Real-time voice conversations are no longer limited to call routing or scripted IVRs. Today, businesses expect voice agents to understand intent, respond naturally, and act instantly. However, achieving accurate real-time conversations over phone calls remains difficult. Background noise, network delays, interruptions, and fragmented AI pipelines often reduce call quality and user trust.
This is where a well-designed voice recognition SDK becomes critical. By enabling low-latency speech processing, continuous streaming, and context-aware interactions, modern voice SDKs directly improve how AI systems perform during live calls.
In this blog, we explore how voice recognition SDKs enhance real-time call accuracy and what technical foundations teams need to build reliable voice agents.
Why Is Real-Time Call Accuracy Still A Major Challenge For Voice AI?
Real-time voice conversations are far more complex than most teams expect. At first glance, improving call accuracy is only about choosing a better speech-to-text model. However, in live calls, accuracy depends on how fast and how reliably the system reacts while the user is still speaking.
Unlike chat systems, voice interactions happen under strict time pressure. People interrupt, change their mind mid-sentence, or speak while background noise is present. Because of this, even a small delay or misinterpretation can break the entire conversation flow.
As a result, many voice agents fail not because the AI is weak, but because the voice layer cannot keep up in real time.
Common challenges include:
- Delayed transcription causing awkward pauses
- Partial sentences being misinterpreted
- Talk-over between the user and the AI
- Loss of context between turns
- Reduced call quality due to network jitter
Therefore, improving real-time call accuracy requires more than better models. It requires a system designed for live conversations from the ground up.
What Does Real-Time Call Accuracy Actually Mean In Modern Voice Systems?
Real-time call accuracy is often misunderstood. Many teams still measure success using transcription metrics alone. While transcription accuracy is important, it is only one part of the problem.
In real-world telephony environments, speech recognition systems often achieve 80%–88% accuracy due to line compression and noise, significantly below ideal studio benchmarks, underscoring why real-time STT accuracy remains challenging in live calls.
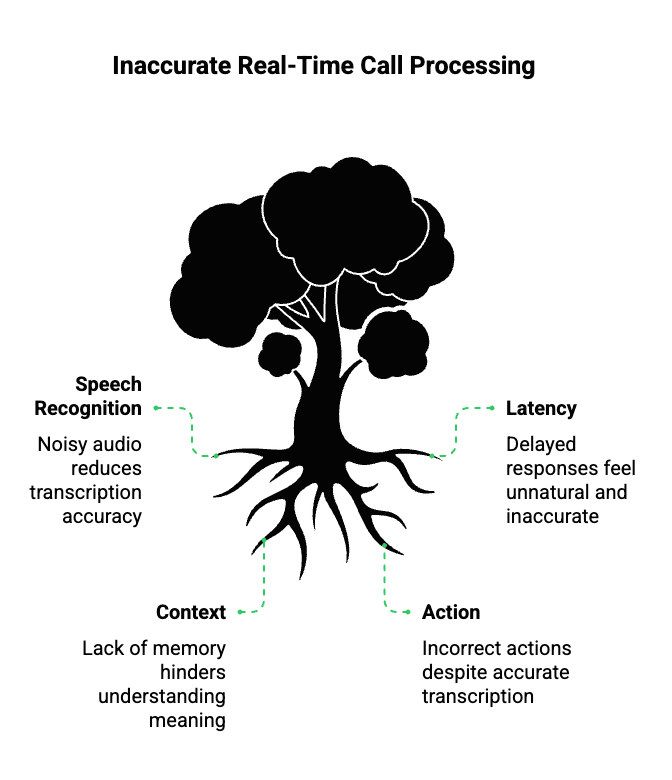
In practice, real-time call accuracy consists of four layers working together.
Speech Recognition Accuracy
This focuses on how correctly spoken words are converted into text. It depends on:
- Acoustic models
- Noise handling
- Accent and language coverage
Latency Accuracy
Latency directly affects how “human” a conversation feels. Even if words are correct, delayed responses reduce accuracy in practice.
Low latency recognition allows:
- Faster intent detection
- Natural turn-taking
- Fewer interruptions
Context Accuracy
Understanding meaning requires memory. The system must track:
- Previous questions
- Corrections
- References like “that” or “same as before”
Action Accuracy
Finally, accuracy must result in correct actions. This includes:
- Correct routing
- Correct API or tool calls
- Correct responses based on business rules
In other words, real-time STT accuracy alone does not guarantee accurate calls. Accuracy only emerges when all four layers work together.
