The landscape of building voice bots is undergoing a seismic shift. Just a few years ago, the process was a complex and rigid affair, dominated by clunky Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems and state-machine-based logic. Today, we stand on the cusp of a new era.
The explosive power of Large Language Models (LLMs) has completely redefined what is possible, transforming the goal from building a simple, menu-driven bot to creating a truly intelligent, conversational agent.
For developers and businesses looking to enter this space in 2025, the crucial question is no longer if you can build a voice bot, but what is the right modern toolkit to build it with.
The answer is not a single, all-in-one product. The modern voice bot is not a monolith; it is a sophisticated, multi-layered stack of specialized tools and services working in perfect, low-latency harmony. Choosing the right components for this stack is the single most important decision you will make. It will determine your bot’s intelligence, its responsiveness, and its ability to scale.
This guide will provide a clear, architectural overview of the foundational components of voice bots and a breakdown of the best SDKs for voice bot development in 2025.
Table of contents
The Modern Voice Bot Architecture: A Decoupled, Three-Layer Stack
To understand the tools, you must first understand the architecture. The days of a single, closed platform that does everything “in the box” are over. The best-in-class approach for building voice bots in 2025 is a decoupled, API-first model that consists of three distinct layers. This approach gives you the ultimate flexibility to choose the best tool for each specific job.
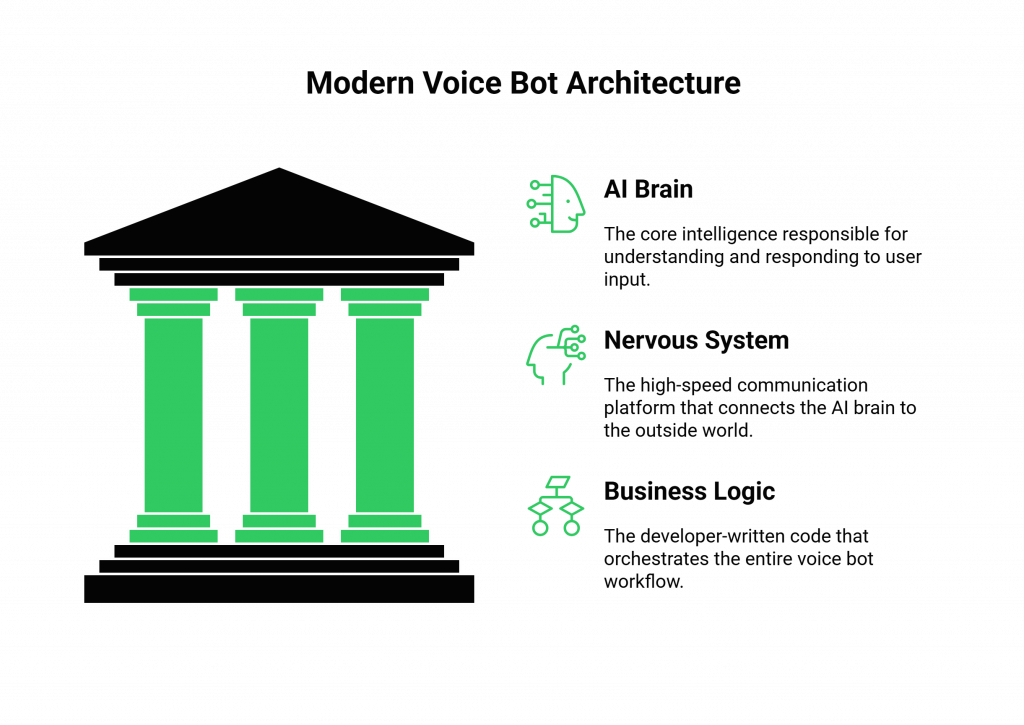
Layer 1: The AI “Brain” – The Intelligence Core
This is where the “thinking” happens. This layer is responsible for understanding the user and generating a response. It is itself a stack of three key components:
- Speech-to-Text (STT): The “ears.” This service transcribes the raw audio from the user into text.
- Large Language Model (LLM): The “brain.” This is the core intelligence that processes the text, understands the user’s intent, manages the conversational state, and formulates a response.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): The “mouth.” This service synthesizes the LLM’s text response into natural-sounding audio.
Layer 2: The “Nervous System” – The Real-Time Voice Infrastructure
This is the high-speed bridge between the AI brain and the outside world. It is a specialized, developer-first communication platform that handles the immense complexity of real-time voice. Its job is not to be intelligent, but to be incredibly fast and reliable.
Layer 3: The “Skeleton” – Your Business Logic and Application Code
This is the code that you, the developer, write. It is the orchestrator that connects the “brain” to the “nervous system.” It handles your specific business rules, integrates with your databases and other APIs, and manages the overall workflow of the conversation.
Also Read: From Chatbots to Callbots: How the Best Voice APIs Are Redefining Business Communication
What Are the Best Voice Bot Development Tools for the AI “Brain”?
In 2025, the key is flexibility. The best approach is to choose best-in-class, specialized services for each part of the AI stack.
