Voice agents are no longer futuristic experiments – they have become a vital component of modern customer interaction, operations, and lead engagement. Organizations are increasingly deploying local LLM voice assistants to handle repetitive queries, automate processes, and provide natural, real-time conversations over VoIP network solutions. However, simply deploying a voice bot does not guarantee success. Without measuring the right indicators, businesses risk low adoption, frustrated users, and missed ROI opportunities.
In this guide, we explore how to evaluate the success of AI-driven voice agents, which key performance indicators (KPIs) matter, and how to implement robust monitoring when running voice agents on edge networks locally. Whether you are a founder, product manager, or engineering lead, this guide offers a structured, technical approach to understanding voice bot performance and scaling intelligently.
What Are Modern Voice Bots And How Do They Work?
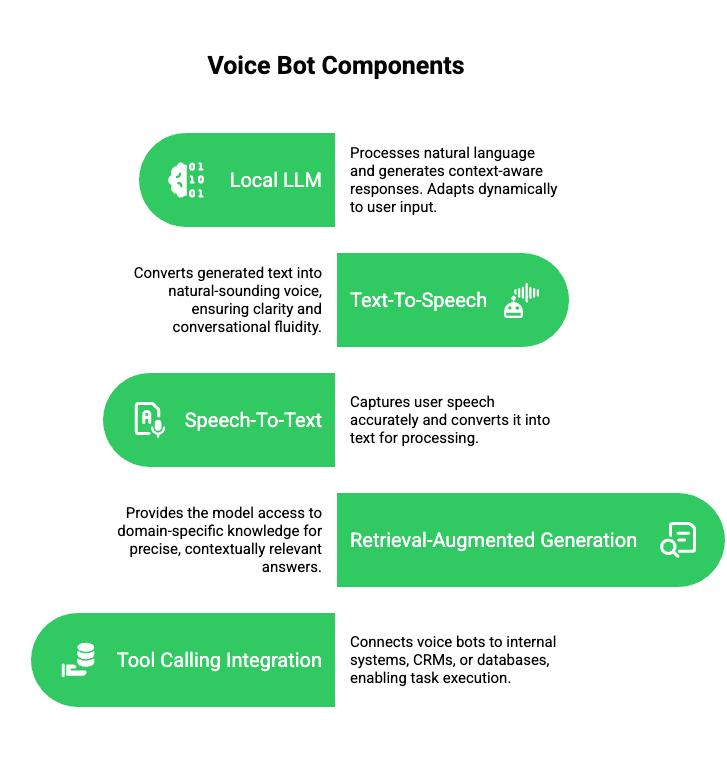
To effectively measure performance, it’s crucial to understand the components and architecture of modern voice bots. Today’s voice agents are more than just automated IVR systems. They integrate multiple AI and communication technologies to enable real-time, human-like interactions.
Core Components of a Voice Bot:
- Local LLM (Large Language Model): Processes natural language and generates context-aware responses. Unlike static scripts, the LLM adapts dynamically to user input.
- Text-To-Speech (TTS): Converts generated text into natural-sounding voice, ensuring clarity and conversational fluidity.
- Speech-To-Text (STT): Captures user speech accurately and converts it into text for processing.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Provides the model access to domain-specific knowledge for precise, contextually relevant answers.
- Tool Calling Integration: Connects voice bots to internal systems, CRMs, or databases, enabling task execution like booking appointments or updating records.
Key Characteristics:
- Bidirectional real-time conversation
- Context retention for multi-turn dialogues
- Edge-compatible deployment for low-latency performance
- Integration with VoIP network solutions for scalable calls
By combining these elements, modern voice bots act as intelligent digital assistants, capable of handling complex conversations without human intervention.
Why Is Measuring Voice Bot Success Different From Traditional Call Systems?
Traditional IVR systems rely on scripted flows and simple routing rules. Their success is often measured by metrics like call volume or hold times. However, AI voice agents behave differently, making traditional metrics insufficient.
According to Gartner, conversational AI – including voice bots, is expected to initiate at least 70% of customer service interactions by 2028, signaling a shift in how success is defined compared to traditional call systems.
