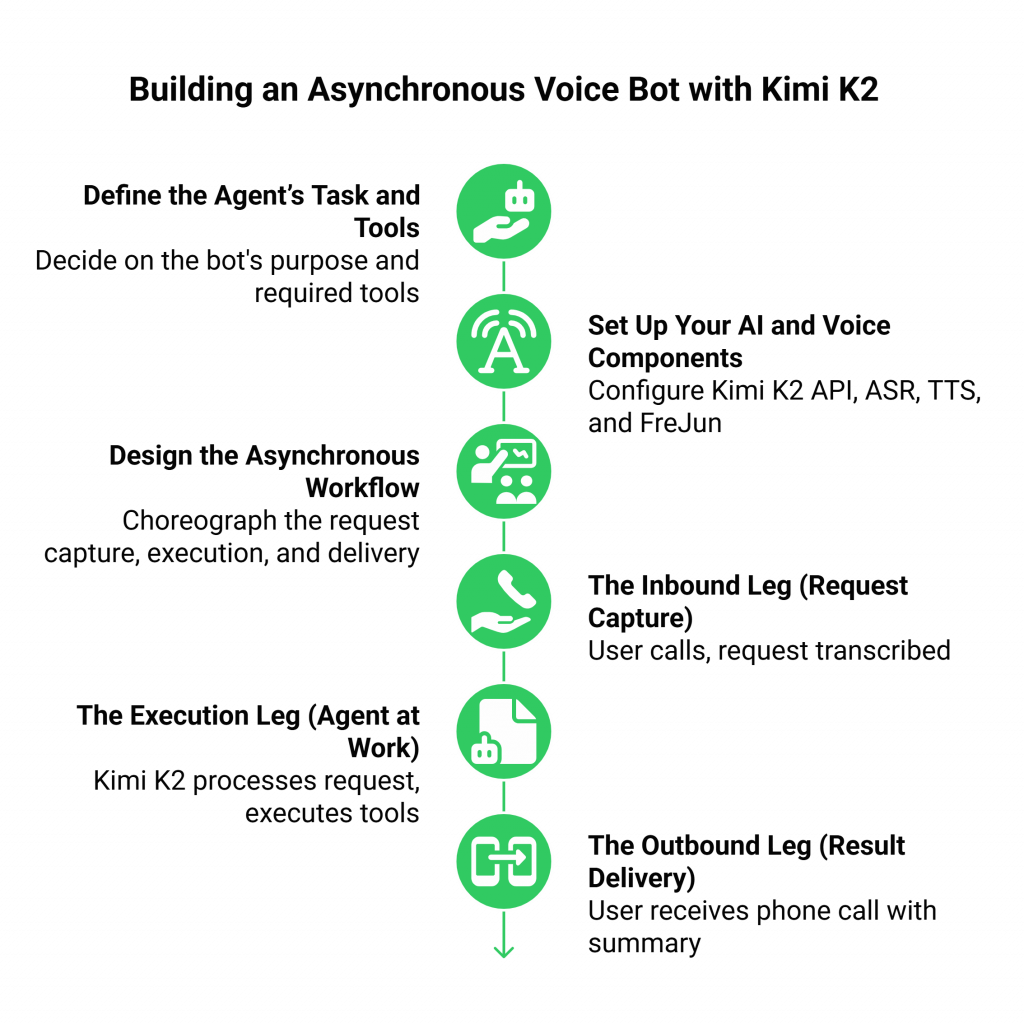
Step 1: Define the Agent’s Task and Tools
First, decide what your agent will do. Let’s imagine a bot that can create a sales summary.
- Task: “Generate a summary of yesterday’s sales performance and email it to the sales leadership team.”
- Required Tools: You’ll need to define functions that Kimi K2 can call:
- get_sales_data(date): An API call to your internal sales database.
- summarize_text(data): An internal prompt to Kimi K2 itself to perform summarization.
- send_email(recipient_list, subject, body): An API call to your email service provider.
- initiate_phone_call(phone_number, message): An API call to FreJun to place an outbound call.
Step 2: Set Up Your AI and Voice Components
Assemble your technology stack.
- Kimi K2 API: Get API access to moonshotai/Kimi-K2-Instruct through a provider like Together AI or an OpenRouter-compatible service.
- ASR & TTS: Choose a fast and accurate ASR service to transcribe the initial command and a high-quality TTS service to generate the final audio message.
- FreJun Account: Set up your FreJun account and get an API key. You will use this for the initiate_phone_call tool.
Step 3: Design the Asynchronous Workflow
This is where you choreograph the entire process.
- The Inbound Leg (Request Capture):
- A user calls a dedicated phone number provided by FreJun.
