Businesses face growing customer expectations for speed, accuracy, and personalized service. Traditional call centers and IVRs struggle to meet these demands, often resulting in inefficiencies and frustrated customers. AI voice agents – powered by LLMs, advanced STT/TTS, and real-time orchestration – are transforming how companies engage over voice. From handling complex inquiries to scaling outbound campaigns, these intelligent systems deliver human-like conversations with minimal latency.
This blog explores why enterprises are shifting to AI voicebots, the underlying technical infrastructure, and how adopting a reliable platform like FreJun Teler can accelerate voice-driven automation while improving customer experience.
What’s Driving the Sudden Shift Toward AI Voice Agents?
Over the past few years, businesses have undergone massive digital transformation. Customer engagement is no longer limited to chat or email – voice has re-emerged as the fastest and most natural way to interact. Yet, managing thousands of inbound and outbound calls using traditional contact center models is both expensive and rigid.
That’s where the AI voice agent comes in.
An AI voicebot doesn’t just follow a script. It listens, understands intent, retrieves context, and responds instantly – almost like a human. Unlike legacy IVR systems that rely on button presses, modern voice AI systems hold real-time, two-way conversations over phone networks or VoIP.
According to Forbes (2025), more than 40% of growing enterprises are now piloting or scaling AI-powered voice interfaces across their support, sales, and internal automation workflows. The push isn’t just about efficiency – it’s about speed, personalization, and scale.
With the rise of automation tools and contact center AI, voice has evolved from being reactive to proactive. Businesses no longer want to answer calls – they want to orchestrate intelligent conversations automatically.
How Do AI Voice Agents Actually Work Under the Hood?
At their core, AI voice agents combine several technologies that work together in real time. The following flow simplifies how these systems function:
| Component | Purpose | Example Functionality |
| Speech-to-Text (STT) | Converts user’s speech into text | Detects intent and transcribes speech accurately in milliseconds |
| Language Model / Agent Logic | Interprets the text and decides how to respond | Understands context, queries knowledge, and triggers actions |
| RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) | Adds real-world knowledge to the AI’s response | Pulls facts, FAQs, or user data from your systems |
| Text-to-Speech (TTS) | Converts AI’s text response into lifelike audio | Delivers smooth, natural-sounding replies |
| Transport Layer (Telephony/VoIP) | Handles real-time streaming of voice data | Ensures low-latency audio flow both ways |
Every successful voice AI system depends on how seamlessly these layers interact. The key challenge is latency – users expect a human-like rhythm with less than 500 milliseconds of delay between speaking and hearing a response.
This is achieved by streaming architectures, where STT, the agent model, and TTS work concurrently. Instead of waiting for full audio completion, data flows continuously – producing nearly instant back-and-forth conversation.
In practical terms:
- The user speaks into a call.
- The STT engine transcribes audio on the fly.
- The AI agent interprets the text, references company data via RAG, and forms a response.
- That response is converted back to speech via TTS.
- The transport layer streams it to the user instantly.
The result is a voice experience that feels alive – not mechanical.
Why Are Businesses Replacing Traditional IVRs With AI Voicebots?
For decades, IVR systems were the backbone of customer communication. They worked – but only to a point. Users pressed 1 for billing, 2 for support, and 3 to speak with an agent. These workflows were slow, rigid, and frustrating.
Now, companies are replacing static menus with AI voicebots capable of dynamic conversation. Let’s explore why.
Limitations of Legacy IVRs
- Rely on predefined scripts that cannot handle unexpected user intent.
- Require constant manual updates when business processes change.
- Offer poor contextual understanding – they treat every call as new.
- Result in long call times and high abandonment rates.
How AI Voice Agents Outperform Them
- Understand natural language, allowing users to speak freely.
- Integrate with backend CRMs, databases, and automation tools.
- Retain context within a session, making conversations more human-like.
- Automate complex tasks like rescheduling, payment, or feedback collection.
For instance, a healthcare provider can use an AI voicebot to confirm appointments, remind patients, and even follow up post-consultation – all without a live representative. Similarly, an insurance company can handle quote requests or claims initiation automatically, reducing average handling time by over 60%.
In short, AI voice agents don’t just replace IVRs – they redefine how businesses talk to their customers.
