For a developer, a modern Large Language Model is like a brilliant brain in a jar. It’s a marvel of intelligence, capable of understanding complex language, reasoning about the world, and generating human-like text with astonishing fluency.
But it is fundamentally isolated. It has no senses. It has no voice. and cannot connect to the messy, analog, and incredibly time-sensitive world of a real human conversation.
This is the central challenge of voice AI. How do you build a “nervous system” that can connect this brilliant brain to the real world? How do you create the digital senses of hearing and the vocal cords for speech, and ensure the signals travel at the speed of thought?
The answer lies in a powerful and elegant piece of modern engineering: the voice API for developers. It is the foundational technology, the essential “nervous system,” that breathes life into the AI’s brain. This guide will take a deep dive into the architecture of this system, explaining how a voice API is the indispensable enabler of the real-time, next-generation AI systems you want to build.
Table of contents
- Why Can’t a Powerful AI Just Talk on Its Own?
- What Exactly is a Voice API and How Does it Function?
- How Does a Voice API Enable the Real-Time Conversational Flow?
- What Advanced AI Capabilities are Unlocked by a High-Performance Voice API?
- How Do You Choose the Right Voice API for a Next-Gen AI System?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why Can’t a Powerful AI Just Talk on Its Own?
To appreciate the power of a voice API, you must first understand the immense complexity of the problem it solves. The world of AI and the world of global telephony are two completely different universes, speaking two completely different languages.
- The AI’s World: This is a clean, digital world of text, JSON, and APIs. It speaks the language of the modern web.
- The Telephony World: This is a chaotic, decades-old world of analog signals, specialized hardware, and arcane protocols like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol). It is a complex web of interconnected carriers, each with its own rules and quirks.
To connect these two worlds from scratch would require a developer to become a world-class expert in both software engineering and telecommunications engineering.
You would be responsible for negotiating with carriers, managing physical hardware, and wrestling with the notorious difficulties of streaming real-time audio across different networks and firewalls.
This is a monumental task that distracts from the core goal: building an intelligent application. A voice API for developers is the abstraction layer that makes this entire nightmare of complexity simply disappear.
Also Read: Top Voice Bot Online Platforms for Small Businesses
What Exactly is a Voice API and How Does it Function?
A voice API is a specialized, cloud-based platform that acts as the universal translator and high-speed transport layer between your application and the global telephone network. It handles all the “dirty work” of telephony and presents you with a clean, simple, and powerful programmatic interface.
The rise of the API economy has been a driving force in modern software development. A 2023 Postman report found that developers now spend nearly 60% of their work week working directly with APIs, and a voice API is a critical tool in this new landscape.
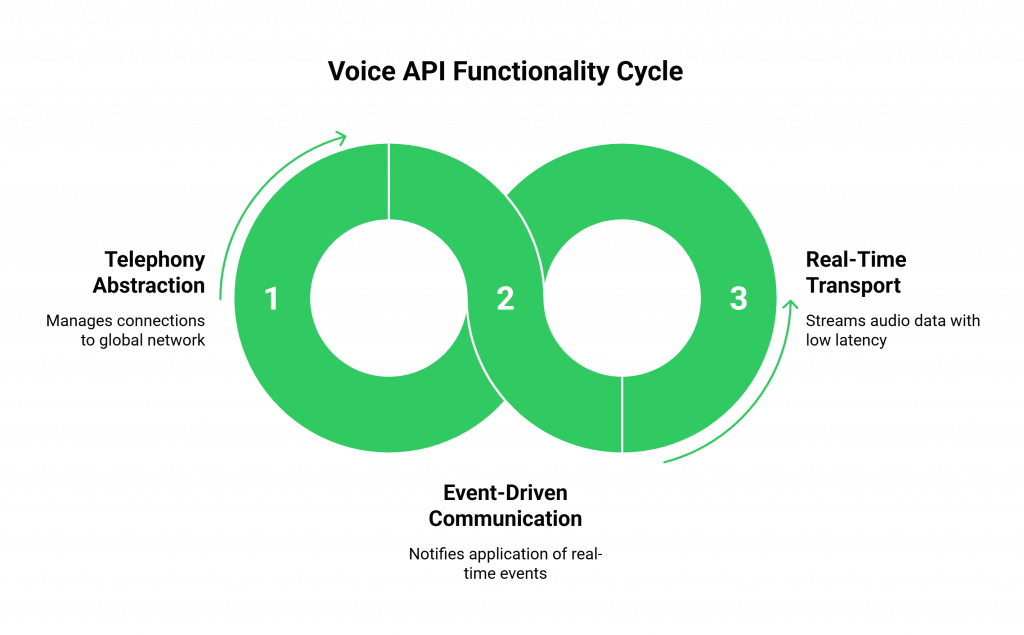
A high-performance voice API provides three core functions:
- Telephony Abstraction: It manages all the connections to the global telephone network, allowing you to buy a phone number in any country with a single API call.