How Do Voice Agents Actually Work During A Live Call?
To understand how a voice recognition SDK improves accuracy, it helps to see what happens during a real call.
A modern voice agent is not a single system. Instead, it is a pipeline of tightly coordinated components that must operate within milliseconds.
A Typical Live Call Flow
- A call connects through PSTN or VoIP
- Audio is captured and streamed in real time
- Speech-to-text processes audio incrementally
- The LLM analyzes intent and context
- RAG enriches the response with domain data
- Tools or APIs are triggered if required
- Text-to-speech generates audio output
- Audio is streamed back to the caller
Each step depends on the previous one. Therefore, if any layer introduces delay or instability, the entire system suffers.
This is why voice agents are best described as:
LLM + STT + TTS + RAG + Tool Calling, operating in real time.
Accuracy is not owned by one component. Instead, it is a shared responsibility across the full pipeline.
Where Do Traditional Calling Platforms Lose Accuracy In Real Time?
Many teams attempt to build voice agents on top of platforms that were originally designed for basic calling or IVR workflows. As a result, accuracy issues appear early and often.
Batch-Based Speech Processing
Traditional systems wait until the speaker finishes talking. Because of this:
- Intent detection is delayed
- The AI responds too late
- Conversations feel robotic
High Audio Buffering
Older architectures buffer audio heavily to ensure quality. However, buffering increases latency and breaks conversational timing.
Telephony-First Design
Platforms built for calls focus on:
- Call routing
- DTMF inputs
- Static IVR flows
They were not designed for:
- Continuous speech understanding
- Partial transcripts
- Context-aware responses
Stateless Conversations
Without state, systems forget:
- Previous answers
- Corrections
- Intent shifts
As a result, users are forced to repeat themselves, which reduces trust and call completion rates.
How Does A Voice Recognition SDK Improve Real-Time STT Accuracy?
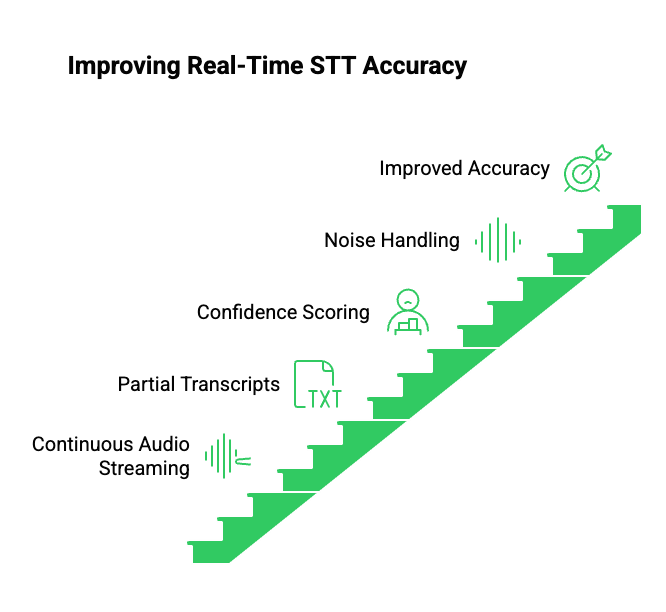
A voice recognition SDK changes how speech is handled during live calls. Instead of treating audio as a file, it treats speech as a stream.
This shift has a direct impact on accuracy.
Continuous Audio Streaming
A voice recognition SDK processes audio frame by frame. Therefore:
- Speech is recognized while the user is speaking
- Partial transcripts become available immediately
Partial And Incremental Transcripts
Rather than waiting for silence, the system receives:
- Early hypotheses
- Updated word predictions
- Confidence changes over time
This allows the AI to:
- Predict intent earlier
- Interrupt naturally
- Prepare responses in advance
Confidence Scoring And Timing Data
Advanced SDKs provide:
- Word-level confidence
- Timestamps
- Speech boundaries
As a result, systems can detect:
- Uncertainty
- Noise interference
- When to ask clarifying questions
Noise And Environment Handling
Because the SDK operates at the audio stream level, it can:
- Filter background noise
- Adapt to microphone quality
- Adjust to network variations
Together, these capabilities directly improve real-time STT accuracy and overall call quality AI outcomes.