Discover how AI is revolutionizing inbound call handling with real-time automation and intelligent voice routing. Learn more insights here.
What Core Business Benefits Are Fueling Adoption?
a. Cost Reduction and Scalable Operations
Traditional contact centers scale linearly – more calls require more human agents. This model is costly and hard to maintain across time zones. One of the most compelling numbers: AI-enabled voice bots can reduce customer service costs by as much as 30 %.
Voice AI changes that. Once deployed, an AI voicebot can handle hundreds of concurrent calls without burnout, salary overheads, or training cycles. Businesses achieve lower cost-per-interaction while maintaining consistent service quality.
Additionally, automation reduces operational errors and ensures 24/7 availability – essential for global businesses that can’t afford downtime.
b. Enhanced Customer Experience (CX)
Customer experience is now the competitive edge. AI voice agents personalize every interaction using stored context and CRM data.
Key improvements include:
- Instant response times: Customers don’t wait on hold.
- Natural communication: Real-time understanding and human-like tone.
- Contextual memory: Recognizing repeat callers or unresolved queries.
- Multilingual support: Instant translation and local language voice synthesis.
Unlike traditional IVRs that feel transactional, voice AI systems feel conversational. They respond empathetically, adjust tone, and adapt in milliseconds.
This creates trust – a metric that directly influences brand loyalty and retention.
c. Catalyst for Digital Transformation
For most enterprises, voice automation isn’t just a support upgrade – it’s part of a larger digital transformation roadmap.
AI-driven automation tools now handle repetitive workflows across chat, email, and now, voice. Integrating these systems into CRMs, ERPs, and support dashboards helps unify customer data and communication flows.
Voice AI becomes the final automation layer – connecting natural speech to structured data. It bridges the gap between how humans talk and how machines process information.
As more companies embrace cloud infrastructure and modular APIs, implementing voice automation becomes both feasible and essential. Businesses that ignore this shift risk being left behind by competitors who operate faster, cheaper, and smarter.
What Makes Today’s Voice Agents Technically Superior?
While early voice assistants were basic, modern systems leverage deep technical innovation in streaming architectures, LLMs, and real-time speech synthesis.
Let’s break down the technical leap that makes this possible.
1. Low-Latency Media Streaming
Real-time interaction depends on milliseconds. Unlike batch transcription, streaming audio allows partial transcription, incremental processing, and concurrent TTS playback.
Modern APIs push latency under 400–500 ms, eliminating awkward pauses. This is crucial for creating fluid, human-like dialogues – especially for contact center AI and customer-facing scenarios.
2. Contextual Understanding via RAG
Static AI models are limited by their training data. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) overcomes this by fetching real-time data from business systems.
Example:
- Caller asks: “What’s my delivery status?”
- The AI voicebot retrieves details from the logistics database and replies with up-to-date tracking info.
This ensures accurate, contextual responses – a major leap from the pre-trained-only approach.
3. Adaptive TTS and Emotional Range
Voice synthesis has evolved beyond robotic tones. New text-to-speech systems can mimic human nuances such as emphasis, emotion, and pauses. This adaptability improves trust and engagement.
Moreover, adaptive TTS supports regional accents and local languages – a key enabler for global deployment.
4. Multi-Model Compatibility
Today’s systems are modular – you can integrate any STT, LLM, or TTS based on accuracy, cost, and latency needs. This flexibility lets engineering teams design optimal voice stacks without vendor lock-in.
For example:
- Use high-accuracy STT for medical transcription.
- Pair with lightweight LLM for task routing.
- Use expressive TTS for outbound sales calls.
This modular approach helps teams achieve balance between performance, cost, and scalability.
Explore modern inbound call handling strategies in 2025 and see how AI voice agents streamline customer support operations efficiently.
How Can Businesses Actually Build and Deploy an AI Voicebot?
While building a proof-of-concept voice AI is easy, deploying one that scales reliably is a different challenge.
Here’s a simplified step-by-step blueprint:
- Capture Voice Input: Start by routing inbound or outbound calls through a secure media gateway or telephony API.
- Process in Real Time: Stream the audio to an STT engine to generate live transcripts.
