Voice-driven interaction is redefining how businesses communicate. With the rise of real-time conversational systems, Voice AI APIs now act as the crucial bridge between human speech and machine intelligence. These APIs combine speech recognition, NLP, and TTS technologies to enable systems that don’t just hear – but truly understand and respond. For founders, product managers, and engineers, this means unlocking scalable, natural, and context-aware voice automation across industries.
In this blog, we explore how Voice AI APIs are bringing intelligence to communication systems, and how platforms like FreJun Teler simplify this transformation with global, low-latency voice infrastructure.
What Makes Voice AI APIs the Next Big Leap in Communication Systems?
Traditional voice systems were built around rule-based IVRs and rigid scripting logic. They worked – but they didn’t understand. Today, Voice AI APIs are redefining how machines interpret, process, and respond to spoken language in real time.
At the core, a Voice AI API acts as the bridge between human speech and machine comprehension, enabling applications to:
- Recognize voice input through speech-to-text (STT) engines.
- Process that input using Natural Language Processing (NLP) or Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Generate intelligent, contextually aware voice output via text-to-speech (TTS) systems.
Unlike legacy telephony APIs that simply connected calls, Voice AI APIs bring intelligence to communication, empowering businesses to create voice agents capable of human-like understanding, dynamic response generation, and continuous contextual awareness.
How Has Voice Communication Evolved with AI Integration?
The evolution from DTMF keypads to conversational AI represents a shift from input-based to intent-based systems.This transition was made possible by three major advancements:
- Streaming Protocols: Real-time media streaming allows bi-directional audio transfer between callers and AI engines within milliseconds.
- Machine Learning Models: AI models trained on voice patterns enable speech recognition across accents, tones, and noise conditions.
- API Abstraction: APIs simplify integration by wrapping complex telephony, transcription, and synthesis logic into developer-friendly interfaces.
The result? A system that can think, listen, and speak – not just respond to pre-coded commands.
Why Is a Voice AI API More Than Just Speech Recognition?
It’s tempting to equate speech recognition AI with voice AI, but the difference is depth.
Speech recognition only converts audio to text; a Voice AI API goes further by embedding intelligence across the entire conversational pipeline.
Let’s break it down technically:
| Component | Function | Purpose |
| STT (Speech-to-Text) | Transcribes user speech into machine-readable text | Captures user intent |
| NLP / LLM | Interprets the transcribed text, identifies context and intent | Generates intelligent response |
| TTS (Text-to-Speech) | Converts AI-generated text into natural-sounding speech | Delivers human-like interaction |
| RAG / Tool Calling | Fetches or computes real-time information | Keeps the conversation contextual and actionable |
In this layered structure, the Voice AI API acts as the glue – orchestrating how these components communicate with one another.
This makes it a critical infrastructure layer for building voice automation, AI voice engines, and context-aware agents.
How Does a Voice AI API Work in Real-Time?
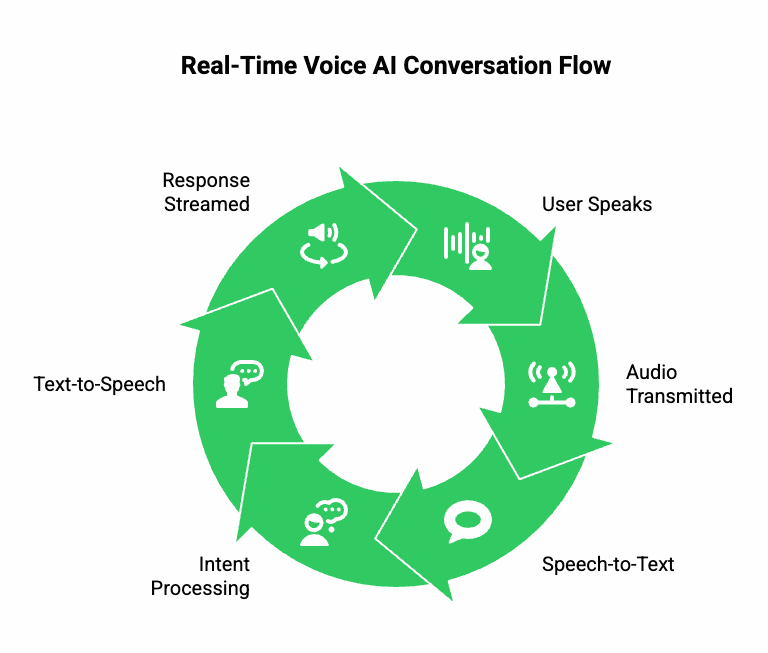
To understand its working mechanism, let’s visualize the real-time conversation flow:
- User Speaks: The audio stream is captured from the microphone or VoIP endpoint.
