For years, the idea of building your own intelligent AI voicebot has felt like an impossible dream for many developers and businesses. The process seemed shrouded in complexity, a domain reserved for elite teams with deep expertise in telephony, machine learning, and distributed systems.
You had to master speech recognition, wrestle with complex telecom protocols, and somehow stitch together a dozen different services. The barrier to entry was a massive, intimidating wall.
That wall has just been completely demolished. A new wave of developer-first platforms and powerful AI models has so radically simplified the process that what once took months of expert engineering can now be achieved in a matter of minutes. This is not an exaggeration. You can genuinely go from a simple idea to a live, conversational AI on a real phone number in the time it takes to drink a cup of coffee.
This guide is a practical, no-nonsense tutorial for the modern developer. We will show you the architectural shift that has made this speed possible and provide a step-by-step, real-world example of how to build and deploy a functional AI voicebot in under 15 minutes.
Table of contents
What is the “Great Abstraction” That Makes This Possible?
To understand how you can build a voicebot so quickly, you first have to understand the mountain of complexity that is being hidden from you. A live, conversational AI is one of the most complex real-time applications in the world. In the past, a developer would have to manually assemble and manage a daunting technology stack.
The “Old Way” (The Mountain of Complexity)
- Telephony: Lease SIP trunks from a carrier, set up a PBX or a Session Border Controller, and manage the physical connections to the phone network.
- Real-Time Transport: Build a server that can handle real-time audio streaming using complex protocols like RTP and WebSockets.
- Audio Codec Management: Write code to handle the dozens of different audio formats (codecs) that a phone call can use.
- Speech Recognition: Integrate a streaming Speech-to-Text (STT) service to transcribe the audio.
- AI Logic: Call a Large Language Model (LLM) API to generate a response.
- Speech Synthesis: Integrate a Text-to-Speech (TTS) service to convert the response back to audio.
- Orchestration: Write the complex, low-latency application logic to glue all of these independent, streaming services together.
This is a monumental task. The “great abstraction” of the modern era is the rise of developer-first voice infrastructure platforms. These platforms have done the incredibly hard work of building and managing the entire telephony and real-time transport layer (steps 1, 2, and 3) and have exposed it all through a simple, elegant API.
This is the core philosophy of a platform like FreJun AI. Our entire purpose is to abstract away the complexity of the “pipe” so you can focus purely on the intelligence that flows through it. We handle the telephony, the codecs, and the real-time streaming, allowing you to build a powerful AI voicebot with just a few simple API calls.
Also Read: Voicebot Online vs Voice Chatbot Online Platforms
What is the Architectural Blueprint for a “15-Minute Voicebot”?
The modern, rapid-deployment architecture is a beautiful example of API-driven design. It consists of three core components:
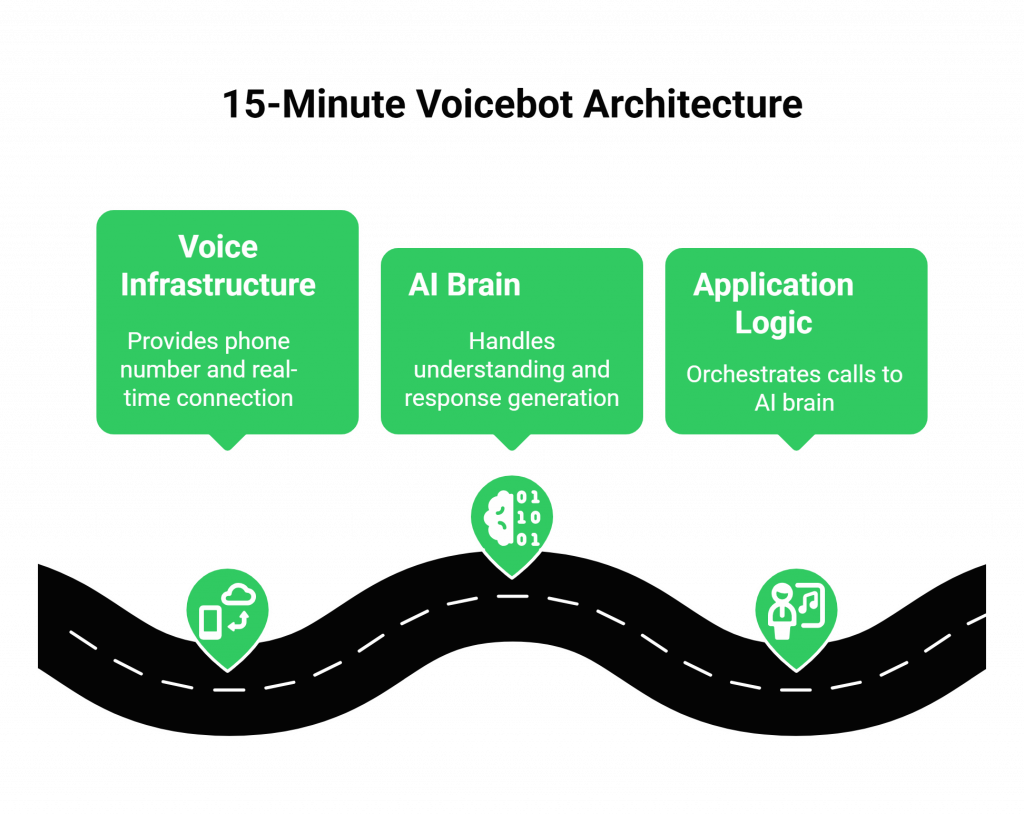
- The Voice Infrastructure (The “Nervous System”): This is your voice API provider. It’s the foundational layer that gives you a phone number and a real-time connection to the call.