Differences to consider:
- Dynamic Interaction: Unlike IVRs, voice agents respond to varying user inputs. Misunderstandings or context loss can affect outcomes even if the call completes.
- Multiple Objectives: Modern bots aim to reduce operational costs, improve customer satisfaction, and perform automated tasks simultaneously.
- Edge Deployment Complexity: Running local LLM voice assistants on edge networks introduces new factors such as latency, compute limitations, and reliability metrics.
Therefore, evaluating success requires a combination of conversation-based, technical, and business KPIs, all tailored to AI-driven interactions.
Which KPIs Really Matter For Voice Bots?
Identifying the right KPIs allows teams to optimize performance, enhance user satisfaction, and quantify ROI. Below is a detailed breakdown.
How Do You Measure Conversation Completion And Success?
Conversation Completion Rate measures how many interactions conclude successfully without escalation to a human agent.
- Calculation: (Number of fully completed conversations ÷ Total conversations) × 100
- Indicators of Success:
- High completion rates indicate a voice bot effectively handles its designed tasks.
- Low completion rates may signal misconfigured intents, unclear prompts, or poor STT accuracy.
- High completion rates indicate a voice bot effectively handles its designed tasks.
Escalation Rate also matters—it reflects the frequency at which bots transfer calls to humans. Tracking both metrics ensures automation efficiency while maintaining customer satisfaction.
How Do You Track Understanding And Accuracy?
Accuracy is a combination of intent recognition, speech transcription fidelity, and response generation quality.
- NLU/Intent Accuracy: Percentage of user intents correctly identified. Misclassifications reduce both user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- STT Fidelity: Measure word error rate (WER) for transcriptions; lower WER indicates better speech recognition performance.
- TTS Naturalness: Evaluate clarity, pronunciation, and latency. Realistic voice output improves engagement.
- RAG Accuracy: Ensures responses sourced from internal knowledge bases are correct and relevant.
For edge-based deployment, maintaining high accuracy requires balancing local compute limitations with optimized model selection and efficient context management.
Which Efficiency Metrics Indicate Performance?
Efficiency KPIs help determine if the voice bot reduces operational overhead and improves throughput.
- Average Handle Time (AHT): Time from call initiation to completion. AI agents typically aim to reduce AHT compared to human agents.
- First Call Resolution (FCR): Percentage of queries resolved without follow-up or escalation. High FCR reflects both comprehension accuracy and process design efficiency.
- Automation Rate: Ratio of interactions handled entirely by AI without human intervention. A high automation rate correlates with cost savings and operational efficiency.
How Can You Measure Customer Experience Effectively?
Customer-centric metrics ensure that AI agents deliver satisfactory interactions, not just task completion.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Immediate feedback after interactions to measure user sentiment.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Evaluates longer-term loyalty and brand perception.
- Engagement Metrics: Includes call drop rates, response latency, and active participation rates. Monitoring these ensures that edge-deployed voice bots provide smooth, real-time communication.
What Operational And Business Metrics Prove ROI?
Beyond technical metrics, measuring the business impact is essential for justifying AI investments.
- Cost Per Conversation: Savings achieved relative to human agent cost.
- Agent Load Reduction: Measures decreased repetitive workload on human teams.
- Lead Qualification Success & Conversions: Tracks the business outcomes directly influenced by voice bots.
- Overall ROI: Combines operational savings and revenue gains, helping leaders quantify success.
Which Technical Metrics Ensure Reliability?
Running voice agents locally or on edge networks introduces new considerations:
- End-to-End Latency: Time between user input and voice response. Lower latency ensures natural, uninterrupted conversation.
- Uptime and Reliability: Measures system availability; essential for mission-critical deployments.
- Error Logging & Handling: Tracks failed API calls, misrouted requests, or model timeouts for continuous improvement.
- Edge Performance Metrics: Monitors CPU, memory, and bandwidth usage on local LLM deployments to maintain quality at scale.
How Do You Track KPIs Across The Full AI Stack?
To gain actionable insights, KPIs should be monitored across all layers:
- LLM Metrics: Response accuracy, prompt handling time, context retention.