- Audio Stream Transmitted: Using low-latency RTP or WebRTC channels, the audio is transmitted to the AI backend.
- Speech-to-Text Engine Processes Audio: The STT model continuously transcribes the speech into text chunks.
- LLM or Conversational AI Processes Intent: The language model interprets the text, applies contextual logic, and formulates a suitable response.
- TTS Engine Generates Speech: The TTS system converts the response into natural speech output.
- Response Streamed Back to User: Using the same media channel, the synthesized voice is played back instantly.
This full-duplex streaming loop ensures round-trip latency of under 300 ms, making the conversation feel seamless and natural.
Technically speaking, the Voice AI API acts as the event bus between voice capture, processing, and playback – managing synchronization, buffering, and session state.
Learn how to integrate Teler with OpenAI’s AgentKit to build real-time, intelligent voice agents in just a few simple steps.
What Are the Key Technical Capabilities of a Modern Voice AI API?
A production-ready Voice AI API must support certain core capabilities to maintain performance, scalability, and reliability.
1. Low-Latency Media Streaming
- Real-time bi-directional audio pipelines (via RTP/WebRTC).
- Sub-500 ms round-trip for conversational naturalness.
- Adaptive jitter buffering to prevent audio clipping.
2. Dynamic Speech Recognition
- Multi-accent and noise-tolerant speech recognition AI.
- Custom vocabulary and domain-specific model adaptation.
- Automatic punctuation and entity detection for structured input.
3. Natural-Sounding Speech Synthesis
- Neural TTS models with controllable pitch and tone.
- Emotional expressivity and speaker-specific voices.
- Real-time streaming TTS for overlapping dialogue.
4. Context Management
- Integration hooks for external context stores or memory services.
- Support for LLM-based conversational memory or RAG pipelines.
- State management through session tokens or message IDs.
5. Developer Flexibility
- RESTful or WebSocket-based APIs.
- SDKs for Node.js, Python, Go, and mobile environments.
- Webhooks for event-driven architecture integration.
6. Scalability & Security
- Horizontal scaling with distributed call handling.
- End-to-end encryption for audio and text payloads.
- OAuth 2.0 / JWT-based authentication.
In essence, a Voice AI API isn’t just an audio interface – it’s an intelligent orchestration layer that enables voice automation across enterprise-scale systems.
How Do LLMs Enhance the Capabilities of Voice AI?
Large Language Models (LLMs) bring reasoning and adaptability to voice systems. Instead of hard-coded responses, they generate context-specific replies dynamically.
Here’s how the synergy works:
- Input Understanding: LLMs decode user intent from transcribed text.
- Context Continuity: They maintain the flow of dialogue across turns.
- Knowledge Retrieval: With Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), LLMs access external data in real time.
- Tool Execution: Through function calling, LLMs can trigger APIs or workflows – booking a meeting, checking inventory, or fetching CRM data.
This pipeline makes voice agents capable of end-to-end automation rather than just conversational responses.
For example:
User: “Can you reschedule my demo call to tomorrow afternoon?”
Voice Agent (via LLM): Understands intent → checks CRM calendar via API → confirms the reschedule → responds vocally.
The LLM isn’t replacing the voice API – it’s powered through it. The Voice AI API ensures every spoken exchange flows efficiently between user, model, and backend systems.
What Does It Take to Build an Enterprise-Grade Voice AI Infrastructure?
Building from scratch involves integrating multiple specialized layers:
| Layer | Function | Technology Stack |
| Telephony Layer | Handles call routing, SIP/VoIP, and connectivity | WebRTC, SIP Trunks |
| Media Layer | Captures, encodes, and streams audio | RTP, Opus Codec |
| AI Processing Layer | Converts speech ↔ text, interprets context | ASR, LLMs, TTS Engines |
| Orchestration Layer | Manages session flow, retries, fallbacks | APIs, Event Queues |
| Application Layer | Business logic, CRM, analytics | REST/GraphQL APIs |
The technical challenge lies in synchronizing these layers to ensure sub-second latency and maintaining context consistency across thousands of concurrent sessions.