- Interpret Using LLM: Pass the transcript to your agent logic, which understands context and makes decisions.
- Retrieve Context: Use RAG to fetch relevant knowledge (FAQs, CRM data, product info).
- Generate Response: Convert AI output into speech using a TTS engine that streams back audio in real time.
- Deliver Back Through Telephony: The streaming audio plays instantly to the user, completing the conversational loop.
Each step involves low-latency data flow, secure connections, and session-level context. Engineers must handle events like jitter, speech overlap, and API synchronization to ensure smooth experience.
To maintain high-quality output, it’s recommended to:
- Use streaming endpoints instead of batch APIs.
- Maintain stateful sessions with context memory.
- Log all events for observability and debugging.
- Use fallback logic to gracefully handle network errors.
This architecture enables both inbound (support) and outbound (proactive engagement) use cases – from customer onboarding to payment reminders.
What Does a Scalable Voice AI Architecture Look Like?
Once the concept is validated, the real engineering challenge is scalability. For large-scale deployments – especially those handling thousands of concurrent calls – system architecture defines success.
A scalable AI voicebot infrastructure generally includes these layers:
| Layer | Purpose | Key Technologies |
| Telephony / VoIP Layer | Handles PSTN or SIP connectivity | Cloud telephony APIs, WebRTC, SIP trunks |
| Media Streaming Layer | Streams live audio in both directions | RTP, WebSocket streaming, gRPC |
| Processing & AI Layer | Runs STT, LLM, RAG, and TTS | Whisper, GPT, Claude, Gemini, ElevenLabs |
| Application Logic Layer | Manages conversation flow and context | Orchestration APIs, state machines |
| Integration Layer | Connects with business systems (CRM, ERP, DBs) | REST APIs, GraphQL, Zapier, internal microservices |
Every millisecond matters here. Traditional HTTP request–response cycles create bottlenecks, so real-time streaming protocols (such as WebSockets or RTP) are essential for smooth dialogue.
To maintain quality at scale:
- Run AI inference asynchronously, streaming tokens as they generate.
- Buffer TTS output dynamically to avoid playback gaps.
- Implement silence detection to optimize speech turn-taking.
- Distribute workloads geographically for latency reduction.
These principles form the backbone of reliable contact center AI infrastructure – capable of serving hundreds of users concurrently with human-level fluidity.
Where Does FreJun Teler Fit Into This Ecosystem?
This is where FreJun Teler changes the game.
For most engineering teams, managing telephony, media streaming, and real-time audio pipelines becomes the toughest part of deploying voice automation. Even if you have the best LLM or AI agent, your product is only as good as its voice infrastructure.
FreJun Teler acts as the global voice infrastructure layer – the missing piece that connects your AI agent to the real world of phone and VoIP calls.
Here’s what that means technically:
1. Real-Time Media Streaming Built for AI
Teler’s architecture captures, processes, and streams voice data with ultra-low latency – often below 300–400 ms round-trip. This ensures users never experience awkward pauses.
It supports both inbound and outbound call streaming, making it ideal for AI-powered customer support, sales automation, or appointment bots.
2. Model-Agnostic Integration
FreJun Teler is fully model-agnostic – you can connect any LLM, TTS, or STT provider.
- Use GPT or Claude for reasoning,
- Whisper or Deepgram for transcription,
- ElevenLabs or Play.ht for voice synthesis.
Teler doesn’t interfere with your AI logic – it simply ensures seamless voice transport between the user and your system.
3. Developer-First SDKs and APIs
Engineers can build voice applications in minutes using Teler’s SDKs. These provide:
- Secure WebSocket endpoints for bi-directional streaming,
- Event-based call control (pause, resume, transfer, record),
- Session state APIs to retain conversational context.
This saves months of infrastructure setup – allowing teams to focus purely on the AI layer and business logic, not on managing call routing or audio encoding.
4. Enterprise Reliability
FreJun Teler operates on a geographically distributed network, ensuring high availability and resilience against call drops or packet loss.
It’s built with enterprise-grade security – including TLS encryption, data isolation, and compliance-ready protocols for regulated industries.
In short, FreJun Teler provides the plumbing – so your AI voicebot can perform without worrying about telephony complexity.
