Real-time AI voice conversations are no longer experimental. As businesses move beyond scripted IVRs, voicebot solutions are expected to listen, reason, and respond with human-like speed and accuracy. However, building such systems is not trivial. It requires more than an AI model or a speech engine. Instead, real-time voicebot solutions depend on tightly orchestrated components – streaming audio, low-latency processing, contextual intelligence, and reliable voice infrastructure.
This blog explains how modern voicebot architectures enable real-time AI conversations, what technical layers make them possible, and how teams can design scalable, low-latency voice bots without locking themselves into rigid platforms.
What Does Real-Time AI Conversation Mean In Voicebot Solutions?
When businesses talk about voice bots, they often mean automation. However, real-time AI conversations mean something very different. In a real-time setup, the AI must listen, think, and respond almost as quickly as a human would.
In practice, this means:
- The caller speaks naturally
- The system processes speech as it happens
- The AI responds without noticeable delay
- The conversation allows interruptions and follow-ups
Because humans are highly sensitive to delays in voice, even a short pause can break trust. As a result, real time voicebot solutions must operate within very tight latency limits. Typically, anything beyond 300 milliseconds starts to feel unnatural.
For real-time AI voice conversations to feel natural, total response latency must typically fall below about 500 ms – a threshold most legacy systems still struggle to achieve without optimized, parallel processing workflows.
Therefore, real-time AI voice conversations are not about automation speed alone. Instead, they are about continuous interaction without friction.
Why Are Traditional Voicebot Solutions Not Truly Real-Time?
Although many platforms claim to offer AI voice bots, most systems still rely on older architectures. These systems were originally designed for IVRs and call routing, not conversational AI.
Common limitations include:
- Audio is recorded first, then processed later
- Speech-to-text runs after the user finishes speaking
- AI responses wait for full transcripts
- Audio playback happens only after processing completes
Because of this sequential flow, conversations feel slow and rigid.
More importantly, traditional systems struggle with:
- Mid-sentence interruptions
- Context switching
- Natural pauses
- Overlapping speech
As a result, users experience robotic interactions rather than real conversations. Therefore, enabling low latency voice bots requires a fundamentally different approach.
What Are The Core Components Of A Real-Time Voicebot Architecture?
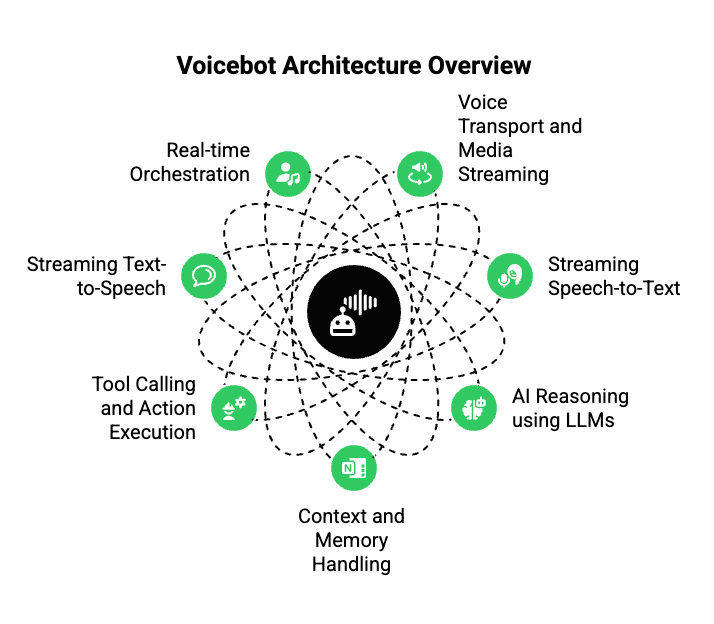
To understand how voice bot solutions enable real-time AI conversations, it helps to look at the system as a whole. A production-grade voicebot is not a single service. Instead, it is a coordinated pipeline of multiple components working in parallel.
At a high level, real time voicebot solutions include:
- Voice transport and media streaming
- Streaming speech-to-text
- AI reasoning using LLMs
- Context and memory handling
- Tool calling and action execution
- Streaming text-to-speech
- Real-time orchestration
Each part must operate continuously. If even one component introduces delay, the entire experience suffers. Therefore, architecture matters more than individual tools.
How Do Voicebot Solutions Capture And Stream Live Voice In Real Time?
Every AI voice conversation starts with audio. However, capturing voice for real-time use is very different from recording calls.