- The AI “Brain” (The LLM): This is a powerful, third-party Large Language Model that you will call via its API. This model will handle both the understanding and the response generation.
- Your Application Logic (The “Conductor”): This is the small piece of code you will write. It’s a simple backend server that acts as the “conductor,” receiving events from the voice infrastructure and orchestrating the calls to the AI “brain.”
How Can You Build a Functional AI Voicebot in Under 15 Minutes?
Let’s get practical. Here is a real, step-by-step tutorial. To follow along, you will need two things: an account with a voice infrastructure provider and an API key for an LLM API.
Step 1: Get Your Phone Number and API Keys (Minutes 1-3)
This is the foundational setup.
- Sign up for a voice infrastructure platform. A developer-first platform is designed for this kind of rapid deployment.
- Get a phone number. In the platform’s dashboard, you can instantly search for and buy a phone number in your country.
- Get your API keys. You will need the API keys for the voice platform and for your chosen LLM provider (like OpenAI, Google, or Anthropic). Store these securely.
Step 2: Set Up Your Backend “Conductor” (Minutes 4-8)
You will now write a small backend application. This can be done in just a few lines of code using a modern framework like Node.js with Express or Python with Flask.
- Create a simple web server. This server needs one single API endpoint (e.g., /handle-call) that can accept POST requests.
- During development, expose this server to the internet. A fantastic tool for this is ngrok. With one command, it can create a secure, public URL that tunnels directly to your local server.
- Configure your webhook. In your voice platform’s dashboard, go to your new phone number’s settings and paste your public ngrok URL into the “Incoming Call Webhook” field.
You have now officially connected your phone number to your code.
Also Read: Building AI Agents with Multimodal Models for Enterprises
Step 3: Write the “Welcome and Listen” Logic (Minutes 9-12)
Now, you will write the code that handles the initial webhook.
- Receive the Incoming Call: When a user calls your number, the voice platform will send a webhook to your /handle-call endpoint.
- Respond with Instructions: Your code’s response to this webhook is a set of simple commands in a format like JSON or XML. You will tell the voice platform to do two things:
- First, play a welcome message. This is often a TTS command: {“action”: “speak”, “text”: “Hello, how can I help you today?”}.
- Second, start listening for the user’s response. This is a speech recognition command: {“action”: “listen”}.
The voice platform will now execute these commands. It will synthesize the welcome message, play it to the caller, and then activate its streaming speech recognition engine.
Ready to build your first voicebot in minutes? Sign up for FreJun AI and get instant access to our API.
Step 4: Implement the “Think and Speak” Loop (Minutes 13-15)
This is the final, conversational part of the loop.
- Receive the Transcript: Once the user has spoken, the voice platform’s speech recognition engine will transcribe their words. It will then send another webhook to your server, this time containing the user’s transcribed text.
- Call the LLM API: Your backend code receives this transcript. It then makes a standard API call to your chosen LLM API, sending the user’s message.
- Get the AI’s Response: The LLM API returns its intelligent response in text format.
- Respond with Speech: Your code now responds to the webhook with a new command for the voice platform. This command is another TTS action, telling the platform to speak the LLM’s response out loud. {“action”: “speak”, “text”: “[The LLM’s response goes here]”}.
- Loop: You’ll typically add another {“action”: “listen”} command after the “speak” command to continue the conversation.
And that’s it. In about 15 minutes, you have created a complete, end-to-end AI voicebot that can have a basic but intelligent conversation. The speed of this process is a testament to the power of modern voice APIs.
Why is a Model-Agnostic Infrastructure the Key to This Speed?
The reason this rapid development is possible is because a model-agnostic platform like FreJun AI separates the “pipe” from the “intelligence.”
