Customer conversations are evolving beyond scripted chatbots and static IVR menus. Businesses now need scalable voice solutions that sound natural, respond instantly, and operate around the clock. Gemma 3 makes this possible with its lightweight, open-source architecture for real-time reasoning and dialogue.
But intelligence alone is not enough, the voice layer must also be seamless. FreJun provides the infrastructure that carries Gemma 3’s capabilities into every phone call with clarity, low latency, and enterprise reliability.
Table of contents
- The AI Revolution in Customer Support: Beyond Text-Based Bots
- Why Building a Voice Bot is More Than Just an AI Challenge
- Architecting Your Solution: The Brain and the Nervous System
- Core Components of an Enterprise-Grade Voice Bot
- How to Build and Deploy a Voice Bot Using Gemma 3?
- DIY Infrastructure vs. FreJun: A Head-to-Head Comparison
- Real-World Use Cases for Your Gemma 3 Voice Bot
- Final Thoughts: Move from Concept to Production, Faster
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The AI Revolution in Customer Support: Beyond Text-Based Bots
For years, businesses have relied on chatbots to manage customer queries, but their limitations are clear. They are often rigid, lack contextual understanding, and fail at the slightest deviation from their script. Today, the availability of lightweight, powerful open-source models like Gemma 3 is changing the landscape, enabling the creation of sophisticated, real-time voice agents that can understand, reason, and converse naturally.
Building a voice bot using Gemma 3 allows you to automate routine queries, provide 24/7 support, and deliver personalized interactions at scale. Unlike text-only bots, these voice agents can handle the nuances of human speech, creating a more intuitive and efficient customer experience. However, creating a successful voice bot involves more than just programming an AI model. The real challenge lies in connecting that AI to your customers over a phone line with the speed and clarity a real conversation demands.
Why Building a Voice Bot is More Than Just an AI Challenge
Developing the “brain” of your voice bot, the part that processes language and generates responses, is only half the battle. The other, more complex half is the infrastructure: the real-time telephony plumbing that connects your AI to the outside world. Many development teams dive into building their AI stack with ASR, Gemma 3, and TTS, only to hit a wall when it comes to deployment.
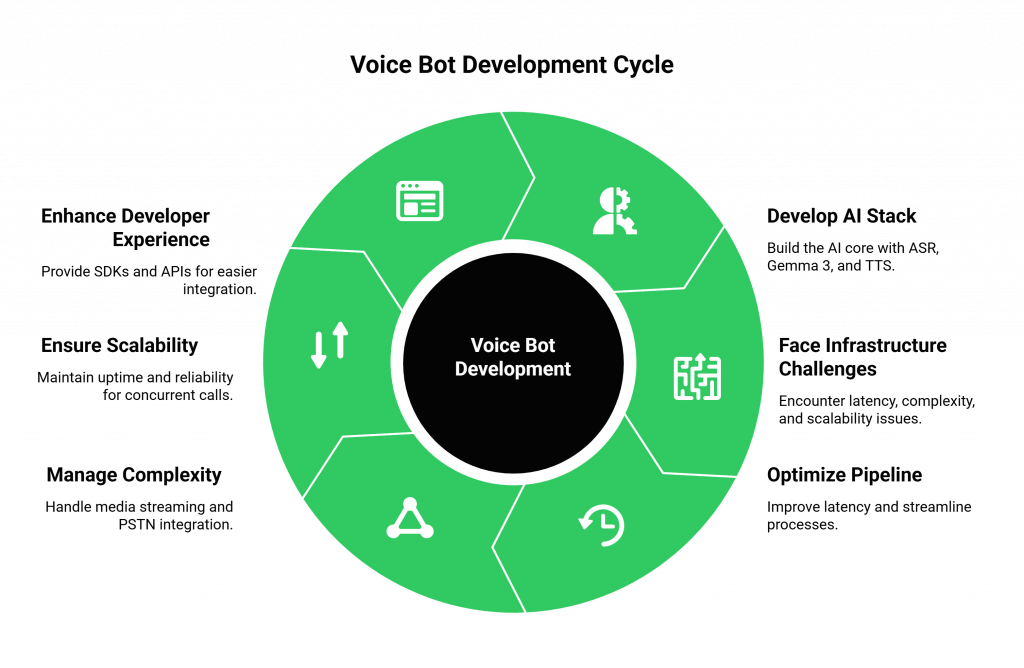
They face significant technical hurdles:
- High Latency: The delay between a customer speaking, your AI processing the audio, and the voice response playing back can create awkward, conversation-breaking pauses. Optimizing this entire pipeline is a massive engineering challenge.
