As a developer, you have built a powerful chatbot. It is a sophisticated “brain,” a masterful conversationalist in the silent, typed world of a chat window. You’ve honed its logic, integrated it with your CRM, and trained it on your company’s knowledge. But for all its intelligence, it remains trapped in a world of text, unable to participate in the most natural and immediate form of human communication: voice.
The next great frontier for your chatbot is to break the sound barrier. It is about taking that brilliant, text-based brain and giving it the power of speech, transforming it from a simple chatbot into a true, multi-channel conversational AI. This is not about rebuilding your bot from scratch; it is a project of strategic chat integration. It is about using modern voice APIs for developers to create a new “voice front-end” for the intelligence you’ve already created.
This guide is the architectural blueprint for that integration. We will explore the technical shift from a text-only to a voice-enabled system, dissect the real-time LLM pipeline required, and provide a step-by-step plan for building a seamless, conversational interface that works at the speed of human thought.
Table of contents
- Why is Adding a Voice Channel a Strategic Upgrade?
- What is the Architectural Shift from Text-Only to Voice-Enabled?
- What Does the Real-Time LLM Pipeline for Voice Look Like?
- What is Your Step-by-Step Integration Plan for Developers?
- What Advanced Considerations Will Elevate Your Integration?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is Adding a Voice Channel a Strategic Upgrade?
Giving your chatbot a voice is more than just adding a new feature; it’s a strategic move that fundamentally enhances your customer experience and expands your business’s reach.
How Does It Create a More Natural and Accessible Experience?
The most fundamental benefit is that it makes your AI more human. Voice is our primary, most intuitive mode of communication. It’s faster than typing, requires less cognitive effort, and is inherently more personal. A voice interface makes your AI accessible to a much broader audience, including those who are multitasking, those with visual or motor impairments, and those who simply prefer the speed and convenience of speaking.
The demand for this is clear; a 2023 PwC survey found that 59% of consumers use their voice assistants on their smartphones at least daily, showing a clear and growing comfort with voice-based interactions.
How Can You Unify Your Customer Experience Across Channels?
A customer’s journey is not confined to a single channel. They might start on your website, then call your support line later. A voice-enabled chatbot, powered by the same backend “brain” as your text chatbot, creates a truly unified, omnichannel experience. The AI has a consistent personality and, with a shared memory, can even recall the context of the user’s previous text-based conversation when they call in.
This eliminates the frustrating experience of having to start over. This seamlessness is a key driver of loyalty. A recent Salesforce report found that 78% of customers have had to repeat themselves to multiple agents, a frustration that a unified AI brain can solve.
Also Read: Voice Assistant Chatbot Use Cases in 2025
What is the Architectural Shift from Text-Only to Voice-Enabled?
The beauty of this project is that you are not starting from scratch. You are building an “adapter” layer that translates the world of voice into the language of text that your existing chatbot already understands. This requires a shift from a simple, asynchronous request-response model to a complex, real-time, streaming architecture.
Think of your existing chatbot as a brilliant author who can only communicate via email. An email is asynchronous; a small delay is acceptable. A voice conversation is a live phone call; any delay is immediately noticeable and jarring. Your new voice integration is the high-speed “translator” and “telecommunications network” that this author needs to participate in a live, real-time conference call.
This “telecommunications network” is the voice infrastructure. A high-performance voice APIs for developers platform like FreJun AI is the essential foundation. It handles the immense complexity of managing the live, real-time audio stream, acting as the perfect “nervous system” for your chatbot’s brain.
What Does the Real-Time LLM Pipeline for Voice Look Like?
To make this work, your backend must become a high-speed orchestration engine, managing a continuous, streaming LLM pipeline. Here are the core components:
- The Voice Gateway (FreJun AI): This is the entry and exit point. It’s the voice API platform that connects the live call to your application, providing a raw, real-time audio stream via a WebSocket.
