The growing power of open-source Large Language Models like InternLM makes it possible for anyone to build advanced AI applications. Yet, moving from a text-based chatbot to a live, phone-ready voice agent introduces complex challenges, including telephony, streaming, and latency chief among them.
FreJun addresses this gap with a developer-first voice infrastructure that connects your AI stack to real-time calls. This guide walks you through creating a production-ready InternLM Voice Bot, combining open-source intelligence with reliable, low-latency voice capabilities.
Table of contents
- The Rise of Open-Source AI and the Voice Barrier
- What is InternLM and Why is it a Game-Changer for Voice AI?
- The Hidden Challenge: Why Voice Infrastructure is the Hardest Part
- FreJun: The Voice Transport Layer for Your InternLM Voice Bot
- Building a Production-Ready InternLM Voice Bot: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
- DIY Voice Infrastructure vs. FreJun: A Head-to-Head Comparison
- Best Practices for Designing Effective Voice Bot Conversations
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Rise of Open-Source AI and the Voice Barrier
The availability of powerful, open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) has democratized artificial intelligence. Models like InternLM offer unprecedented capabilities for reasoning and text generation, making it possible for nearly any organisation to develop sophisticated AI applications. Businesses are eager to deploy these models to automate complex workflows, from customer support to proactive sales outreach.
However, a significant gap exists between creating a text-based chatbot and deploying a fully functional, real-time voice agent. While the “brain” of the operation, the LLM, is now accessible, giving it a voice that can interact seamlessly over a phone call introduces a host of complex engineering challenges.
Developers quickly discover that managing telephony, real-time audio streaming, and latency is a fundamentally different and more demanding problem than handling text via a web interface.
Also Read: Google Gemini 1.5 Pro Voice Bot Tutorial
What is InternLM and Why is it a Game-Changer for Voice AI?
InternLM is an open-source series of instruction-tuned language models celebrated for their advanced reasoning and general-purpose task capabilities. Models within this series, such as InternLM3-8B-Instruct, are engineered to provide high-quality outputs while being remarkably cost-effective to train. For instance, some versions use over 75% less training data compared to similar models without compromising performance, making them an excellent choice for businesses looking to build custom AI solutions without exorbitant costs.

The power of InternLM lies in its ability to understand user intent and generate human-like, contextually relevant responses. This makes it an ideal candidate to serve as the core intelligence for an automated voice bot. By leveraging such a model, businesses can create voice agents that go beyond simple IVR scripts to handle dynamic, nuanced conversations for applications like:
- 24/7 automated customer support.
- Scalable appointment scheduling and reminders.
- Intelligent lead qualification and follow-ups.
- Automated feedback collection and surveys.
Getting a model like InternLM running for a text-based chat demo is relatively straightforward, often involving a simple script and a web interface like Streamlit. But to transform this text-based intelligence into a conversational InternLM Voice Bot, you need to solve the voice communication puzzle.
Also Read: How to Get a Virtual Number for WhatsApp Business Integration in India?
The Hidden Challenge: Why Voice Infrastructure is the Hardest Part
Building a voice bot is not a monolithic task. It requires orchestrating three distinct technologies in real-time:
- Speech-to-Text (STT): To accurately transcribe the caller’s spoken words into text.
- The Language Model (LLM): To process the text, understand intent, and generate a response. This is where InternLM fits.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): To convert the LLM’s text response back into natural-sounding spoken audio.
While you can source powerful services for each component, for instance, using AssemblyAI for STT, InternLM as the LLM, and ElevenLabs for TTS, the real challenge is the “plumbing” that connects them over a live phone call. This plumbing, the voice transport layer, must handle the complexities of telephony: establishing calls, streaming audio bi-directionally, and minimizing latency to prevent awkward, conversation-breaking pauses.
Managing this infrastructure yourself is a resource-draining endeavor that distracts from your core goal: building a smart and effective voice AI.
Also Read: How to Build a AI Voice Agents Using OpenAI GPT-3.5 Turbo?
FreJun: The Voice Transport Layer for Your InternLM Voice Bot
This is precisely the problem FreJun solves. FreJun is not an LLM, STT, or TTS provider. Instead, we provide the robust, developer-first voice infrastructure that handles all the complex telephony, so you can focus exclusively on your AI logic. Our platform is designed from the ground up for speed and clarity, serving as the critical transport layer that turns your text-based InternLM Voice Bot into a powerful, production-grade voice agent.
With FreJun, you bring your AI stack. Our model-agnostic API allows you to connect any STT, LLM (like InternLM), and TTS service you choose. We manage the real-time media streaming, ensuring every word is captured from the caller and every response is delivered back with minimal delay. Your application maintains full control over the dialogue state and conversational context, while our platform ensures the connection is stable, clear, and scalable.
Also Read: Virtual Phone Providers for Enterprise Growth in Nigeria
Building a Production-Ready InternLM Voice Bot: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Let’s walk through the conceptual process of building and deploying a sophisticated voice agent using InternLM and FreJun’s infrastructure.