In real-time systems:
- Audio must be streamed, not stored
- Voice packets are processed as they arrive
- Bidirectional streaming is required
- Latency and jitter must be minimized
Most phone calls still travel over PSTN, SIP, or VoIP networks. While these networks are reliable, they were not designed for AI processing. As a result, voicebot solutions must extract live audio streams and forward them immediately to downstream services.
Key technical requirements include:
- Continuous media streaming
- Packet loss handling
- Echo and noise suppression
- Real-time buffering control
Without this foundation, low latency voice bots are not possible.
How Does Streaming Speech-To-Text Enable Low-Latency Voice Bots?
Speech-to-text plays a critical role in real-time AI voice conversations. However, not all STT systems are suitable for live calls.
Traditional STT systems work in batches. They wait until speech ends, process the audio, and then return a transcript. While this works for analytics, it fails for conversations.
Streaming STT works differently:
- Audio is processed chunk by chunk
- Partial transcripts are generated in real time
- The AI can react before speech ends
Because of this, streaming STT reduces response delay significantly.
However, it also introduces challenges:
- Handling incomplete sentences
- Managing corrections in partial transcripts
- Dealing with background noise and accents
Therefore, voicebot solutions must balance speed and accuracy. When done correctly, streaming STT becomes the first step toward real-time interaction.
How Do LLMs Power Natural AI Voice Conversations?
Large Language Models act as the reasoning engine behind AI voice conversations. However, LLMs do not understand audio directly. Instead, they operate on text and structured data.
In a voicebot setup, LLMs are responsible for:
- Understanding user intent
- Managing dialogue flow
- Generating relevant responses
- Deciding when actions are needed
It is important to note that LLMs are stateless by default. This means they do not remember previous interactions unless context is provided. Therefore, conversation history must be managed externally.
Additionally, response time matters. Even a powerful model becomes unusable if it responds too slowly. As a result, real time voicebot solutions often optimize:
- Prompt size
- Context window usage
- Decision logic outside the model
In short, LLMs provide intelligence, but they rely heavily on the surrounding system.
How Is Conversational Context Maintained In Real-Time Voicebot Solutions?
Context is what separates simple bots from real conversational agents. Without context, AI voice conversations feel repetitive and disconnected.
Context typically includes:
- Current conversation state
- Past user inputs
- Business data such as user profiles
- External knowledge sources
Many systems use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to inject relevant data into each AI response. This allows the voicebot to answer questions based on real information rather than assumptions.
For example:
- Account status from a CRM
- Order details from a database
- Policies from internal documents
However, context handling must be fast. If data retrieval slows down the response, the conversation breaks. Therefore, real time voicebot solutions often decouple context management from voice streaming.
How Do Voicebot Solutions Perform Actions Using Tool Calling?
AI voice conversations are not just about talking. In most business use cases, the voicebot must take action.
Tool calling allows the AI to:
- Trigger workflows
- Update records
- Fetch external data
- Schedule tasks
From a system perspective, tool calls must be asynchronous. If the AI waits for a tool to respond before continuing the conversation, delays increase.
For example:
- The bot can acknowledge the request
- Then perform the action in the background
- Finally confirm completion
This design keeps the conversation fluid. Therefore, action execution must never block the voice pipeline.
How Is AI Speech Generated Without Breaking Conversational Flow?
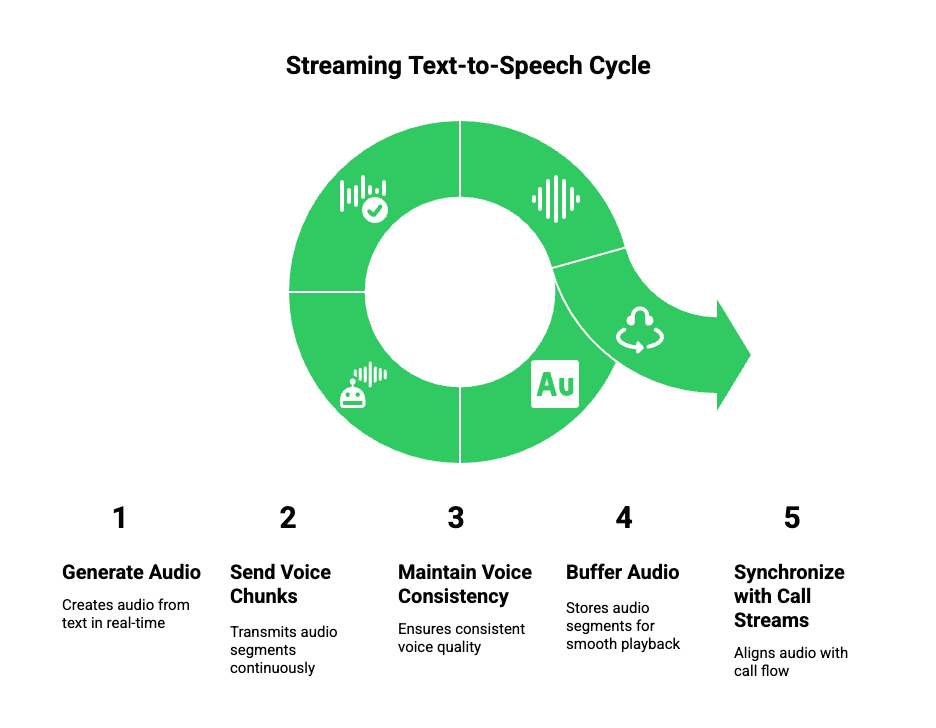

Text-to-speech is the final step in AI voice conversations. However, like STT, TTS must also operate in streaming mode.