- Infrastructure Complexity: Managing real-time media streaming, call routing, and integration with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) requires specialized telecom expertise. It’s a complex, resource-intensive task that distracts from your core goal: building great AI.
- Scalability and Reliability: A self-built voice infrastructure may work for a demo, but can it handle thousands of concurrent calls? Ensuring enterprise-grade uptime and geographically distributed reliability is a full-time job.
- Developer Experience: Without proper SDKs and APIs, connecting your AI logic to the voice layer becomes a tangled mess of custom code, making it difficult to maintain and iterate.
These infrastructure challenges are precisely why FreJun exists. We handle the complex voice transport layer so you can focus on what you do best: building a powerful voice bot using Gemma 3.
Also Read: How to Build a Voice Bot Using MiniMax-Text-01 for Customer Support?
Architecting Your Solution: The Brain and the Nervous System
To build a production-ready voice bot, you need two distinct but interconnected systems: the AI Brain and the Voice Nervous System.
- The AI Brain (Your Application): This is the logic center you build and control. It consists of three key services working in tandem:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): Converts the caller’s spoken words into text.
- Large Language Model (LLM): Gemma 3 processes the text to understand intent, manage dialogue, and generate a response.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): Converts the AI’s text response back into audible speech.
- The Voice Nervous System (FreJun’s Infrastructure): This is the transport layer that carries signals between the customer and your AI Brain. FreJun manages the entire real-time communication pipeline, providing a robust API and developer-first SDKs to handle:
- Inbound & Outbound Calling: Connecting to the global telephone network.
- Real-Time Audio Streaming: Capturing the caller’s voice and streaming it to your ASR with minimal delay.
