The ability to develop a sophisticated Audio Chat Bot, a system that can intelligently listen and speak in real time, has been thoroughly democratized. Thanks to powerful and accessible APIs for Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Large Language Models (LLMs), and Text-to-Speech (TTS).
Table of contents
- What is an Audio Chat Bot? A Developer’s Perspective
- The Hidden Roadblock: Why Your Bot Can’t Answer the Phone
- FreJun: The Voice Infrastructure for Your Audio Chat Bot
- A Tale of Two Architectures: DIY Telephony vs. FreJun
- How to Build an Audio Chat Bot That Answers Calls? A 5-Step Guide
- Best Practices for a Production-Grade Audio Chat Bot
- Final Thoughts: Focus on the Conversation, Not the Connection
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Any skilled developer can now architect a bot that engages in natural, hands-free conversations. The path seems clear: set up a backend, wire up a few APIs, and create a stunning conversational experience.
Thousands of developers have followed this path, building impressive demos that work flawlessly on their local machines. But a frustrating and often project-killing roadblock emerges the moment they try to deploy this bot for a real-world business use case. They discover that the architecture that powers a bot in a browser is fundamentally incapable of handling the most critical communication channel of all: the telephone.
What is an Audio Chat Bot? A Developer’s Perspective
From a technical standpoint, an Audio Chat Bot is an elegant pipeline of interconnected services, orchestrated by a backend application. The process, designed for low-latency interaction, follows a clear and logical flow:
- Audio Input: The system captures a user’s voice through a microphone.
- Speech Recognition (ASR): The raw audio is streamed to an ASR service (like OpenAI’s Whisper or Google Speech) which transcribes it into text in real time.
- Language Understanding (LLM): The transcribed text is sent to the “brain” of the operation a language model like GPT-4, which analyzes the user’s intent, manages context, and generates a response.
- Speech Synthesis (TTS): The AI’s text response is sent to a TTS engine (such as one from ElevenLabs or Coqui) to be converted into a lifelike audio stream.
- Audio Output: The synthesized audio is streamed back to the user for playback.
The Hidden Roadblock: Why Your Bot Can’t Answer the Phone
You’ve successfully built this pipeline. Your bot is intelligent, responsive, and works perfectly when you speak into your computer’s microphone. Now, your business wants to put it to work on the customer service hotline. This is where the project grinds to a halt.

Technologies like the Web Audio API or mobile app audio tools capture audio effectively in browsers and apps but don’t interface with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). The global phone system is a completely different ecosystem, with its own complex protocols and infrastructure.
To make your Audio Chat Bot answer a phone call, you would need to become a telecom engineer overnight, building a complex infrastructure stack to solve problems like:
- PSTN Connectivity: Managing SIP trunks, carrier negotiations, and phone number provisioning.
- Real-Time Media Servers: Building and maintaining specialized servers to handle raw audio streams from thousands of concurrent calls.
- Call Control and Signaling: Programmatically managing the entire lifecycle of a phone call from ringing and connecting to holding and terminating.
- Network Imperfections: Engineering solutions to mitigate the jitter, packet loss, and latency issues that are common on phone networks and can ruin a conversation.
This is the hidden roadblock that turns a promising AI project into a grueling infrastructure build, diverting your focus and delaying your time to market indefinitely.
FreJun: The Voice Infrastructure for Your Audio Chat Bot
This is the exact problem FreJun was created to solve. We are not another AI service provider. FreJun is the specialized voice infrastructure platform that acts as the essential bridge between your intelligent backend and the global telephone network.
We provide a simple, developer-first API that handles all the complexities of telephony. We manage the infrastructure, the protocols, and the real-time audio streaming. All your backend application sees is a clean, bi-directional audio stream delivered over a standard WebSocket connection.
FreJun is model-agnostic, meaning you can continue to use your preferred ASR, LLM, and TTS providers. We simply provide the reliable and scalable transport layer that makes the Audio Chat Bot you’ve already built work seamlessly over a real phone call.
A Tale of Two Architectures: DIY Telephony vs. FreJun
| Feature | The DIY Telephony Approach | The FreJun Platform Approach |
| Infrastructure Focus | Building and maintaining voice servers, SIP trunks, and PSTN interconnects. | Integrating a single, simple voice API into your existing backend. |
| Developer’s Role | Becomes a hybrid backend developer and telecom engineer. | Remains focused on backend logic, AI orchestration, and business value. |
| Time to Market | Months, or even years, to build a stable, scalable system. | Days or weeks to deploy a production-ready telephony voice bot. |
| Scalability | Extremely difficult and costly to scale for high call concurrency. | Built on a globally distributed, enterprise-grade platform that scales on demand. |
| Maintenance | Continuous, complex maintenance of telephony hardware and software. | Zero telephony maintenance. FreJun handles all infrastructure and uptime. |
Pro Tip: Design a Channel-Agnostic Backend
The most robust and future-proof way to architect your Audio Chat Bot is to create a core AI logic that is channel-agnostic. Design your backend to simply process an incoming audio stream and produce an outgoing one, without caring if the source is a web browser or a phone call. This allows you to use the same intelligent “brain” to power an in-app assistant and a FreJun-powered telephone agent, maximizing code reuse and ensuring a consistent user experience.
How to Build an Audio Chat Bot That Answers Calls? A 5-Step Guide
This guide outlines the modern, efficient process for developing a voice bot that can handle real phone calls, using FreJun as the infrastructure layer.