Streaming TTS:
- Generates audio as text is produced
- Sends voice chunks continuously
- Reduces perceived response time
This approach avoids long pauses before the bot speaks. Additionally, it allows more natural pacing and tone.
Key considerations include:
- Voice consistency
- Audio buffering
- Synchronization with call streams
When implemented correctly, streaming TTS completes the real-time conversational loop.
Why Is Real-Time Orchestration The Hardest Part Of Voicebot Solutions?
By now, it is clear that real-time AI conversations involve many moving parts. However, the most difficult challenge is not any single component. Instead, it is orchestration.
Real time voicebot solutions must manage multiple pipelines at the same time:
- Incoming audio stream
- Streaming speech-to-text
- AI reasoning
- Context retrieval
- Tool execution
- Streaming text-to-speech
- Outbound audio playback
All of these processes must run in parallel. If they run sequentially, latency increases. As a result, the conversation feels slow and unnatural.
Additionally, orchestration must handle:
- User interruptions
- Network fluctuations
- Partial responses
- Retries and fallbacks
Because voice conversations are continuous, failures cannot be hidden. Therefore, orchestration logic must be precise, resilient, and fast.
How Do Real Time Voicebot Solutions Manage Interruptions And Turn-Taking?
Human conversations are rarely linear. People interrupt, pause, and change direction often. As a result, AI voice conversations must support dynamic turn-taking.
Key requirements include:
- Detecting when the user starts speaking
- Stopping or adjusting AI speech output
- Re-routing audio streams instantly
- Preserving conversational context
This is especially important for low latency voice bots. Even small delays in interruption handling can frustrate users.
To achieve this, voicebot solutions rely on:
- Real-time audio activity detection
- Streaming control signals
- Adaptive response logic
Without these mechanisms, conversations become rigid and unnatural.
How Can Voicebot Solutions Be Built Using Any LLM, STT, And TTS?
One of the most important design principles in modern voicebot solutions is modularity. Rather than relying on a single vendor, systems are built using interchangeable components.
A flexible voicebot architecture allows teams to:
- Choose any LLM based on use case
- Switch STT providers for accuracy or cost
- Experiment with different TTS voices
- Upgrade models without rewriting voice logic
This is possible because each component communicates through well-defined interfaces. As a result, innovation happens faster and risk is reduced.
More importantly, this approach prevents lock-in. Teams remain free to adopt better AI models as the ecosystem evolves.
Where Does FreJun Teler Fit In A Real-Time Voicebot Architecture?
At this stage, the missing piece becomes clear. While LLMs provide intelligence and STT/TTS handle speech, real-time voice infrastructure is what connects everything together.
FreJun Teler serves as the voice transport and streaming layer in real time voicebot solutions.
Specifically, Teler is responsible for:
- Capturing live audio from inbound and outbound calls
- Streaming voice data with minimal latency
- Maintaining stable, bidirectional media connections
- Delivering AI-generated speech back to callers in real time
At the same time, Teler does not control AI logic. Instead:
- Developers retain full control over LLMs
- Context and memory stay within the application
- Tool calling logic remains external
Because of this separation, teams can focus on building intelligent AI agents while relying on Teler for reliable voice delivery.
How Does Teler Enable Low Latency Voice Bots At Scale?
Low latency voice bots require more than fast models. They require infrastructure designed specifically for real-time media.