- TTS Metrics: Voice clarity, streaming latency, intelligibility under different network conditions.
- STT Metrics: Transcription speed, word error rate, handling diverse accents.
- RAG & Tool Calls: Correct retrieval of knowledge, execution of system commands, error rates in automation workflows.
Implementing dashboards that combine these technical and operational metrics allows teams to pinpoint bottlenecks, optimize models, and maintain performance across edge deployments.
How Can FreJun Teler Help You Measure Success And Run Voice Agents Smoothly?
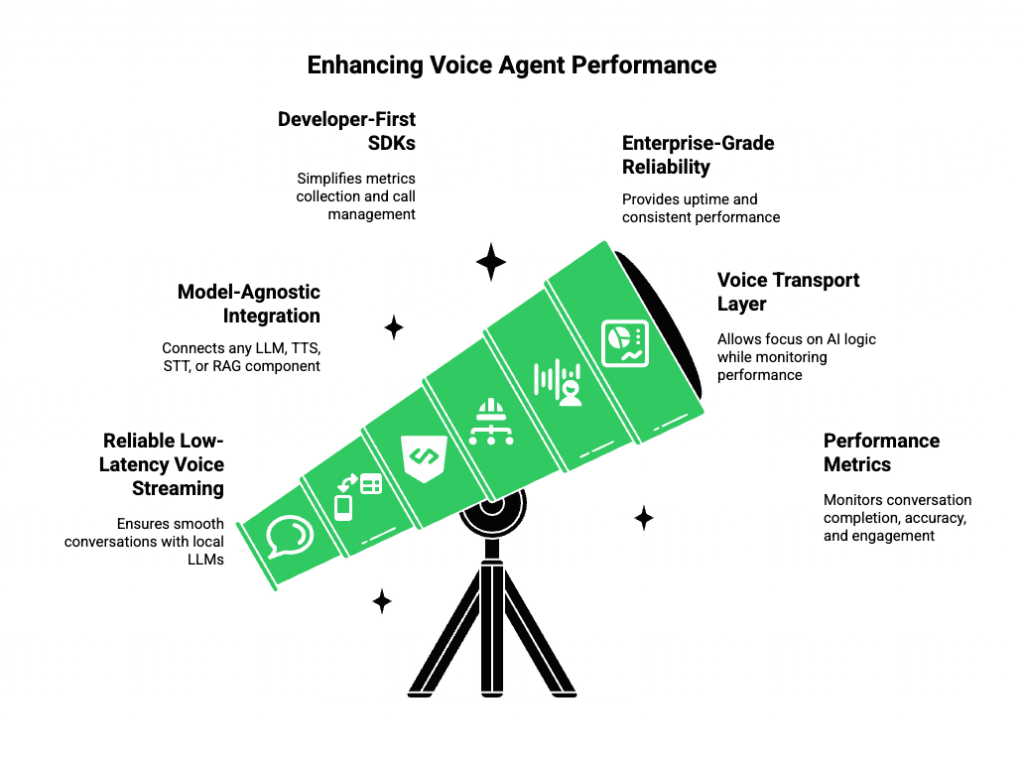
Deploying and measuring AI voice bots can be complex, especially when handling edge networks, local LLMs, and VoIP network solutions. This is where FreJun Teler offers significant advantages.
Technical Benefits of Teler:
- Reliable Low-Latency Voice Streaming: Ensures seamless conversation even with local LLM voice assistants.
- Model-Agnostic Integration: Connect any LLM, TTS, STT, or RAG component without vendor lock-in.
- Developer-First SDKs: Simplify metrics collection, call management, and context tracking.
- Enterprise-Grade Reliability: Distributed infrastructure ensures uptime and consistent performance for critical operations.
By acting as the voice transport layer, Teler allows teams to focus on AI logic while maintaining comprehensive insight into performance metrics. This makes monitoring conversation completion, accuracy, efficiency, and engagement straightforward and scalable.
How Do You Run Voice Agents On Edge Networks Locally Without Losing Performance?