Sign Up With FreJun Teler Today and Experience Seamless Business Calling!
How Do You Integrate Teler with Your AI Stack?
Implementation is surprisingly straightforward. You can think of Teler as the “bridge” that connects your LLM-driven AI agent with the outside world through phone or VoIP.
A simple workflow looks like this:
- Initiate a Call: Your app triggers a voice call via Teler’s REST or WebSocket API.
- Stream Real-Time Audio: Teler sends the live user audio stream to your server or AI endpoint.
- Process via AI Agent: Your system transcribes speech (STT), interprets via LLM, and generates a response.
- Stream Back the Response: The AI’s response (via TTS) is streamed back to Teler, which plays it instantly to the caller.
- Maintain Context: Throughout the call, your backend keeps session-level memory, enabling the AI to remember prior exchanges or user preferences.
This modular approach supports plug-and-play flexibility – you can experiment with different AI providers without rebuilding the telephony base each time.
That’s why Teler fits perfectly into the modern voice AI stack, sitting between cloud telephony and AI processing – ensuring low latency, reliability, and scalability across regions.
What Are the Most Common Use Cases for Voice AI Today?
AI voice agents are now being deployed across verticals – from startups to large enterprises. Let’s explore where the adoption is accelerating.
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Impact |
| Customer Support | Automated receptionists, 24/7 helplines | Reduced wait times, faster resolution |
| Healthcare | Appointment scheduling, patient reminders | Lower no-shows, higher engagement |
| Finance & Insurance | Claims intake, lead qualification | Improved compliance and call tracking |
| E-commerce | Order updates, delivery confirmations | Proactive communication and feedback |
| Recruitment & HR | Interview scheduling, screening | Faster candidate workflows |
Across these scenarios, the benefits are consistent – speed, accuracy, and personalization.
Moreover, by leveraging Teler’s infrastructure, businesses can launch multi-region deployments with minimal engineering effort, maintaining audio quality and compliance at scale.
What Should You Evaluate Before Choosing a Voice Infrastructure Partner?
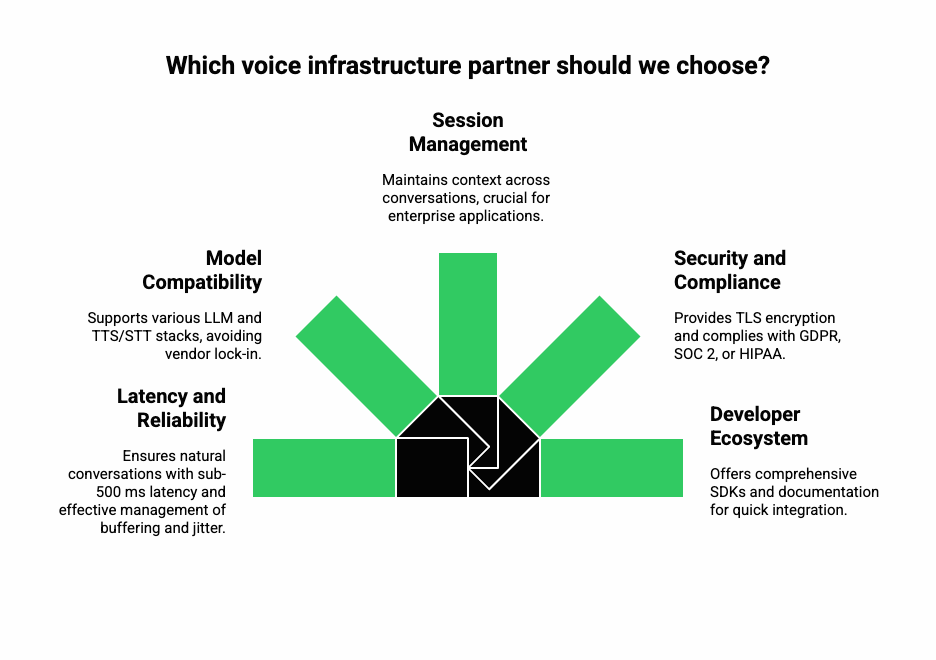
When selecting a voice infrastructure platform (like Teler), product and engineering leaders should evaluate key technical parameters:
1. Latency and Reliability
Sub-500 ms latency is non-negotiable for natural conversations. Test how the provider manages buffering, jitter, and geographic routing.