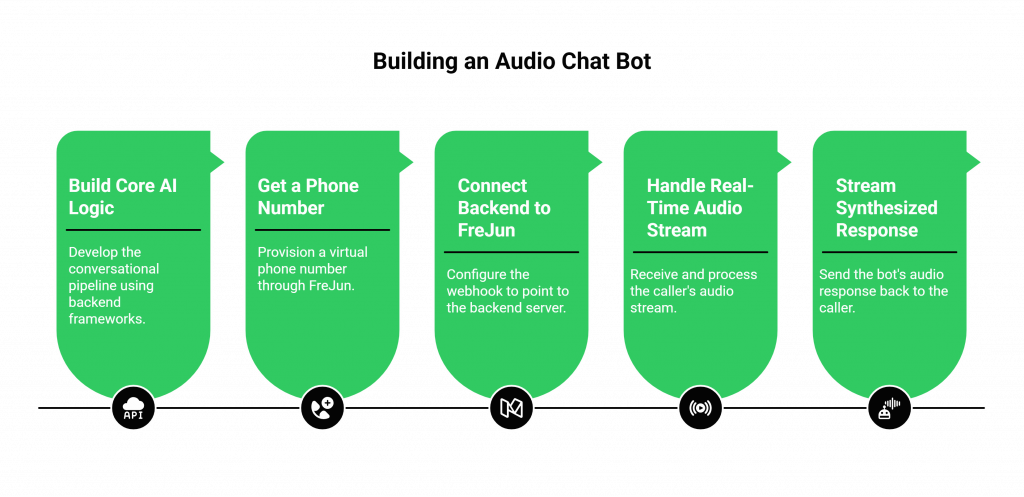
Step 1: Build Your Core AI Logic (The Part You Already Know)
First, build your conversational pipeline. Using your preferred backend framework (like FastAPI or Express), orchestrate the API calls to your chosen ASR, LLM, and TTS services. Get this working so it can process an audio input and generate an audio output.
Step 2: Get a Phone Number with FreJun
Instead of wrestling with telecom carriers, simply sign up for FreJun and provision a virtual phone number through our dashboard. This process takes minutes and gives your bot a public-facing identity.
Step 3: Connect Your Backend to FreJun’s API
In the FreJun dashboard, configure your new number’s webhook to point to your backend server’s WebSocket endpoint. This tells our platform where to send live call audio. Our server-side SDKs make handling this connection straightforward.
Step 4: Handle the Real-Time Audio Stream from the Call
When a customer dials your FreJun number, our platform answers the call and immediately begins streaming the caller’s raw audio to your backend. Your application code will receive this stream and pipe it directly into the ASR engine of your existing AI pipeline. The rest of your conversational logic proceeds exactly as you designed it.
Step 5: Stream the Synthesized Response Back to the Caller
Once your TTS engine generates the bot’s audio response, you simply stream it back to the FreJun API. Our platform handles playing it to the caller over the phone with ultra-low latency, creating a natural and fluid conversational loop.
Key Takeaway
Developing a production-grade Audio Chat Bot is a two-part challenge that requires two different skill sets. The first is AI orchestration, which most developers can master using modern APIs. The second is telecommunications infrastructure, a highly specialized and complex domain. The most effective strategy is to focus on your core competency building a brilliant AI and leverage a specialized platform like FreJun to handle the voice transport layer. This allows you to get to market faster with a more reliable and scalable product.
Best Practices for a Production-Grade Audio Chat Bot
- Optimize for Latency: Aim for an end-to-end latency of under 700 milliseconds to make conversations feel natural. While FreJun provides a low-latency transport, you should also select ASR, LLM, and TTS providers that are optimized for speed.
- Handle Interruptions (Barge-In): Real conversations are not always turn-based. FreJun’s bi-directional streaming allows your backend to detect incoming user speech even while playing a response. Design your logic to handle these interruptions gracefully by stopping the playback and processing the new input.
- Manage Session State: An intelligent bot needs memory. Use a fast database or in-memory cache (like Redis) to store the conversation history for each unique call. This enables more sophisticated, multi-turn dialogues.
- Ensure Security and Privacy: Voice data is sensitive. Encrypt all audio streams, manage API keys securely, and comply with all relevant data protection regulations. Always disclose to users that they are speaking with an AI.
Final Thoughts: Focus on the Conversation, Not the Connection
The power to build a truly interactive Audio Chat Bot is now in the hands of every developer. The opportunities are boundless, from revolutionizing customer service to creating entirely new forms of entertainment and accessibility tools. However, the path to a successful deployment is not about building everything from scratch.
The smartest teams understand the importance of focus. They concentrate their efforts on crafting the personality, intelligence, and usefulness of their AI agent the parts of the system that create unique value. They leave the complex, undifferentiated heavy lifting of voice infrastructure to a specialized partner.
By building on top of the FreJun platform, you are making a strategic decision to accelerate your development, reduce your operational burden, and build on a foundation of enterprise-grade reliability. Let us handle the complexities of the connection, so you can perfect the art of the conversation.
Further Reading – The Benefits of Using AI Insight for Call Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No. FreJun is a model-agnostic voice infrastructure platform. We provide the essential API that connects your backend application to the telephone network, giving you the freedom to choose and integrate any AI services you prefer.
You can use any backend framework that can handle a standard WebSocket connection. Asynchronous frameworks like FastAPI (Python) or Express.js (Node.js) are particularly well-suited for the real-time, I/O-bound nature of streaming voice.
WebRTC is a protocol designed for real-time communication between web browsers and applications. It does not natively interface with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). FreJun provides this critical PSTN connection, allowing anyone to call your bot from a regular phone number.
Yes. Our API provides full call control, including the ability to programmatically initiate outbound calls. This is ideal for use cases like automated appointment reminders, feedback surveys, or proactive sales outreach.