Why Is Low Latency The Foundation Of Accurate Voice Conversations?
Latency is often treated as a performance metric. However, in voice systems, latency is also an accuracy factor.
When latency increases:
- Users speak over the AI
- The AI interrupts the user
- Intent detection becomes unreliable
On the other hand, low latency recognition allows the system to behave predictably.
How Latency Affects Accuracy
| Latency Range | User Experience | Accuracy Impact |
| < 150 ms | Natural conversation | High |
| 150–300 ms | Slight delay | Medium |
| > 300 ms | Noticeable lag | Low |
Low latency allows:
- Real-time turn-taking
- Early intent extraction
- Better alignment between STT, LLM, and TTS
Therefore, the best voice SDKs for 2026 prioritize streaming, not batch processing.
How Does Conversational Context Improve Call Accuracy Beyond Transcription?
Even perfect transcription fails without context. In real conversations, meaning depends on what was said before.
For example:
- “Yes” depends on the last question
- “That one” depends on previous options
- “Change it” depends on earlier actions
Context Management In Voice Systems
Accurate systems maintain:
- Dialogue history
- Intent continuity
- State transitions
This context is passed to the LLM, allowing it to reason correctly.
Role Of RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation improves accuracy by:
- Injecting business rules
- Fetching customer data
- Grounding responses in real information
As a result, the AI avoids hallucinations and gives precise answers during live calls.
How Can You Combine Any LLM, Any STT, And Any TTS Without Losing Accuracy?
As voice AI systems mature, most teams avoid locked stacks. Instead, they prefer flexibility. They want to choose:
- The LLM that fits their reasoning needs
- The STT engine that works best for their accents and domains
- The TTS engine that matches their brand voice
However, flexibility introduces a new challenge. Each component operates at a different speed and expects data in a specific format. Therefore, without careful coordination, accuracy degrades quickly.
Common Integration Issues
When combining multiple vendors, teams often face:
- Timing mismatch between STT output and LLM input
- Delayed TTS playback after the LLM responds
- Lost conversational state during interruptions
- Inconsistent turn-taking behavior
As a result, even high-quality models fail to deliver consistent call accuracy.
Why Synchronization Matters
Accuracy improves when:
- Partial transcripts are forwarded immediately
- The LLM receives updates instead of final-only text
- TTS playback is aligned with conversation timing
Therefore, the system must coordinate streams, not messages.
This is why voice recognition SDKs work best when paired with infrastructure that understands real-time media behavior.
Why Is A Stable Voice Transport Layer Critical For Call Accuracy?
At this stage, many teams realize an important truth:
Most accuracy issues originate outside the AI models.
Even the best voice recognition SDK cannot compensate for:
- Dropped audio packets
- Jittery network conditions
- Inconsistent call connections
Voice As A Real-Time System
Unlike text, voice cannot be retried without consequences. If audio arrives late or out of order:
- Words are missed
- Context breaks
- The LLM reasons on incomplete data
Therefore, the transport layer must guarantee:
- Continuous streaming
- Predictable latency
- Bi-directional audio flow
Without this foundation, real-time STT accuracy and call quality AI both suffer.
How Does FreJun Teler Improve Real-Time Call Accuracy For Voice Agents?
FreJun Teler addresses this exact gap. Instead of acting as an AI model or transcription service, Teler operates as the voice infrastructure layer that connects calls to AI systems reliably.
It is important to clarify what Teler is – and what it is not.
What FreJun Teler Is
- A real-time voice transport and streaming platform
- A bridge between telephony and AI pipelines
- A developer-first API and SDK layer
What FreJun Teler Is Not
- Not an LLM
- Not an STT or TTS provider
- Not a closed or opinionated AI stack
How Teler Enhances Accuracy
FreJun Teler improves real-time call accuracy through several technical capabilities:
Real-Time Bi-Directional Audio Streaming
Audio flows continuously from the call to your AI system and back. As a result:
- STT engines receive clean, low-latency streams
- Partial transcripts arrive on time
- Responses can be prepared early
Stable Low-Latency Media Pipelines
Teler’s infrastructure is optimized to reduce jitter and buffering. Therefore:
- Turn-taking feels natural
- Interruptions are handled smoothly
- Talk-over scenarios reduce significantly
Model-Agnostic Architecture
Because Teler does not enforce specific models:
- You can switch STT engines without rewriting call logic
- You can experiment with different LLMs
- You can evolve your stack without breaking accuracy
SDK-Controlled Call Logic
Developers retain control over:
- When to listen
- When to respond
- When to interrupt or wait
This level of control is essential for building accurate voice agents at scale.