- Event-Driven Communication (Webhooks): It uses webhooks to instantly notify your application of real-time events on a call (e.g., “a new call is incoming,” “the user hung up”).
- Real-Time Transport (WebSockets): It uses WebSockets to create a persistent, two-way “tunnel” between the live call and your backend server, allowing raw audio data to be streamed back and forth with a delay of only a few milliseconds.
How Does a Voice API Enable the Real-Time Conversational Flow?
Let’s walk through the high-speed data dance of a single turn in a conversation to see how a voice API integration makes it all possible.
- The Call Starts: A user dials your phone number. The voice API provider’s platform answers the call and immediately sends an incoming call webhook to your backend server.
- The Stream Begins: Your server receives this webhook and responds with a command, sent via a REST API call, instructing the voice platform to start a real-time audio stream. The platform then establishes a secure WebSocket connection to your server. The live audio from the call begins flowing to your application. This is where a high-performance voice infrastructure like FreJun AI is critical, providing this raw, high-fidelity audio stream with carrier-grade reliability.
- The AI “Hears”: Your server receives the raw audio packets from the WebSocket and immediately forwards them to the streaming API of your chosen Speech-to-Text (STT) engine.
- The AI “Thinks”: The STT engine sends a live transcript back to your server. Your server then constructs a prompt for your LLM and makes an API call to its endpoint.
- The AI “Speaks”: The LLM returns a text response. Your server immediately streams this text to your chosen Text-to-Speech (TTS) engine, which returns a stream of generated audio data.
- The Loop Completes: Your server sends this generated audio data back down the open WebSocket to the voice platform, which then plays it to the user on the live call.
This entire round trip, orchestrated by the voice API for developers, happens in under a second, creating a seamless, real-time conversation.
Ready to start architecting your own real-time voice AI? Sign up for a FreJun AI to begin building.
Also Read: Chatbot Voice Assistant Design Patterns to Follow
What Advanced AI Capabilities are Unlocked by a High-Performance Voice API?
A truly powerful voice API for developers goes beyond the basics. It provides the granular control and advanced features needed to build the next generation of intelligent systems.
- Interruptibility (“Barge-In”): A great voice AI can be interrupted. This requires a voice API that supports full-duplex audio, allowing your application to detect incoming user audio even while it is playing back the bot’s audio.
- Multimodal Integration: The voice API acts as the perfect “auditory nerve” for a multimodal agent. While another part of your system handles the video stream, a specialized voice API can manage the complex, low-latency audio channel.
- Real-Time Agent Assist: A sophisticated voice API can “fork” a live audio stream. This allows you to send a copy of the audio from a call between a human agent and a customer to a silent AI “listener.” This AI can then provide real-time suggestions to the agent’s screen.
- Secure Data Capture (DTMF): The API can be instructed to listen for keypad tones (DTMF) and capture them as data, completely bypassing the audio stream. This is essential for securely handling sensitive information like credit card numbers.
Also Read: Voice API Integration Best Practices for Enterprises
How Do You Choose the Right Voice API for a Next-Gen AI System?