- The “Ears” (Streaming STT): Your backend receives the audio and immediately forwards it to a streaming Speech-to-Text engine. This engine transcribes the audio as it is spoken.
- The “Brain” (Your Existing Chatbot’s API): Your backend takes the final transcript and sends it to your existing chatbot’s API endpoint.
- The “Mouth” (Streaming TTS): Your backend takes your chatbot’s text response and immediately streams it to a Text-to-Speech engine, which begins generating audio for the first few words before it has even received the full sentence.
- The Orchestrator (Your Backend Code): This is the custom code you write that sits in the middle, managing this high-speed flow of data between all the other components.
Also Read: Best Practices for Voice API Integration in SaaS
What is Your Step-by-Step Integration Plan for Developers?
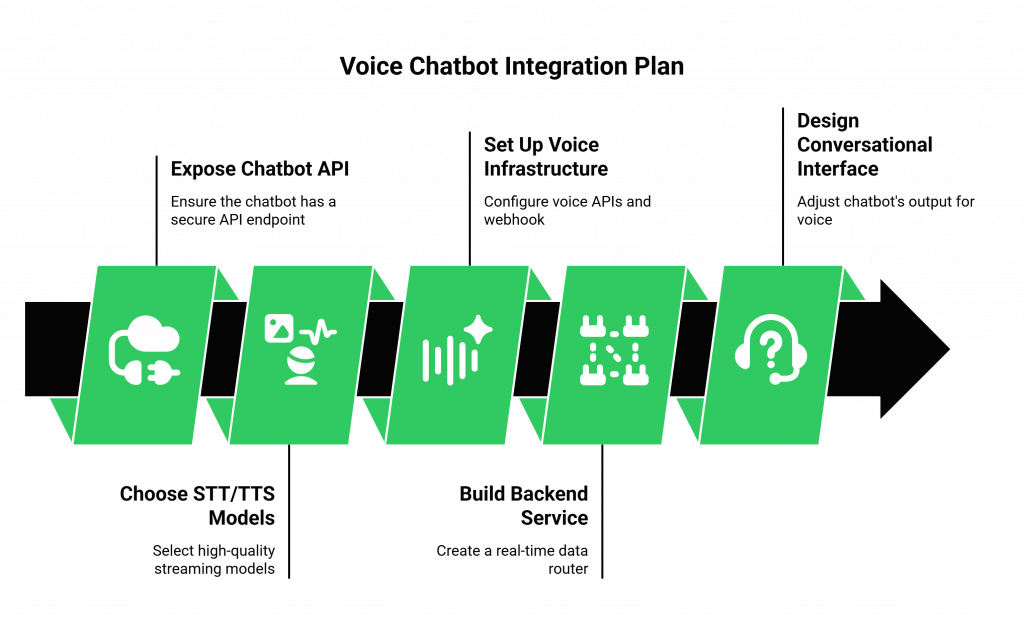
Here is a practical, high-level plan for building the backend service that adds a voice to your existing chatbot.
- Expose Your Chatbot’s Logic via an API: This is the non-negotiable prerequisite. Your existing text-based chatbot must have a secure, well-documented API endpoint that accepts and returns text.
- Choose Your “Senses” (STT/TTS): Select high-quality, streaming STT and TTS models. The “streaming” part is critical for achieving low latency. A model-agnostic voice infrastructure is a major advantage here, as it gives you the freedom to choose the best models for the job.
- Set Up the Voice Infrastructure: This is where you connect to the real world. With a voice APIs for developers platform like FreJun AI, this is a simple process. You will:
- Sign up and get your API keys.
- Acquire a phone number.
- Configure a webhook URL to point to your backend application. This webhook is the “doorbell” that tells your application when a new call has arrived.
- Build the Backend Orchestration Service: This is the core of the project. This new service will be a real-time data router:
- It will listen for the initial webhook from the voice platform.