2. Model Compatibility
Ensure the infrastructure supports any LLM and TTS/STT stack – avoiding vendor lock-in and enabling experimentation.
3. Session Management
Persistent sessions help maintain context across conversations, crucial for enterprise-grade contact center AI applications.
4. Security and Compliance
Look for TLS encryption, data retention controls, and compliance with GDPR, SOC 2, or HIPAA (if applicable).
5. Developer Ecosystem
Comprehensive SDKs, detailed documentation, and sandbox environments accelerate proof-of-concept builds and reduce integration time.
FreJun Teler scores strongly across these parameters – its architecture is built for speed, reliability, and interoperability – aligning perfectly with modern automation tools and enterprise digital strategies.
What Does the Future of AI Voice Agents Look Like?
The next evolution of voice AI will go beyond reactive communication. We’re moving toward autonomous, context-aware agents that can act, reason, and learn across channels.
Some emerging trends include:
- Multi-turn context retention: AI agents will remember historical interactions across time.
- Tool calling and automation: Agents will execute tasks – booking appointments, updating CRMs, triggering workflows – not just talk.
- Emotion-aware synthesis: TTS models will adapt tone based on sentiment, improving empathy.
- Cross-channel orchestration: Unified AI agents managing both chat and voice seamlessly.
As infrastructure and AI models continue to converge, businesses will no longer ask “Should we automate voice?” – instead, they’ll ask “How fast can we scale it globally?”
Why Is Now the Right Time to Adopt Voice AI?
Several factors make this the perfect time for businesses to make the shift:
- Mature Infrastructure: Reliable APIs like FreJun Teler remove the hardest technical barriers.
- Advanced Models: Modern LLMs and TTS/STT tools are accurate, faster, and more expressive.
- Lower Costs: Cloud pricing and open models have dramatically reduced the cost of AI operations.
- Customer Expectation: Voice-first experiences are now the norm, not a novelty.
In short, AI voicebots are no longer experimental. They are becoming mission-critical for business communication, customer engagement, and operational efficiency.
Final Thoughts – Building the Voice-Driven Enterprise
Adopting AI voice agents is no longer optional; it’s a critical step in digital transformation and operational efficiency. Businesses that integrate voice AI today enhance customer experience, streamline workflows, and lay the groundwork for autonomous, voice-first operations. For founders, product managers, and engineering leads, the focus should remain on designing intelligent AI logic while leveraging a reliable voice infrastructure.
FreJun Teler simplifies this by managing real-time audio streaming, telephony integration, and low-latency voice delivery – allowing teams to scale their AI voicebots seamlessly across regions. Start accelerating your voice automation journey and deploy production-ready voice AI in days, not months.
FAQs –
- What is an AI voicebot?
An AI voicebot is a system that handles real-time voice interactions using LLMs, STT, TTS, and contextual automation. - How does voice AI improve customer support?
It automates inquiries, reduces wait times, maintains context, and delivers personalized, human-like conversations around the clock. - Can AI voice agents replace human agents entirely?
For routine and high-volume tasks, yes; complex decision-making still requires human supervision for compliance or nuanced scenarios. - What technologies power voice AI?
Key technologies include LLMs, STT, TTS, RAG for context, and telephony integration for real-time audio streaming. - Is AI voicebot integration difficult?
Not with modular platforms like FreJun Teler, which handles streaming, telephony, and low-latency audio infrastructure efficiently. - Can AI voicebots handle multilingual calls?
Yes, modern TTS/STT engines support multiple languages and accents, enabling global customer engagement without regional constraints. - How does AI retain context during conversations?
It uses session memory and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to track dialogue across multiple turns reliably. - What are common use cases for voice AI?
Inbound support, outbound reminders, lead qualification, surveys, appointment scheduling, payment processing, and personalized customer engagement. - Are AI voice agents secure?
Yes, enterprise-grade platforms implement encryption, data isolation, and compliance protocols like GDPR, SOC 2, and HIPAA.
How quickly can businesses deploy AI voicebots?
With platforms like Teler, deployment can occur in days, supporting real-time voice interactions and scalable production use.