- Low-Latency Playback: Delivering the synthesized voice response from your TTS back to the caller instantly.
By separating these concerns, you can build a sophisticated voice bot using Gemma 3 without becoming a telecom infrastructure expert. You bring the intelligence; we provide the connection.
Core Components of an Enterprise-Grade Voice Bot
A truly effective voice bot is a symphony of several technologies working together seamlessly. Here’s a breakdown of the essential components.
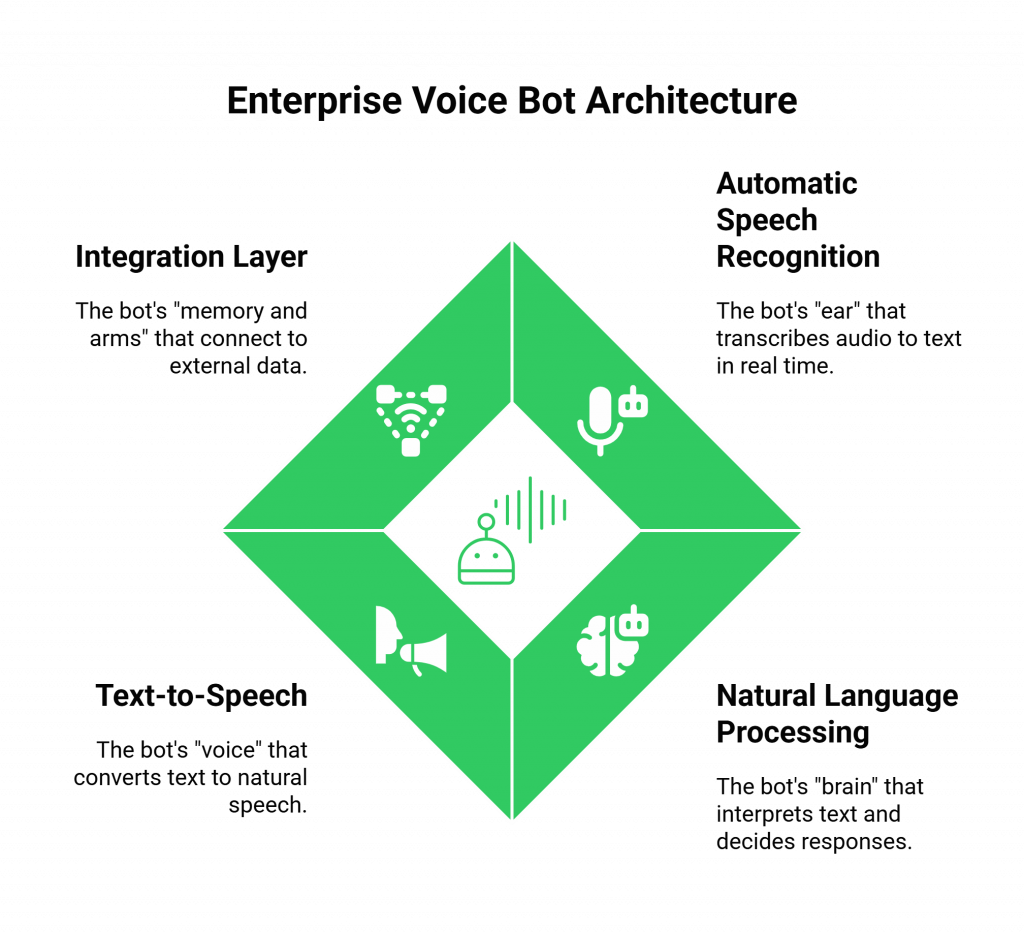
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): This is the bot’s “ear.” It listens to the raw audio from the call and transcribes it into text in real time. Popular services include Google Speech-to-Text and Whisper AI. FreJun streams the call audio directly to your chosen ASR service, ensuring a clean, low-latency input.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Reasoning: This is the bot’s “brain.” The transcribed text is fed to your Gemma 3 model, which interprets the user’s intent, understands the context of the conversation, and decides on the appropriate response. Its lightweight nature makes it highly efficient for real-time applications.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): This is the bot’s “voice.” Once Gemma 3 generates a text response, a TTS engine like Amazon Polly or Azure TTS converts it into natural-sounding speech. You then pipe this audio output back to FreJun’s API, which plays it to the caller, completing the conversational loop.
- Integration Layer: This is the bot’s “memory and arms.” To provide useful answers, your AI needs access to external data. This layer connects your Gemma 3 application to your CRM, knowledge bases, and internal APIs to fetch information like order status, account details, or appointment availability.
Also Read: How to Get a Virtual Number for WhatsApp Business Integration in India?
How to Build and Deploy a Voice Bot Using Gemma 3?
Here is a practical, step-by-step guide to bringing your voice AI from concept to a live, production-grade application.