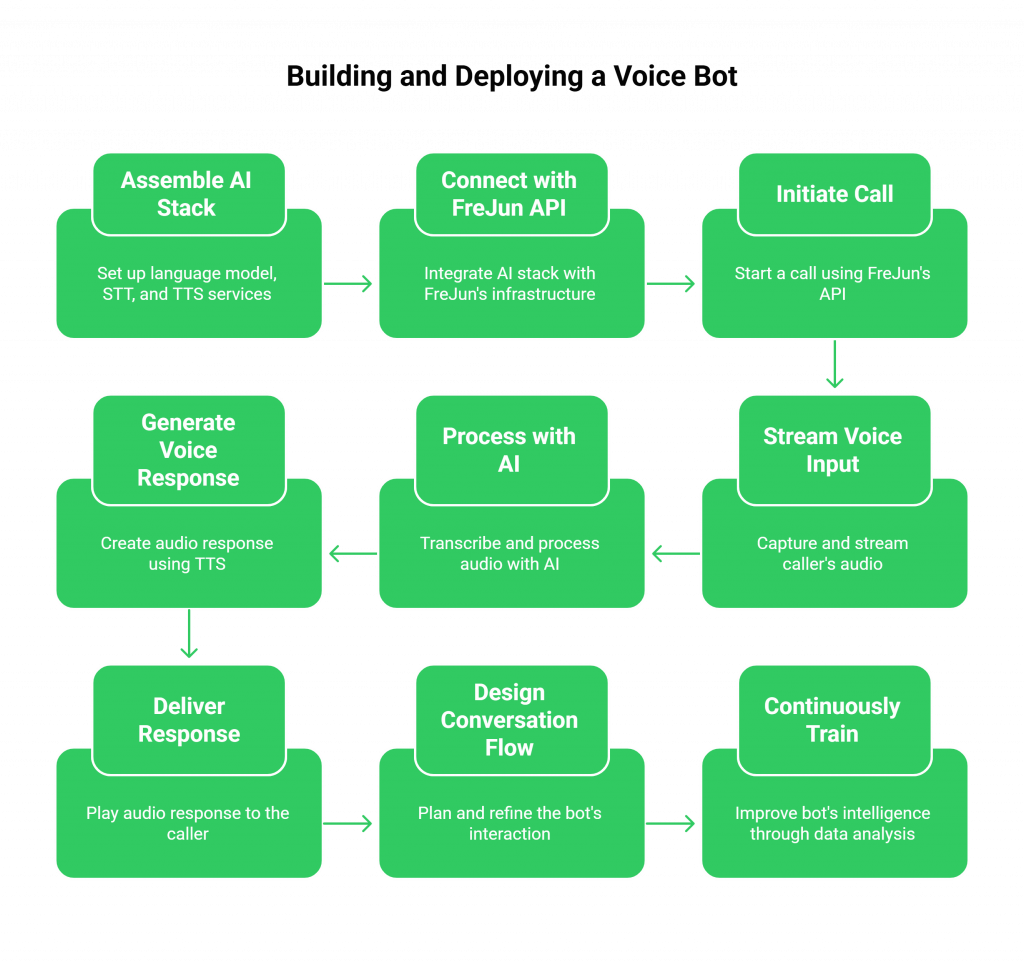
Step 1: Assemble Your AI Stack
Before you can make a call, you need your bot’s core components ready. This is the part of the process that is independent of the voice infrastructure.
- Set up the Language Model (InternLM): Deploy your chosen InternLM model on a server where it can receive text inputs and generate text outputs via an API. You would follow a process similar to setting up the web demo, but containerize it for production use.
- Choose an STT Service: Select a real-time speech-to-text provider that offers streaming transcription. This is crucial for capturing the user’s speech as they talk.
- Choose a TTS Service: Select a text-to-speech provider known for low-latency audio generation and natural-sounding voices.
At the end of this step, you should have three independent, API-callable services: one for transcription, one for intelligence, and one for speech synthesis.
Step 2: Connect Your Stack with the FreJun API
This is where FreJun orchestrates the entire real-time conversation. The flow is seamless and managed entirely through our developer-first SDKs and APIs.
- Initiate a Call: Using FreJun’s API, you can place an outbound call or configure a FreJun-provided virtual number to handle inbound calls.
- Stream Voice Input: Once the call connects, FreJun captures the caller’s audio in real-time and streams it directly to your application’s backend.
- Process with Your AI: Your backend receives this raw audio stream and forwards it to your STT service. The resulting text transcript is then sent to your InternLM Voice Bot for processing.
- Generate a Voice Response: Your bot’s text response is sent to your TTS service, which generates an audio stream.
- Deliver the Response: You pipe this response audio back to the FreJun API, which plays it to the caller with ultra-low latency, completing the conversational loop.