How Do Voice AI APIs Differ from Traditional Telephony APIs?
Let’s clarify the distinction:
| Feature | Telephony API (Legacy) | Voice AI API (Modern) |
| Functionality | Call routing, IVR menus | Real-time speech interaction |
| Intelligence | Rule-based | AI-driven understanding |
| Latency | Buffered audio | Streaming audio |
| Customization | Script-based logic | Dynamic LLM + NLP |
| Output | Pre-recorded | Real-time TTS synthesis |
| Integration | PSTN & SIP only | Cloud telephony, VoIP, WebRTC |
| Use Case | Static IVR or notification | Conversational agents & automation |
The key difference is intelligence and adaptability.
A Voice AI API listens, thinks, and responds dynamically, whereas a telephony API only connects voices.
Why Are Businesses Moving Toward NLP-Based APIs for Voice Automation?
Because customer conversations are becoming data-rich, multilingual, and fast-paced, rule-based call flows no longer suffice.
With NLP-based APIs, businesses can:
- Decode complex voice commands beyond scripted flows.
- Support multiple languages seamlessly.
- Personalize responses based on user profiles or context.
- Integrate sentiment and emotion analysis for adaptive tone.
- Automate repetitive tasks such as lead qualification, appointment scheduling, or status updates.
Ultimately, voice automation powered by conversational AI isn’t just about efficiency – it’s about delivering more human communication at scale.
How Does FreJun Teler Fit into the Voice AI Ecosystem?
Until now, we’ve seen how Voice AI APIs combine STT, TTS, LLMs, and NLP-based APIs to enable intelligent, real-time conversations.
But implementing all of this from scratch – while ensuring global reliability, low latency, and scalability – is complex.
That’s where FreJun Teler enters the picture.
FreJun Teler is a global voice infrastructure built for AI agents and LLMs.
It allows developers to plug in their preferred AI model, Speech Recognition, and Text-to-Speech (TTS) service – and get a fully functional, real-time conversational agent running within minutes.
Unlike legacy voice APIs that only route calls, Teler acts as the intelligent transport layer, handling real-time audio streaming, call orchestration, and latency management, while your AI engine manages the logic.
What Makes FreJun Teler Technically Different?
Let’s break down its core architecture and how it bridges voice with intelligence:
1. Model-Agnostic Integration
Teler doesn’t lock you into a single AI provider. You can connect any LLM or agent, whether it’s OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Vertex, or your in-house model.
You maintain full control over conversation logic, prompt design, and contextual flow.
2. Real-Time Media Streaming
- Built on low-latency RTP and WebSocket protocols for bi-directional audio transfer.
- Ensures a sub-300ms delay between user speech and AI response.
- Optimized for both VoIP and PSTN connections.
3. Developer-First SDKs
- SDKs for Node.js, Python, and Go allow quick embedding into web or backend systems.
- Supports direct connection from mobile and browser-based applications.
- Offers hooks for AI event handling, message streaming, and call state management.
4. Full Conversational Context
- Maintains a persistent session layer, allowing your LLM to track user intent across multiple turns.
- Integrates easily with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems for live data fetching.
- Enables tool calling – so your voice agent can perform real actions (book meetings, query databases, send notifications, etc.).
5. Scalable and Secure Infrastructure
- Globally distributed voice nodes ensure high availability and consistent audio quality.
- End-to-end encryption and compliance with enterprise-grade security standards.
- Built-in failover and retry mechanisms for mission-critical applications.
How Can You Implement Teler with Your AI Stack?
One of the biggest advantages of Teler is flexibility. It doesn’t dictate how your AI should behave – it just ensures the voice layer performs flawlessly.
Here’s a simplified integration workflow:
| Step | Function | What You Do |
| 1. Initialize a Voice Session | Create a session using Teler API for inbound or outbound call. | Define webhook endpoints for media stream. |
| 2. Stream Voice Input | Teler captures real-time audio from user. | Send the audio to your Speech-to-Text model (e.g., Whisper, Deepgram). |
| 3. Process Text with LLM | Your AI interprets text and generates a response. | Use OpenAI GPT-4, Claude, or any local model for reasoning. |
| 4. Convert Text to Speech | Your TTS model synthesizes the AI’s response. | Stream the audio output back to Teler. |
| 5. Deliver Real-Time Voice Response | Teler streams synthesized voice to user instantly. | Maintain continuous, human-like dialogue. |
The developer retains complete control over AI behavior while Teler ensures uninterrupted, low-latency voice streaming.