Running voice agents on edge networks locally is becoming a practical requirement rather than an architectural preference. Teams adopt local LLM voice assistants to reduce latency, improve data privacy, and maintain availability even during network disruptions. However, edge execution introduces constraints that directly impact KPI outcomes.
Therefore, success depends on aligning infrastructure design with measurable performance goals.
Key Technical Challenges Of Edge-Based Voice Agents
- Limited compute and memory compared to cloud environments
- Network variability across regions and VoIP carriers
- Real-time speech processing requirements
- Context persistence across multi-turn conversations
To address these challenges, teams often use a hybrid architecture.
Recommended Hybrid Execution Model
| Component | Runs Locally (Edge) | Runs Centrally (Cloud) |
| STT | ✅ | ❌ |
| TTS | ✅ | ❌ |
| LLM (small / distilled) | ✅ | ❌ |
| RAG Index | ❌ | ✅ |
| Analytics & Logs | ❌ | ✅ |
| Call Transport | ❌ | ✅ |
This approach ensures:
- Faster response times
- Reduced call drop rates
- Stable conversational flow
- Easier KPI aggregation
As a result, latency-sensitive KPIs remain strong while analytics stay centralized.
Which KPIs Change When Voice Agents Run On Edge Networks?
Edge deployments shift the importance of certain metrics. While business KPIs remain consistent, technical KPIs become more influential.
Edge-Specific KPIs To Track
- Speech-to-Speech Latency: Measures total delay from user speech to voice response.
Target: under 400ms for natural flow. - Packet Loss Rate: Impacts STT accuracy and TTS playback quality.
- Context Retention Accuracy: Evaluates whether the local LLM preserves intent across turns.
- Failover Recovery Time: Measures how quickly calls recover from network or process failure.
- Compute Saturation: Tracks CPU and memory thresholds to prevent call degradation.
Because edge environments vary, KPIs must be monitored per region, per node, and per use case.
How Do You Build A KPI Monitoring Pipeline For Voice Agents?
A voice agent KPI pipeline must collect signals from every layer of the stack. Without this visibility, teams struggle to diagnose failures or improve outcomes.
Recommended KPI Instrumentation Layers
- Call Layer
- Call start/end events
- Audio packet timing
- Drop and retry rates
- Call start/end events
- Speech Layer
- STT transcription confidence
- TTS rendering delay
- Audio buffering events
- STT transcription confidence
- LLM Layer
- Prompt execution time
- Token usage
- Response confidence scoring
- Prompt execution time
- Conversation Layer
- Intent resolution
- Conversation completion
- Escalation triggers
- Intent resolution
- Business Layer
- Conversion events
- Task success rate
- Cost per interaction
- Conversion events
By correlating these layers, teams can trace why a KPI moved—not just that it moved.
How Do You Design Dashboards That Engineering And Business Teams Both Use?
One common mistake is building dashboards that only engineers understand. However, leadership teams need clarity without technical overload.
Best Practice: Dual Dashboard Strategy
Engineering Dashboard Focus
- Latency percentiles (P50, P95)
- STT word error rate
- LLM response time
- Node health metrics
Business Dashboard Focus
- Automation rate
- Cost savings per 1,000 calls
- CSAT trends
- Conversion lift
Because both dashboards pull from the same data pipeline, alignment improves decision-making. Consequently, optimization efforts move faster.
How Does FreJun Teler Simplify Edge-Based Voice Agent Deployment?
When running voice agents at scale, managing real-time call transport becomes a major risk. This is where FreJun Teler plays a critical technical role.
Teler’s Role In The Voice Stack
Teler operates as the real-time voice infrastructure layer, handling:
- Bidirectional low-latency media streaming
- VoIP network interoperability
- Stable audio transport across regions
- Reliable call session management
Because Teler is model-agnostic, teams can:
- Use any LLM (local or cloud-based)
- Swap TTS or STT engines without refactoring
- Maintain full control over AI logic
As a result, teams focus on conversation design and KPI improvement, not call reliability issues.
How Do You Optimize Voice Agent KPIs Over Time?
Launching a voice agent is only the starting point. Continuous optimization determines long-term success.