In short:
You bring the AI intelligence. FreJun Teler ensures the voice layer does not compromise it.
What Makes A Voice Recognition SDK “Future-Ready” For 2026?
As voice AI adoption grows, expectations will rise. The best voice SDK for 2026 will not be defined by transcription accuracy alone.
Instead, decision-makers should evaluate SDKs across multiple dimensions.
Key Evaluation Criteria
- Native real-time streaming support
- Sub-200ms low latency recognition
- Partial transcript access
- Word-level timing and confidence scores
- Compatibility with multiple STT and TTS engines
- Support for context-rich conversations
Infrastructure Compatibility
Equally important, the SDK must integrate cleanly with:
- Telephony systems
- Voice transport platforms
- Scalable backend services
Without this alignment, even the best SDK becomes difficult to operate in production.
How Should Founders And Engineering Leads Measure Real-Time Call Accuracy?
Measurement is often overlooked. However, without clear metrics, accuracy cannot improve.
Metrics Beyond Word Error Rate
While WER is useful, it does not reflect conversational success.
Teams should also track:
- Average response latency
- Interruption frequency
- Intent recognition accuracy
- Task completion rate
- Clarification request rate
Continuous Feedback Loops
Accuracy improves when:
- Call logs are reviewed regularly
- Edge cases are analyzed
- Models and prompts are tuned iteratively
Additionally, infrastructure metrics such as packet loss and jitter should be monitored alongside AI metrics.
Why Call Quality AI Depends On Systems, Not Models Alone
At this point, a clear pattern emerges. Call quality AI is a systems problem.
Even advanced AI audio engines fail when:
- Latency spikes unexpectedly
- Context is lost between turns
- Audio streams degrade
On the other hand, simpler models perform well when:
- The voice pipeline is stable
- Streaming is consistent
- Timing is predictable
Therefore, the path to higher real-time call accuracy lies in:
- Strong voice recognition SDKs
- Reliable transport layers
- Thoughtful system design
Final Thoughts
Real-time call accuracy is not achieved by improving speech recognition alone. Instead, it emerges from a carefully designed system where low-latency audio streaming, contextual understanding, and AI coordination work together. Voice recognition SDKs play a foundational role by enabling continuous speech processing, early intent detection, and smoother conversational flow. However, without reliable voice infrastructure, even the most advanced AI models struggle in production environments.
FreJun Teler helps teams bridge this gap by providing a real-time voice transport layer that connects calls seamlessly with any LLM, STT, or TTS engine. By handling streaming, latency, and call reliability, Teler allows teams to focus on building intelligent voice agents without compromising accuracy.
Build accurate, low-latency voice agents with FreJun Teler.
Schedule a demo.
FAQs –
- What is a voice recognition SDK?
A voice recognition SDK enables real-time speech processing, streaming audio input, and accurate transcription for live conversational applications. - How does a voice SDK improve call accuracy?
It reduces latency, provides partial transcripts, and enables early intent detection, resulting in smoother and more accurate conversations. - Is real-time STT accuracy different from transcription accuracy?
Yes. Real-time STT accuracy includes timing, context handling, and responsiveness, not just word correctness. - Why is low latency important for voice agents?
Low latency prevents talk-over, enables natural turn-taking, and improves user trust during live voice interactions. - Can I use any LLM with a voice recognition SDK?
Yes, most modern SDKs are model-agnostic and can integrate with any LLM or AI agent. - What causes voice agents to misinterpret users?
High latency, poor streaming, noise interference, and loss of conversational context are common causes. - How does streaming audio help AI performance?
Streaming enables incremental processing, faster responses, and better intent prediction before the user finishes speaking. - Is infrastructure as important as AI models?
Yes. Without stable voice infrastructure, even advanced AI models perform poorly in real-time calls. - Can voice agents handle interruptions accurately?
Yes, if the system supports partial transcripts, low latency streaming, and context-aware dialogue handling. - Who should invest in voice recognition SDKs?
Founders, product teams, and engineers building real-time voice agents or AI-powered calling systems should prioritize voice SDKs.