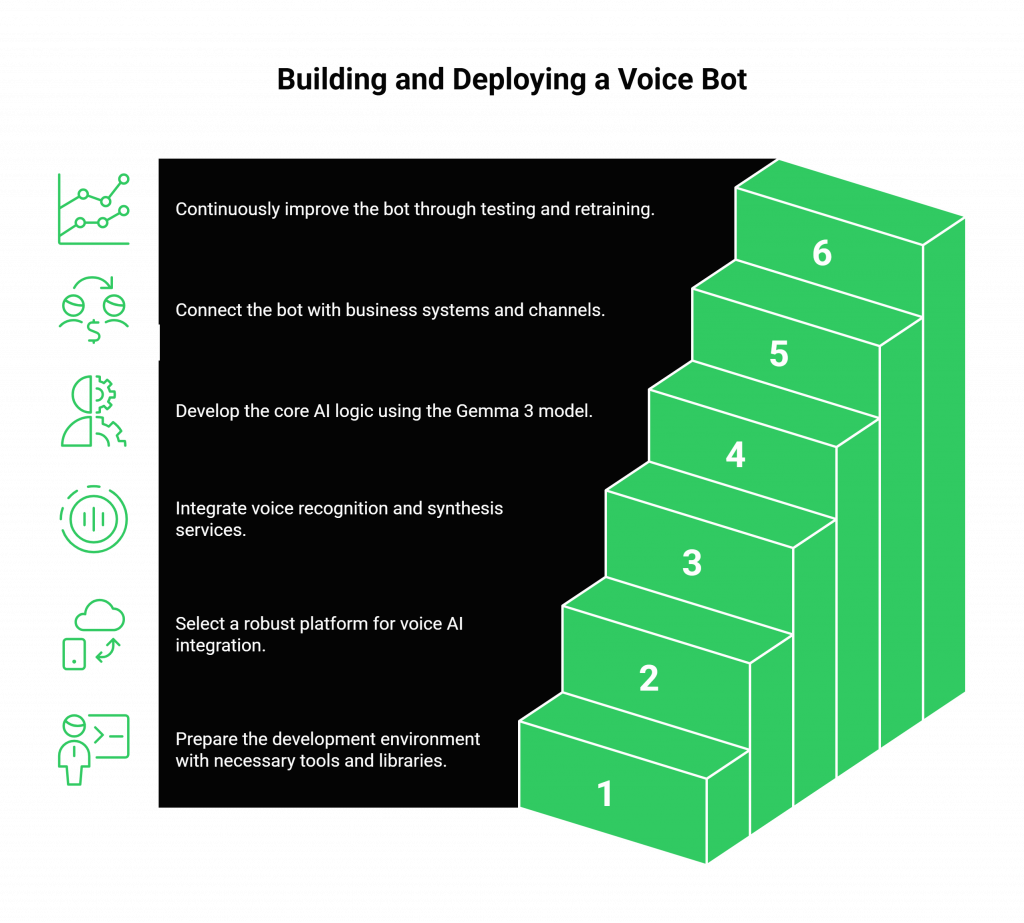
Step 1: Set Up Your AI Environment
First, prepare your development environment. You’ll need Python or Node.js to orchestrate the services. Install the necessary libraries to interact with Gemma 3 and your chosen ASR and TTS providers. This is where you’ll define the core logic of your conversational agent.
Step 2: Choose a Robust Voice Transport Layer
Before you write a single line of AI logic, solve the infrastructure problem. Instead of building a complex telephony stack from scratch, integrate a platform designed for voice AI.
With FreJun, you get:
- Developer-First SDKs: Easily embed voice capabilities and manage call logic from your backend.
- Real-Time Media Streaming: A low-latency pipeline to send audio to your ASR and receive it from your TTS.
- Full Control: FreJun acts as a pure transport layer, giving you complete control over your AI dialogue state.
This step simplifies deployment and ensures your bot can handle real-world conversations without frustrating delays.
Step 3: Connect Your ASR and TTS Services
Integrate your ASR and TTS services with your application. Your code will receive a raw audio stream from the FreJun API, send it to your ASR service for transcription, and pipe the resulting text to your Gemma 3 model. After Gemma 3 generates a response, your application sends it to the TTS service and streams the synthesized audio back to the FreJun API for immediate playback.
Step 4: Implement Your Gemma 3 Logic
This is the core of your AI. Use the Gemma 3 model to handle intent recognition, manage conversational context, and generate accurate, helpful responses. Fine-tune the model with your company’s FAQs, customer interaction logs, and domain-specific knowledge to improve its performance and relevance.
Step 5: Integrate with Business Systems and Channels
Connect your application to your CRM, helpdesk software, and other internal systems via APIs. This allows your voice bot using Gemma 3 to perform actions like looking up order information, booking appointments, or creating support tickets. Finally, deploy the bot to your desired channels, such as an inbound support line (IVR), WhatsApp, or a website click-to-call button.