This entire process happens in milliseconds, creating a fluid and natural interaction. FreJun manages the telephony session, ensuring the connection remains stable while your backend manages the AI-driven conversation logic.
Step 3: Design and Refine the Conversation Flow
With the technical plumbing in place, you can focus on the user experience. Your application logic should define how the conversation starts, proceeds, and handles exceptions.
- The Initial Greeting: Configure a short, friendly greeting to be played as soon as the call connects. This confirms to the caller that they’ve reached an automated agent.
- Contextual Personalization: Use any available data about the caller (e.g., from your CRM) to personalize the opening lines.
- Intent Recognition: Train your InternLM Voice Bot to understand various user intents, including common commands like “repeat that” or “speak to an agent.”
- Fallback Logic: Design graceful fallback flows for moments when the bot misunderstands the user, preventing conversational dead-ends.
Step 4: Continuously Train and Improve
A voice bot’s intelligence is not static. FreJun’s reliable call recording and data transport capabilities make it easy to gather the data needed for continuous improvement. By analyzing transcripts and audio from real-world interactions, you can:
- Identify common misunderstandings or friction points.
- Teach the bot to recognize different accents and linguistic variations.
- Refine its responses to be more helpful and accurate over time.
This iterative process of feedback and retraining is key to transforming a functional bot into an exceptional one.
Also Read: How to Build an AI Voice Agents Using GPT-4o for Customer Support?
DIY Voice Infrastructure vs. FreJun: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Building It Yourself (DIY) | Using FreJun’s Infrastructure |
| Primary Focus | Divided between AI logic, telephony, and infrastructure management. | 100% focused on building and refining your InternLM Voice Bot AI. |
| Infrastructure | Must procure, configure, and manage SIP trunks, WebRTC servers, and telephony protocols. | Fully managed, enterprise-grade voice infrastructure provided via a simple API. |
| Latency | A constant engineering battle. Optimizing the entire stack for low latency is complex and costly. | Engineered for low latency. Our entire platform is optimized for real-time conversational AI. |
| Scalability | Scaling requires significant investment in new hardware, software licenses, and network capacity. | Seamlessly scales from one to thousands of concurrent calls on our geographically distributed infrastructure. |
| Time to Market | Months of development and testing to build a stable, scalable voice layer. | Launch a production-ready voice agent in days, not months. |
| Reliability | Reliant on your own infrastructure’s uptime and resilience. Single points of failure are common. | Guaranteed uptime and reliability, backed by an enterprise-grade platform. |
| Support | You are solely responsible for troubleshooting every issue, from dropped calls to audio artifacts. | Dedicated integration support from our team of voice experts to ensure your success. |
Also Read: Enterprise Virtual Phone Solutions for Professional B2B Expansion in the UAE
Best Practices for Designing Effective Voice Bot Conversations
Building the technology is only half the battle. A successful deployment depends on thoughtful conversational design.
- Be Transparent: Let callers know they are speaking with an AI agent at the beginning of the call.
- Keep Prompts Concise: Avoid long, complex sentences. Guide the user with clear and direct questions.
- Confirm Understanding: Have the bot periodically confirm critical information (e.g., “So, you’d like to book an appointment for 3 PM tomorrow. Is that correct?”).
- Offer an Escape Hatch: Always provide a clear and easy way for the user to be transferred to a human agent if they get stuck or frustrated.
- Leverage CRM Integration: Use FreJun’s native CRM integrations to pull caller context and push conversation summaries, making every interaction smarter and more efficient.
Final Thoughts
The decision of how to voice-enable your AI is a strategic one. Attempting to build and manage your voice infrastructure is not a core competency for most businesses. It is a distraction that pulls valuable engineering resources away from what truly creates competitive advantage: the intelligence and effectiveness of your AI model.
By partnering with FreJun, you are not just buying an API; you are adopting a strategy of focus. You are empowering your development team to dedicate their time and talent to training a better InternLM Voice Bot, designing more effective conversational flows, and integrating deeper into your business workflows.
We handle the immense complexity of global, real-time voice communication, providing a reliable and performant foundation upon which you can build the next generation of voice automation. This allows you to move faster, reduce operational overhead, and deliver a superior customer experience.
Also Read: Virtual Phone Providers for Enterprise Operations in Norway
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No. FreJun is a model-agnostic voice infrastructure provider. Our platform is designed to work with any AI chatbot or Large Language Model you choose to bring, including InternLM. This gives you complete control over your AI logic.
You will need three core components in your own backend: a Speech-to-Text (STT) service for transcription, your LLM (like InternLM) for response generation, and a Text-to-Speech (TTS) service for audio synthesis. FreJun acts as the transport layer that connects these components to the live phone call.
Our entire platform is built around real-time media streaming. From the moment a call connects, our stack is optimized to minimize the delay between the user speaking, your AI processing the input, and the voice response being played back.
Yes. FreJun’s platform supports both inbound call handling on virtual numbers and programmatic outbound calling via our API, enabling a wide range of automated voice applications.