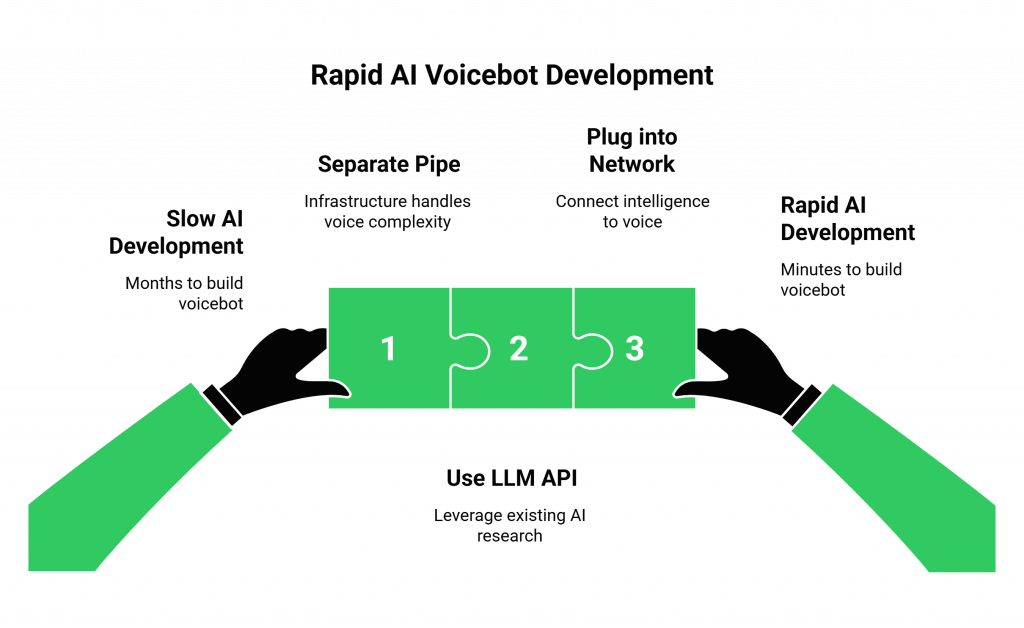
Our philosophy is simple: “We handle the complex voice infrastructure so you can focus on building your AI.”
We don’t force you to use our own, proprietary AI. This is a critical advantage. It means you can use the most powerful, most accessible, and most well-documented LLM API on the market.
You can leverage the billions of dollars of research that companies like Google and OpenAI have invested in their models and plug that intelligence directly into our high-performance voice network. This separation of concerns is the architectural choice that enables a developer to build a world-class AI voicebot in minutes, not months.
The enterprise world is rapidly adopting AI, with a 2024 report from IBM showing that 42% of enterprise-scale companies have actively deployed AI. This new accessibility will only accelerate that trend.
Also Read: Why Businesses Are Shifting to AI Voice Agents
Conclusion
The barrier to entry for building a powerful, intelligent AI voicebot has been completely erased. The “great abstraction” provided by modern voice APIs has hidden the immense complexity of telephony, allowing developers to focus on the creative and exciting work of building a conversational experience.
By combining the power of a world-class LLM API with the simplicity and performance of a developer-first voice infrastructure, you now have the ability to go from a simple idea to a live, functioning voice AI in a single afternoon. The future of voice is not just for the giant tech companies; it’s for every developer with a great idea.
Want to see just how fast you can build a powerful AI voicebot? Schedule a demo for FreJun Teler!
Also Read: How Automated Phone Calls Work: From IVR to AI-Powered Conversations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An AI voicebot is a conversational AI that uses a voice interface to communicate with users. It leverages technologies like speech recognition (STT), a Large Language Model (LLM), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) to have natural, human-like conversations over the phone or a web interface.
Yes. For a basic, conversational voicebot, the combination of a modern voice API and a powerful LLM API has dramatically simplified the process. The core logic can often be written in just a few dozen lines of code.
The three core components are speech recognition (STT) to listen, a Large Language Model (LLM) to think, and Text-to-Speech (TTS) to speak.
A webhook is an automated notification sent from one application to another when a specific event occurs. In a voice API, webhooks are used to inform your application about real-time events, such as an incoming call or the user finishing their sentence, so your code can react instantly.
Ngrok is a popular development tool that creates a secure, public URL that tunnels directly to a server running on your local machine. It’s essential for testing webhooks during development, as it allows the cloud-based voice platform to send messages directly to the application you’re building on your computer.
No. This is the key benefit. A developer-first voice API platform handles all the deep, complex telephony, so you only need to work with familiar web technologies like APIs and webhooks.
The LLM API acts as the “brain” of your bot. Your application sends it the user’s transcribed text, and the LLM uses its vast knowledge and reasoning capabilities to generate an intelligent, human-like response in text format.
A model-agnostic voice infrastructure, like FreJun AI, is not tied to a specific AI provider. It gives you the freedom to choose your own “best-of-breed” STT, LLM, and TTS models from any company, allowing you to build the most powerful and cost-effective solution.
FreJun AI enables this by providing a high-level abstraction over the complex world of telephony. Our simple webhook and command structure (like speak and listen) allows a developer to create a complex conversational flow with very simple instructions, dramatically reducing the amount of code they need to write.
The next steps involve adding more robust features, such as “contextual memory” to remember the conversation, “tool calling” to connect to other APIs, and detailed error handling and security measures like webhook signature validation.