Step 6: Test, Train, and Iterate
Deployment is just the beginning. Continuously monitor your voice bot’s performance. Use conversation logs and analytics to identify areas for improvement. Regularly retrain your Gemma 3 model with new data to expand its knowledge and refine its accuracy, ensuring it always provides the best possible customer experience.
Also Read: How to Build AI Voice Agents Using DeepSeek-V3?
DIY Infrastructure vs. FreJun: A Head-to-Head Comparison
When deploying a voice bot, you have two choices for the underlying infrastructure: build it yourself or use a managed platform. Here’s how they stack up.
| Feature | Building on Your Own Infrastructure | Building with FreJun’s Voice Infrastructure |
| Development Time | Months of complex telephony engineering and integration work. | Days. Use robust APIs and SDKs to connect your AI instantly. |
| Latency | High risk of latency issues; requires deep optimization across stack. | Engineered for low-latency; real-time media streaming is core. |
| Scalability | Difficult and expensive to scale; requires managing servers and carriers. | Built on resilient, geographically distributed infrastructure for high availability. |
| Call Management | Requires building call routing, queueing, and state management from scratch. | Comes with enterprise-grade call management features built-in. |
| Focus | Divided between building AI logic and managing telecom infrastructure. | 100% focused on building and refining your AI application. |
| Security & Compliance | You are solely responsible for all security protocols and compliance. | Security by design; platform adheres to robust protocols. |
| Support | No external support for infrastructure issues. | Dedicated integration support from pre-launch to post-optimization. |
Real-World Use Cases for Your Gemma 3 Voice Bot
Once deployed, a voice bot using Gemma 3 can transform your customer support operations across various functions.
- 24/7 Automated Helpline: Offer round-the-clock support for common issues like password resets, order tracking, and account balance inquiries without needing human agents available.
- Intelligent Call Routing: The bot can understand a customer’s needs in natural language and route them to the correct department or agent, bypassing complex and frustrating IVR menus.
- Proactive Outbound Notifications: Automate appointment reminders, delivery status updates, and feedback collection calls with a natural, conversational voice.
- Seamless Human Handoff: For complex or sensitive issues, the bot can gather initial information and then seamlessly transfer the call along with the full conversational context, to a human agent, ensuring a smooth customer experience.
Also Read: Enterprise Virtual Phone Solutions for B2B Communication in Israel
Final Thoughts: Move from Concept to Production, Faster
The era of intelligent voice automation is here, and open-source models like Gemma 3 have made it more accessible than ever. However, the path from a proof-of-concept to a production-grade voice AI application is paved with infrastructural challenges. Focusing your engineering resources on telephony instead of AI logic is a strategic misstep.
By leveraging a dedicated voice transport layer like FreJun, you abstract away the complexity of real-time communication. You get a reliable, secure, and scalable foundation to build upon, allowing you to launch sophisticated voice agents in days, not months. Let your team build the best possible AI; we will make sure it can talk to the world.
Also Read: How to Build AI Voice Agents Using Claude Sonnet 4?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No. FreJun is a model-agnostic voice infrastructure platform. We provide the real-time streaming and call management APIs that allow you to connect your own AI stack, including any LLM (like Gemma 3), ASR, and TTS services you choose. This gives you full control over your AI logic.
FreJun offers comprehensive server-side SDKs for popular languages like Python and Node.js, making it easy to integrate our voice layer with your backend application.
Our entire platform is engineered for low-latency media streaming. We optimize the transport of audio from the caller to your ASR and from your TTS back to the caller, minimizing delays and eliminating the awkward pauses that can break a conversation’s flow.
Absolutely. Gemma 3 is designed for customization. You should train it with your own domain-specific data, such as product documentation, historical support tickets, and call transcripts, to improve its accuracy and relevance for your use case.
A typical stack includes a programming language (Python), an ASR service (e.g., Google Speech-to-Text), an NLP engine (Gemma 3), a TTS service (e.g., Amazon Polly), and an integration API for call handling (FreJun).