- FreJun routes the call to your application. You play a pre-recorded prompt: “Please state your request after the beep.”
- The user’s voice is captured, sent to your ASR, and transcribed into text. The call can then end.
- The Execution Leg (Agent at Work):
- The transcribed text is sent to your Kimi K2 voice bot along with the schemas for your available tools.
- Kimi K2 reasons through the request. It determines it needs to call get_sales_data, then summarize_text, then send_email.
- Your backend executes these tool calls as directed by Kimi K2.
- Once the email is sent, Kimi K2 determines its final task is to confirm completion. It decides to call the initiate_phone_call tool, passing the user’s original phone number and a message like, “The sales summary for yesterday has been generated and emailed to the leadership team.”
- The Outbound Leg (Result Delivery):
- Your backend receives the instruction from Kimi K2. It uses the message text and your TTS service to generate an audio file.
- It then makes an API call to FreJun, instructing it to call the user and play the generated audio file.
This workflow perfectly leverages the power of the Kimi K2 voice bot for complex tasks while completely bypassing its latency limitations for real-time conversation.
Also Read: How to Build a Voice Bot Using MiniMax-Text-01 for Customer Support?
Real-Time vs. Agentic Voice Bots: A Comparison
It is crucial to understand that these are two different types of tools for two different jobs.
| Feature | Real-Time Conversational Bot | Asynchronous Agentic Kimi K2 Bot |
| Primary Goal | Answer questions and guide users through simple, turn-by-turn conversations. | Understand complex commands and autonomously execute multi-step tasks. |
| Core Technology | Low-latency LLM optimized for fast, conversational responses. | High-reasoning LLM (like Kimi K2) optimized for tool use and planning. |
| Interaction Model | Synchronous (user waits for an immediate response). | Asynchronous (user submits a request and gets the result later). |
| Latency Requirement | Ultra-low (sub-second) is critical for user experience. | Latency is not a primary constraint; task completion accuracy is key. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Customer support FAQs, appointment booking, simple information retrieval. | Report generation, data analysis, complex workflow automation, system integrations. |
| FreJun’s Role | Provides the low-latency voice transport for the real-time conversation. | Provides the voice infrastructure for both capturing the initial request and delivering the final result via a callback. |
Also Read: Virtual Number Setup for B2B Communication with WhatsApp Business in South Korea
Best Practices for Deploying Your Kimi K2 Voice Bot
- Robust Error Handling: Define fallback tools and error-handling logic. What should Kimi K2 do if an API call fails or the user’s request is ambiguous? It should be able to report the failure or ask for clarification.
- Invest in Quality ASR/TTS: The performance of your agent is still dependent on the quality of its “ears” and “mouth.” A high-quality ASR is needed to accurately capture complex commands, and a clear TTS is needed to deliver the results professionally.
- Set Clear Expectations: In your initial voice prompt, let the user know that their request will be processed and they will receive a callback. Managing user expectations is key in an asynchronous model.
- Thorough Testing: Test your bot with a wide variety of commands, accents, and background noises to ensure reliability.
The Strategic Shift from Voice Bots to Voice Agents
The ability to automate complex, multi-step tasks using a simple voice command is transformative. It frees up your team from repetitive, high-effort work and allows them to focus on strategic initiatives. Models like Kimi K2 provide the intelligence to make this a reality.
However, this intelligence needs a reliable way to communicate with the world. Building and maintaining telephony infrastructure is a complex distraction from your core mission of creating intelligent automation.
By partnering with FreJun, you adopt a strategy of focus. You concentrate on designing powerful agentic workflows and defining the tools your business needs, while we provide the enterprise-grade communication backbone that brings your Kimi K2 voice bot to life. This combination of world-class AI and world-class voice infrastructure is what will define the next generation of business automation.
Also Read: Mistral 8x7B Voice Bot Tutorial
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A standard bot is designed for real-time conversation and answering questions. A Kimi K2 voice bot is designed for agentic intelligence, it can understand complex, multi-step commands, use external tools (like APIs), and autonomously complete tasks in the background.
Its powerful Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and deep reasoning capabilities introduce processing latency. This delay makes it unsuitable for the rapid, turn-by-turn nature of a live conversation but perfect for more complex, asynchronous tasks.
You define the tools (like send_email or get_database_info) as functions in your code and provide a schema for them in your API call to Kimi K2. The model can then intelligently decide when to invoke these tools to complete a user’s request.
FreJun provides the voice infrastructure for the communication points. We handle the initial inbound call to capture the user’s command and the final outbound call, initiated by the Kimi K2 agent via our API, to deliver the completed task’s results.