- It will then establish a persistent WebSocket connection to receive the live audio.
- It will manage the entire LLM pipeline described above, orchestrating the calls to the STT, your chatbot’s API, and the TTS in a continuous, low-latency loop.
- Design for a Conversational Interface: The way your chatbot “writes” might need to be adjusted for a conversational interface. Text that is easy to read (like a long paragraph with links) can be very difficult to listen to. You may need to create a new “voice-first” prompt for your chatbot’s brain, instructing it to use shorter sentences, simpler language, and to avoid trying to “say” things like URLs.
Ready to give your intelligent chatbot the powerful voice it deserves? Sign up for a FreJun AI and start your integration today.
What Advanced Considerations Will Elevate Your Integration?
- Contextual Handoff: Your orchestration service should be able to intelligently transfer the call from the AI to a human agent, passing along the full conversation history to the agent’s screen.
- Interruptibility (“Barge-In”): For a truly natural conversation, your system should be able to handle user interruptions, a feature that requires a high-performance voice API.
- Security: Your backend must be a fortress. This includes validating the signature of all incoming webhooks to ensure they are authentic.
Also Read: Best AI Call Agent Platforms for Lead Qualification
Conclusion
Your intelligent chatbot is a powerful asset. But as long as it is silent, its full potential remains untapped. By leveraging a modern voice APIs for developers, you can create a powerful chat integration that transforms your existing text-based brain into a fully-fledged, voice-enabled conversational AI.
This upgrade is not a teardown; it’s a strategic enhancement. It’s about building a new, more natural “front door” for the intelligence you have already created. By focusing on a robust, real-time backend architecture and building on a foundation of a flexible, high-performance voice infrastructure, you can create a seamless conversational interface that will delight your customers and set your brand apart.
Want to see a technical walkthrough of how our API connects to a chatbot’s LLM pipeline? Schedule a one-on-one demo for FreJun Teler!
Also Read: What Is an Auto Caller? Features, Use Cases, and Top Tools in 2025
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The main benefit is creating a more natural, accessible, and efficient user experience. Voice is faster than typing and allows for hands-free interaction, which is what modern customers expect.
No. As long as your existing text-based chatbot can be accessed via an API, you can add a voice interface to it. The new voice system will act as a “translator,” converting speech to text for your bot and your bot’s text back to speech for the user.
A streaming API allows you to send and receive data in a continuous flow of small chunks. Using streaming APIs for STT, LLMs, and TTS is the key technique for reducing the overall latency and creating a responsive, real-time voice experience.
Webhooks are automated notifications sent from the voice platform to your application. They are the “event triggers” that inform your code about key moments in the call, such as a new call starting or the user finishing their sentence, so your application knows when to take action.
The LLM pipeline is the sequence of real-time processes that a user’s utterance goes through. It typically includes the audio being transcribed by an STT, the resulting text being understood and responded to by an LLM, and the LLM’s text response being converted back to audio by a TTS.
You may need to create a “voice-first” version of your chatbot’s prompts. This means instructing the LLM to use shorter sentences, avoid complex formatting (like bullet points or links), and use a more natural, conversational tone in its text responses.
Yes. This is a major advantage of a backend-driven architecture. The same core orchestration service can be used to power a voice experience over a traditional phone line (telephony) and a voice experience on a website (via WebRTC), all connecting to the same chatbot brain.
A model-agnostic voice API, like the one from FreJun AI, is not tied to a specific AI provider. It gives you the freedom to use your own existing chatbot “brain” and to choose the best STT and TTS models on the market.
Security is handled in layers. You must use API keys for authenticating all your API calls, webhook signature validation to protect your endpoints, and a voice provider that encrypts all audio in transit.
FreJun AI provides the essential voice infrastructure layer. We handle the complex telephony and the high-speed, ultra-low-latency streaming of audio between the user and your backend orchestration service. We are the reliable “nervous system” for your chatbot’s brain.