For a developer building a high-performance AI, not all voice APIs are created equal. You must choose a provider that is not just a utility, but a true infrastructure partner. The best voice API for business communications must have:
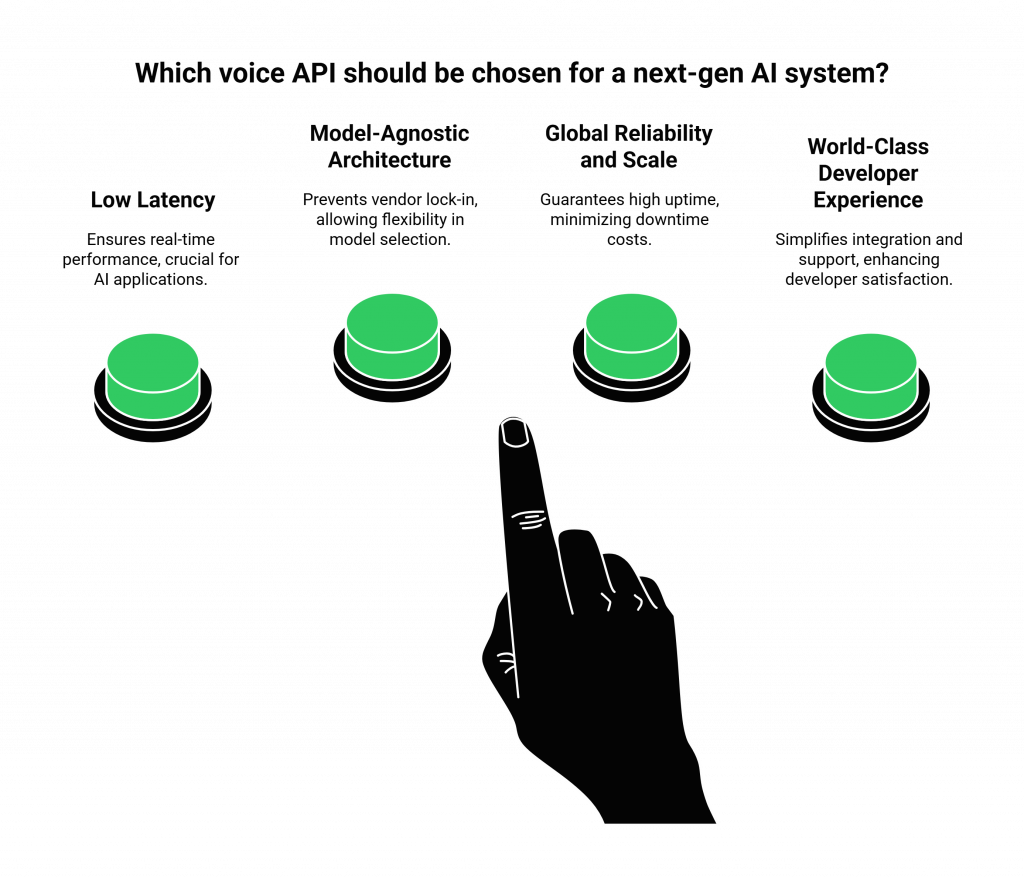

- An Obsessive Focus on Low Latency: This is the number one priority. The provider’s entire global network must be engineered for speed.
- A Model-Agnostic Architecture: This is the key to future-proofing your application. A model-agnostic platform like FreJun AI gives you the freedom to always use the best-in-class STT, LLM, and TTS models from any provider, preventing vendor lock-in.
- Global Reliability and Scale: The platform must have a globally distributed network with guaranteed high uptime. The cost of downtime in a customer-facing application is enormous. A recent ITIC survey found that for 44% of large enterprises, a single hour of downtime costs over $1 million.
- A World-Class Developer Experience (DX): The API must be clean, the documentation must be meticulous, and the support must be expert.
Conclusion
The voice API for developers is the unsung hero of the conversational AI revolution. It is the critical enabling technology, the powerful and reliable “nervous system” that gives a brilliant AI “brain” its senses and its voice. It transforms the immense complexity of global telephony into a simple, elegant, and powerful set of programmatic tools.
By choosing a high-performance, developer-first voice API, you are not just selecting a vendor; you are building on a foundation of speed, reliability, and flexibility. This is the essential first step to creating the next generation of truly intelligent, real-time voice systems.
Want to see how our API architecture can provide the low-latency foundation for your AI? Schedule a demo with our team at FreJun Teler.
Also Read: How Automated Phone Calls Work: From IVR to AI-Powered Conversations
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The main purpose is abstraction. It simplifies the complex process of connecting to the global telephone network. It offers a simple, programmatic interface that web and app developers can easily use.
A voice API handles the telephony and audio transport, it’s the bridge to the phone call. An AI model API is the intelligence, it processes the data (e.g., converts audio to text). A complete voice API integration involves using a voice API to get the audio and then sending it to an AI model API.
No. This is one of the primary benefits. The voice API for developers handles all the complexity of protocols like SIP and RTP, so you only need to work with familiar web technologies like HTTP and WebSockets.
No. This is one of the primary benefits. The voice API for developers handles all the complexity of protocols like SIP and RTP, so you only need to work with familiar web technologies like HTTP and WebSockets.
A webhook is an automated notification. The voice API platform uses webhooks to send HTTP requests to your application. These requests notify it of real-time call events, such as incoming calls or when a call ends.
Security is managed using API keys to authenticate your platform requests. Webhook signature validation ensures that all events your app receives come from your trusted voice provider.
Yes. A full-featured voice API for developers allows you to programmatically make outbound calls. It is essential for use cases like proactive reminders or lead qualification.
A model-agnostic voice API, like the one from FreJun AI, is not tied to a specific AI provider. It gives you the freedom to choose your own STT, LLM, and TTS models from any company, allowing you to build a “best-of-breed” solution.
Latency is the delay in the conversation. High latency results in unnatural pauses after a user speaks, which makes the bot feel slow, unintelligent, and frustrating to talk to.