Teler enables this through:
- Real-time media streaming rather than call recording
- Optimized audio pipelines for minimal delay
- Stable session handling across networks
- Support for global telephony and VoIP systems
Additionally, Teler is built to handle concurrency. As call volume grows, the system continues to deliver consistent performance. This is critical for production-grade deployments.
Because the voice layer is abstracted, scaling does not impact AI logic. As a result, teams can expand usage without architectural changes.
How Do Real Time Voicebot Solutions Support Enterprise Reliability And Security?
For enterprise use cases, reliability and security are non-negotiable. Voicebot solutions must operate continuously while protecting sensitive data.
Key requirements include:
- Secure audio transmission
- Encrypted data handling
- High availability infrastructure
- Geographic redundancy
In real-time systems, downtime directly affects user trust. Therefore, infrastructure must be designed to handle failures gracefully.
By separating voice infrastructure from AI logic, organizations can enforce security controls at each layer. This layered approach improves both resilience and compliance.
What Are Common Use Cases For Real-Time AI Voice Conversations?
With the right architecture in place, real-time AI voice conversations unlock a wide range of use cases.
Intelligent Inbound Call Handling
- AI receptionists
- Natural language IVRs
- Automated customer support
- Call routing based on intent
Personalized Outbound Engagement
- Appointment reminders
- Lead qualification
- Feedback collection
- Proactive notifications
In each case, low latency voice bots improve user experience by making conversations feel natural rather than scripted.
What Should Product And Engineering Teams Consider Before Building Voicebot Solutions?
Before implementing voicebot solutions, teams should evaluate several factors.
Technical Considerations
- End-to-end latency budget
- Streaming vs batch processing
- Failure handling and retries
- Observability and monitoring
Product Considerations
- Conversational flow design
- Interruption handling
- Context depth requirements
- Voice tone and pacing
By addressing these early, teams avoid costly rework later.
How Do Voicebot Solutions Enable The Future Of AI Conversations?
Voice is the most natural interface for human communication. As AI continues to evolve, voice will become the primary way people interact with intelligent systems.
Real time voicebot solutions make this possible by:
- Removing latency barriers
- Supporting natural dialogue
- Enabling scalable deployment
- Allowing continuous innovation
Ultimately, successful AI voice conversations depend on strong infrastructure as much as smart models. When voice streaming, AI reasoning, and orchestration work together, AI stops feeling like a system and starts feeling like a conversation.
Final Takeaway –
Real-time AI voice conversations are built on systems, not shortcuts. While LLMs provide intelligence and STT/TTS enable speech, true conversational quality depends on how these components work together under strict latency constraints. Successful voicebot solutions treat voice as a continuous stream, maintain context externally, and orchestrate AI reasoning without blocking conversation flow. This architectural approach allows teams to build flexible, future-ready AI voice agents that scale across use cases and regions.
FreJun Teler fits naturally into this model by handling the most complex layer—real-time voice transport and streaming, while leaving full control of AI logic to developers. If you are building low latency voice bots using any LLM, STT, or TTS, Teler provides the infrastructure foundation to move faster and deploy with confidence.
FAQs –
1. What is a real-time voicebot solution?
A real-time voicebot processes speech, AI reasoning, and responses continuously, enabling natural conversations without noticeable delays or rigid turn-taking.
2. How is a voicebot different from a traditional IVR?
Voicebots understand natural language and context, while IVRs rely on predefined menus and sequential user inputs.
3. Why is low latency critical for AI voice conversations?
Delays above a few hundred milliseconds break conversational flow and reduce user trust in AI-driven voice interactions.
4. Can I use any LLM with a voicebot system?
Yes, modern voicebot architectures are LLM-agnostic and support flexible integration with different AI models.
5. What role does streaming play in voicebot solutions?
Streaming allows audio, transcription, and responses to flow continuously, enabling faster and more natural AI conversations.
6. How is conversation context maintained in voicebots?
Context is managed externally using session memory, databases, and RAG pipelines rather than inside the voice or model layer.
7. Are real-time voicebots suitable for enterprise use cases?
Yes, with proper infrastructure, they support scale, reliability, security, and global deployment requirements.
8. How do voicebots handle interruptions during calls?
They detect live speech activity and dynamically adjust audio playback and AI responses in real time.
9. Does real-time voice AI require specialized infrastructure?
Yes, standard telephony alone cannot meet latency requirements without optimized real-time media streaming infrastructure.
10. How long does it take to build a production voicebot?
With modular architecture and the right voice infrastructure, teams can deploy real-time voicebots in weeks, not months.