This separation of concerns is what makes Teler ideal for scalable voice automation – the intelligence layer is yours, the infrastructure layer is Teler’s.
Where Does Teler Excel in Real-World Use Cases?
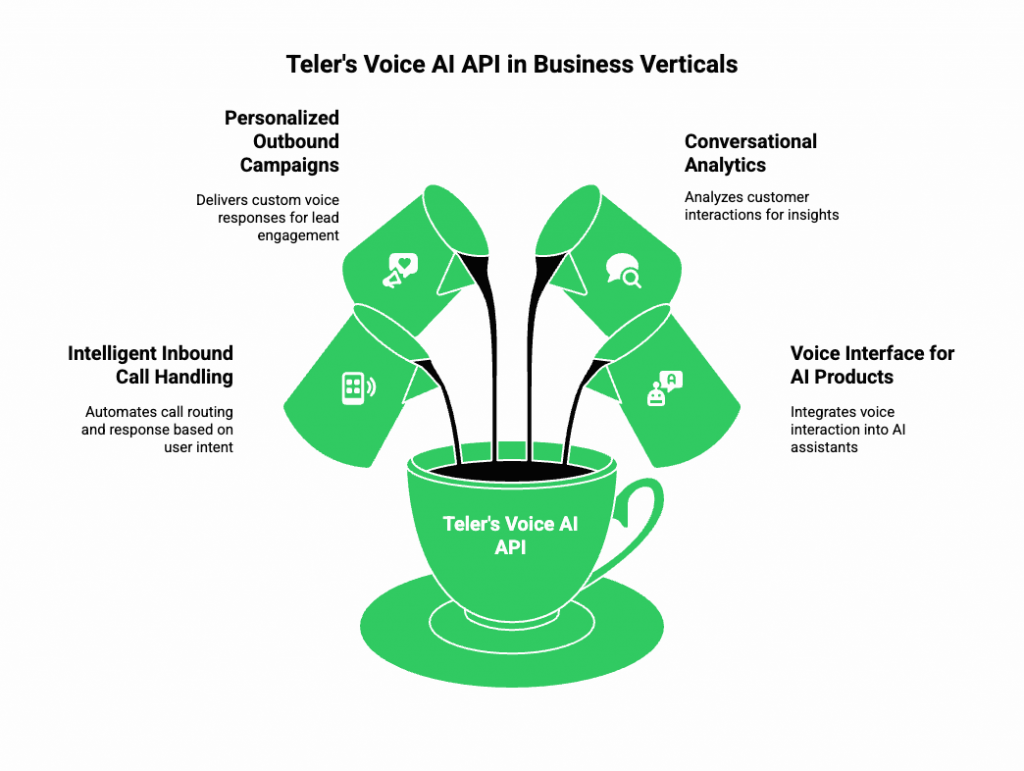
Let’s explore how FreJun Teler’s Voice AI API empowers different business verticals:
Intelligent Inbound Call Handling
- Build AI-powered receptionists or support agents that understand natural speech.
- Automatically route calls based on user intent (e.g., “I want to check my order status”).
- Integrate with CRMs or databases in real time to fetch and deliver responses.
Personalized Outbound Campaigns
- Execute scalable, conversational outreach without robotic tones.
- Combine LLM reasoning with Teler’s low-latency voice channel to deliver custom responses for every lead.
- Automate appointment scheduling, reminders, and follow-ups.
Conversational Analytics and Feedback Systems
- Use AI to summarize customer interactions automatically.
- Detect sentiment, emotion, and keyword trends.
- Feed insights back into business systems for training and quality optimization.
Voice Interface for AI Products
- Developers can embed Teler into existing chatbots or AI assistants.
- Turn any text-based LLM into a fully voice-interactive agent using a simple API call.
- Works across web, mobile, and SIP/VoIP endpoints.
What Makes Voice AI APIs Essential for Future Communication?
Communication is no longer static – it’s contextual and continuous.
Voice is the most natural medium humans use, and APIs like Teler are bringing that naturalness to digital systems.
Here’s why this shift is accelerating:
- Reduced Friction: Users prefer speaking over typing. Voice AI bridges that gap.
- Higher Accessibility: Voice-based interfaces help non-technical or visually impaired users.