KPI-Driven Optimization Loop
- Measure
- Capture baseline metrics across all KPIs
- Capture baseline metrics across all KPIs
- Diagnose
- Identify where failures occur (speech, intent, latency)
- Identify where failures occur (speech, intent, latency)
- Refine
- Improve prompts
- Adjust model parameters
- Enhance RAG data quality
- Improve prompts
- Test
- Run controlled experiments on a subset of calls
- Run controlled experiments on a subset of calls
- Deploy
- Roll out improvements incrementally
- Roll out improvements incrementally
- Re-measure
- Compare KPI movement against baseline
- Compare KPI movement against baseline
This loop ensures that improvements are measurable, controlled, and repeatable.
Which KPIs Matter Most At Different Stages Of Adoption?
Not all KPIs matter equally at every stage.
KPI Priorities By Maturity Stage
| Stage | Primary KPIs |
| Pilot | Accuracy, Latency, Call Stability |
| Early Scale | Completion Rate, Escalation Rate |
| Growth | Automation Rate, Cost Per Call |
| Mature | ROI, Conversion Lift, CSAT |
By adjusting focus over time, teams avoid premature optimization and stay aligned with business goals.
How Do You Avoid Common Voice Bot Measurement Mistakes?
Several pitfalls reduce the effectiveness of KPI tracking.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
- Measuring volume instead of outcomes
- Ignoring latency impact on user behavior
- Treating all calls as equal across use cases
- Over-optimizing cost at the expense of experience
- Failing to segment metrics by geography or network
Instead, successful teams segment KPIs by:
- Use case
- Region
- Language
- Network type
This segmentation reveals patterns that aggregate metrics hide.
How Do You Prove ROI To Stakeholders?
Leadership approval depends on clear, defensible ROI metrics.
Simple ROI Formula For Voice Agents
ROI = (Operational Savings + Revenue Impact – Infrastructure Cost) ÷ Infrastructure Cost
Operational Savings Include:
- Reduced agent hours
- Lower training costs
- Faster resolution times
Revenue Impact Includes:
- Higher lead conversion
- Improved retention
- Faster follow-ups
When paired with stable infrastructure like Teler, ROI calculations become predictable and repeatable.
Conclusion
Measuring voice bot success is not about how advanced the AI sounds – it is about how reliably it delivers outcomes. High-performing voice agents consistently resolve conversations, maintain low latency, retain context, and create measurable business value. When KPIs are tracked across speech, AI logic, infrastructure, and business layers, teams gain clarity on what to improve and how to scale confidently.
This is where FreJun Teler fits naturally into the stack. Teler provides the real-time voice infrastructure that allows teams to run local LLM voice assistants over global VoIP networks with reliability, low latency, and full control. By separating voice transport from AI logic, teams can iterate faster, monitor KPIs accurately, and scale without friction.
Schedule a demo.
FAQs –
- What is a voice bot in simple terms?
A voice bot combines speech recognition, AI reasoning, and voice synthesis to handle phone conversations automatically. - How are voice bots different from IVRs?
Voice bots understand natural language and context, while IVRs rely on fixed menus and scripted responses. - Which KPIs matter most for voice bots?
Conversation completion, latency, intent accuracy, automation rate, customer satisfaction, and cost per interaction matter most. - Can voice bots run locally on edge networks?
Yes, local LLM voice assistants can run on edge networks to reduce latency and improve data privacy. - Why is latency critical for voice agents?
High latency breaks conversational flow, reduces trust, and increases call drop or escalation rates. - How do I measure voice bot accuracy?
Track intent recognition accuracy, speech-to-text error rate, and response relevance across conversations. - Do voice bots reduce operational costs?
Yes, effective voice bots reduce agent workload, shorten handle times, and lower cost per conversation. - What role does VoIP play in voice agents?
VoIP network solutions enable scalable, real-time voice streaming across regions and telecom networks. - Can I use any LLM with my voice bot?
Yes, modern architectures allow using any LLM with compatible STT, TTS, and voice infrastructure. - How does FreJun Teler help voice bot deployments?
Teler provides low-latency voice infrastructure, VoIP connectivity, and reliable call streaming for AI-driven voice agents.