Top-Tier Speech-to-Text (STT) Engines
The accuracy of your STT is paramount. “Garbage in, garbage out” is the rule.
- Google Cloud Speech-to-Text: Still a top contender, offering high accuracy, broad language support, and powerful features like speaker diarization.
- Deepgram: A rising star that is hyper-focused on speed and accuracy, often delivering transcriptions with lower latency than its larger competitors.
- AssemblyAI: Another excellent choice, offering a robust API and advanced features like automatic punctuation and PII redaction.
The Powerhouses: Large Language Models (LLMs)
This is the heart of your bot’s intelligence.
- OpenAI (GPT-4 and beyond): The undisputed leader in conversational fluency, reasoning, and the ability to handle complex, open-ended dialogues.
- Anthropic (Claude series): A major competitor to OpenAI, known for its large context windows and a strong focus on AI safety and “constitutionality,” which can be a key consideration for enterprise use cases.
- Google (Gemini series): Google’s flagship models are incredibly powerful and offer the advantage of deep integration with the rest of the Google Cloud ecosystem.
The Voices: Text-to-Speech (TTS) Engines
The quality of your TTS engine is what determines your bot’s personality and how pleasant it is to interact with.
- ElevenLabs: Widely regarded as the market leader for hyper-realistic, natural-sounding, and emotionally expressive voices. They also offer powerful voice cloning capabilities.
- PlayHT: Another top-tier option that offers a wide range of incredibly realistic voices and a powerful API for real-time synthesis.
- Google Cloud Text-to-Speech & Amazon Polly: The offerings from the major cloud providers are also excellent, providing a huge variety of high-quality voices and deep integration with their respective platforms.
A recent study on user trust in AI found that the perceived “humanness” of an AI’s voice can significantly impact the user’s trust and willingness to engage, making the choice of your TTS engine a critical one.
This table provides a high-level AI telephony SDK comparison for the “brain” components.
| Component | Top Contenders in 2025 | Key Strength |
| STT (Ears) | Deepgram, Google Cloud Speech-to-Text, AssemblyAI | Speed and Accuracy. |
| LLM (Brain) | OpenAI (GPT-4), Anthropic (Claude), Google (Gemini) | Conversational Intelligence and Reasoning. |
| TTS (Mouth) | ElevenLabs, PlayHT, Google Cloud TTS | Realism and Expressiveness. |
Also Read: Best Voice API for Global Business Communication: What to Look for Before You Build
What are the Best SDKs for the Voice “Nervous System”?
This is the most critical and often overlooked layer. Your brilliant AI brain is useless if it cannot be connected to a real-time phone call with low latency. This is where a developer-first Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS) comes in. These are the real-time voice API frameworks that handle the telephony.
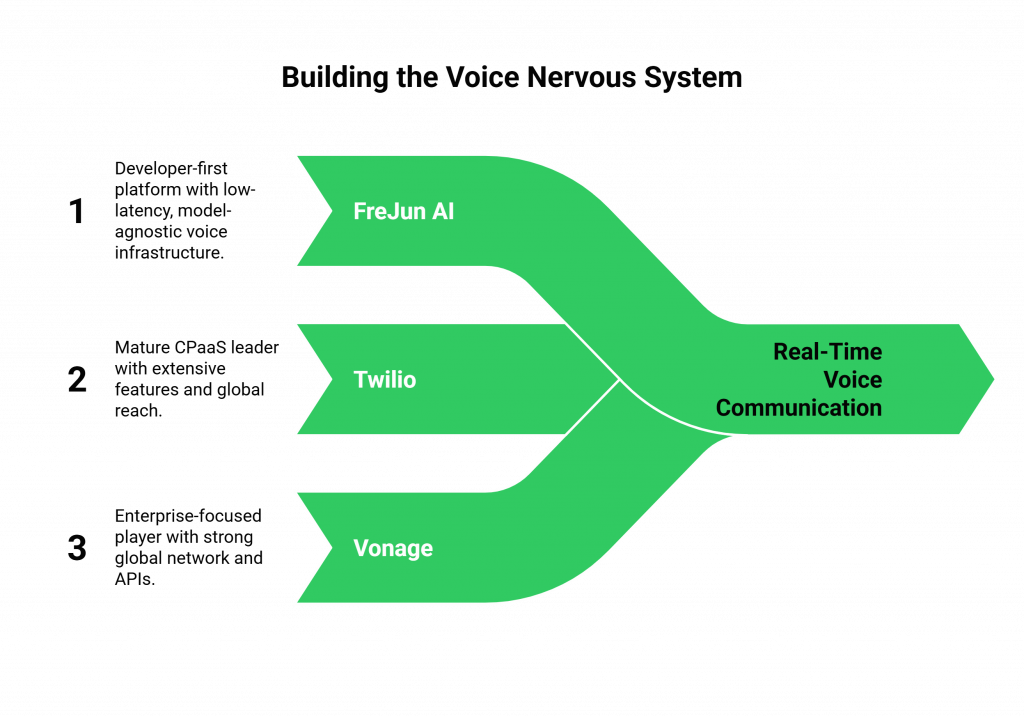
FreJun AI
- Core Philosophy: FreJun AI is a prime example of a modern, developer-first voice infrastructure platform. Our core philosophy is to provide a powerful, reliable, and low-latency “nervous system” and to be completely model-agnostic. Our tagline is “We handle the complex voice infrastructure so you can focus on building your AI.”