- Automation Efficiency: Businesses can handle 10x more conversations without additional human support.
- Scalability: With model-agnostic APIs, companies can upgrade AI stacks without re-engineering the voice layer.
- Data-Driven Personalization: NLP and LLMs enable adaptive responses tuned to each user’s profile or intent.
Essentially, Voice AI APIs are transforming communication systems from reactive tools into proactive, intelligent ecosystems.
How Does Teler Ensure Reliability and Performance at Scale?
For enterprise adoption, reliability isn’t optional – it’s fundamental.
Teler’s infrastructure is designed with resilience and latency optimization at every layer:
- Geographically Distributed Nodes: Reduces packet loss and maintains sub-300ms response times across continents.
- Redundant SIP Gateways: Automatic failover ensures calls stay connected even during network fluctuations.
- Continuous Media Health Checks: Monitors jitter, packet delay, and buffer underruns in real time.
- Dynamic Scaling: Automatically scales concurrent sessions during high-volume traffic.
- Dedicated Integration Support: Helps teams design their AI voice workflows efficiently.
Together, these ensure consistent voice quality, high uptime, and developer agility, even when managing thousands of concurrent AI-driven calls.
How Are Voice AI APIs Powering the Future of Conversational Automation?
The modern communication stack is evolving into Voice + AI + Cloud synergy.
This evolution will be driven by systems that can learn, adapt, and act in real time.
Future-ready Voice AI APIs will:
- Blend NLP-based reasoning with speech synthesis for hyper-personalized conversations.
- Integrate multimodal context – combining voice, text, and visual data.
- Offer API-first modularity, so developers can plug-and-play AI components.
- Optimize cost and compute, using edge inference for faster response times.
FreJun Teler already lays this foundation, providing the infrastructure layer for tomorrow’s conversational agents.
As AI models advance, Teler’s voice transport capabilities will remain essential – enabling machines not just to talk, but to converse intelligently at global scale.
Conclusion: The Voice of AI-Driven Communication
The age of static IVRs is over.
Businesses now demand systems that can listen, think, and respond intelligently – across any telephony or VoIP network.
Voice AI APIs are the bridge to that future, and FreJun Teler is leading that evolution with its developer-first, low-latency, globally distributed voice infrastructure.
By combining Teler’s infrastructure with your LLM + TTS + STT stack, you can deploy voice agents that feel genuinely human – capable of reasoning, acting, and personalizing interactions at scale.
It’s not just about adding speech to AI.
It’s about building the next generation of intelligent voice communication systems that can power businesses, products, and customer experiences for years to come.
Ready to build your Voice AI experience?
Start for free at FreJun Teler and transform your AI into a voice-ready agent today.
Schedule Demo Here!!
FAQs –
1. What does a Voice AI API actually do?
It connects voice input to AI engines, enabling real-time speech understanding, processing, and natural human-like responses.
2. Can I use my preferred speech recognition engine with Teler?
Yes, Teler supports any STT service like Whisper, Deepgram, or Google Speech, offering complete flexibility for developers.
3. How fast is the response time in Teler?
Teler’s optimized architecture ensures end-to-end latency under 300 milliseconds, maintaining smooth and natural conversational flow.
4. Does Teler work with OpenAI or custom LLMs?
Yes, it’s model-agnostic—integrate OpenAI, Anthropic, or your proprietary AI seamlessly with the Teler voice infrastructure.
5. Can Teler support multilingual conversations?
Absolutely. It supports global telephony and integrates with multilingual STT/TTS models for region-specific, natural-sounding voice conversations.
6. Is it difficult to integrate Teler into existing apps?
No, developer-first SDKs for Python, Node.js, and Go make integration fast, flexible, and scalable within existing systems.
7. What industries benefit most from Voice AI APIs?
Industries like customer support, healthcare, fintech, logistics, and education use them for automation, personalization, and real-time assistance.
8. How secure is Teler for enterprise use?
Teler provides end-to-end encryption, data privacy, and geographically distributed redundancy for maximum uptime and data protection.
9. Can Teler handle outbound calling automation?
Yes, it can scale intelligent outbound campaigns for lead engagement, surveys, reminders, and personalized user follow-ups globally.
10. What makes Voice AI APIs future-ready?
They combine NLP-based reasoning, voice synthesis, and contextual automation – enabling scalable, human-like conversations across digital and telephony networks.