- Key Strengths: Our Teler engine is a globally distributed, edge-native infrastructure, which is architecturally designed to minimize the latency that is the enemy of a natural conversation. We provide a powerful voice calling SDK and a Real-Time Media API that gives developers the deep, programmatic control they need for a sophisticated LLM-based voice bot toolkits. The entire platform is built for the specific demands of AI.
Other Major Players
- Twilio: The long-standing leader in the CPaaS market, offering a very mature and feature-rich platform with a massive global reach.
- Vonage (formerly Nexmo): Another major, enterprise-focused player with a strong global network and a comprehensive set of communication APIs.
Ready to connect your AI brain to a world-class nervous system? Sign up for FreJun AI and explore our powerful, low-latency voice calling SDK.
How Do You Choose the Right Toolkit for Your Project?
The beauty of this modern, decoupled architecture is that you can mix and match to create the perfect stack for your needs. Here are some key considerations for choosing your tools:
- For Maximum Conversational Fluency: You might choose a stack with OpenAI’s GPT-4 as the LLM, ElevenLabs for the most realistic voice, Deepgram for the fastest possible transcription, all running on top of FreJun AI’s low-latency infrastructure to tie it all together.
- For a Google-Centric Environment: If your business is already heavily invested in Google Cloud, a stack using Google’s Speech-to-Text, Gemini LLM, and Google’s TTS, all connected via a provider like FreJun AI, might make the most sense for seamless integration.
- For a Budget-Conscious Prototype: You could start with lower-cost or open-source models and then upgrade to more premium services as your application scales.
Also Read: LLMs + Voice APIs: The Perfect Duo for Next-Gen Business Communication
Conclusion
The era of building voice bots as simple, menu-driven IVRs is over. In 2025, the game is all about creating intelligent, fluid, and genuinely helpful conversational agents powered by the magic of LLMs. The key to success is not to search for a single, all-in-one “voice bot builder.”
It is to embrace a modern, decoupled architecture and to choose the best-in-class tool for each layer of the stack.
By combining a powerful AI “brain” from a leading model provider with a high-performance, low-latency “nervous system” from a developer-first voice infrastructure platform like FreJun AI, you have the ultimate toolkit for building the future of voice.
Want to do a deep dive into how to architect a modern voice bot and see how different AI models can integrate with our low-latency platform? Schedule a demo with our team at FreJun Teler.
Also Read: Call Center Reporting Automation: Real-Time Analytics for Better Decisions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The three foundational components of voice bots are: 1) the AI “Brain” (the STT, LLM, and TTS models), 2) the “Nervous System” (the real-time voice infrastructure provider, like FreJun AI), and 3) the “Skeleton” (your own application code that orchestrates everything).
For the core voice connectivity (the “nervous system”), the best SDKs for voice bot development come from developer-first Communication Platforms as a Service (CPaaS). FreJun AI is a prime example, specifically designed for low-latency AI. Other major players include Twilio and Vonage.
For the “brain,” you’ll need to choose from top-tier voice bot development tools like STT engines (e.g., Deepgram), LLMs (e.g., OpenAI’s GPT-4 or Anthropic’s Claude), and TTS engines (e.g., ElevenLabs or PlayHT).
The single most important factor is low latency. The delay between a user speaking and the AI responding must be as short as possible for the conversation to feel natural and not robotic.
When doing an AI telephony SDK comparison, you should look at the provider’s architectural design. A globally distributed, edge-native infrastructure is a key indicator of a platform that is optimized for low latency, which is essential for building voice bots.
LLM-based voice bot toolkits refer to the combination of technologies needed to create a voice agent that uses a Large Language Model as its core intelligence. This includes the voice SDK, the STT/TTS engines, and the LLM itself.
No. The beauty of the modern, decoupled architecture is that you can “mix and match” the best tool for each job. You can use an LLM from OpenAI, a TTS from ElevenLabs, and a voice infrastructure from FreJun AI, all working together.
FreJun AI provides the critical “nervous system” layer. We are not the AI’s brain; we are the high-performance, low-latency voice infrastructure and the voice calling SDK that connects your chosen AI brain to the global telephone network.
A decoupled architecture gives you far greater flexibility, control, and future-proofing. You are never locked into a single provider’s AI models, and you can always swap out a component for a new, better one as the technology evolves.
With a modern, developer-first voice platform and the powerful AI models available today, a skilled developer can often build a surprisingly sophisticated proof-of-concept for a voice bot in a matter of days or weeks, not the months or years it would have taken in the past.
