You have done the hard part. You have built an intelligent agent in your AgentKit, a sophisticated AI brain, powered by a state-of-the-art LLM, that is ready to solve problems and delight customers. It is a masterpiece of logic and data. But right now, it is sitting in silence, trapped in the digital world.
The final, critical step is to give it a voice and connect it to the most universal communication network on the planet: the telephone. The challenge is how to connect AgentKit to realtime voice calls without getting lost in the dizzying complexity of telephony.
This is not a simple file transfer. A real-time voice call is a dynamic, unpredictable, and incredibly time-sensitive stream of data. Bridging this stream to your AI’s logic requires a specialized infrastructure designed for speed, reliability, and control. This is the precise role of FreJun AI’s Teler engine.
By understanding how to use Teler as the powerful bridge between the phone network and your AgentKit, you can transform your silent AI into a fully interactive voice agent, ready to handle real-world conversations at scale.
Table of contents
What Are the Two Halves of a Voice AI Application?
To build a voice agent, you need to master two fundamentally different domains. A successful deployment is not about choosing one over the other, but about creating a perfect, seamless connection between them.
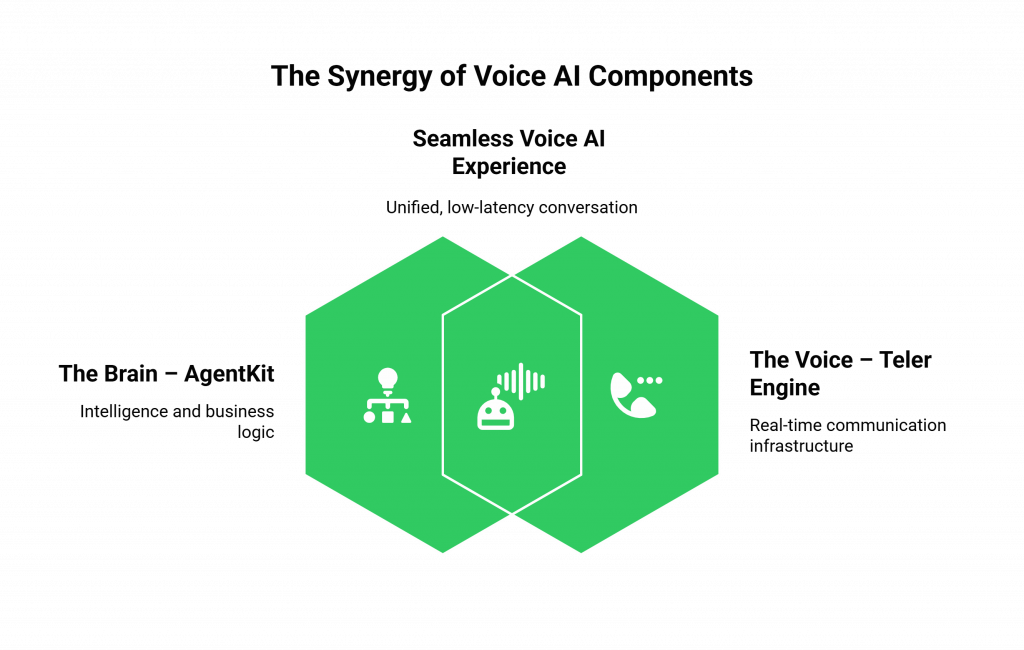
The Brain – Your AgentKit
This is the domain of intelligence and logic. It is the part of the system that you, the developer, have complete control over.
- AI Models: It contains your chosen stack of Speech-to-Text (STT), Large Language Model (LLM), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) services.
- Business Logic: It is where your application’s rules live. It connects to your databases, your CRMs, and your APIs to perform the actual work, whether that is looking up an order, processing a payment, or scheduling an appointment.
- Conversational State: This is the memory of your agent, keeping track of the conversation’s history to provide context for the next turn.
Your AgentKit is the “why” and the “what” of the conversation.
The Voice – FreJun AI’s Teler Engine
This is the domain of real-time communication infrastructure. It is the highly specialized, low-level engine that handles the raw mechanics of the phone call.
- Telephony: Teler manages the phone numbers, the connections to global carriers, and the complex signaling protocols (like SIP) that make a call possible.
- Real-Time Media: Its most critical job is to handle the real-time streaming of audio packets (RTP) with ultra-low latency.
- Call Control: It provides the fundamental controls for the call state, such as answering a call, hanging up, or playing an audio stream.
Teler is the “how” of the conversation. The challenge is to make these two halves work as one.
Also Read: How to Integrate Teler with AgentKit: Real-time Voice Agents through the MCP Server
How Does the Teler Act as the Bridge?
The key to understanding how to connect AgentKit to realtime voice calls is to see Teler not as a simple phone line, but as a programmable, real-time media server that your AgentKit can control remotely. The communication between them is managed through a powerful set of APIs and real-time events.
Let’s walk through the life of a typical inbound call to see how Teler and your AgentKit work in a continuous, high-speed loop.
Step 1: Teler Answers the Call and Notifies Your AgentKit
A user dials a phone number that you have configured on the FreJun AI platform.
- Teler springs into action: Our Teler engine, located at an edge data center close to the user, answers the call.
- A webhook is sent: As soon as the call is connected, Teler sends a real-time event notification (a webhook) to an endpoint that you have specified. This is the “bat signal” that tells your AgentKit, “Wake up! We have a live call.”
Step 2: AgentKit Takes Control
Your AgentKit receives this initial webhook. It now knows the unique CallSid for this new call and can begin to orchestrate the conversation.
- The first command: Your AgentKit’s first action is usually to greet the user. It sends an API command back to Teler. This command might be a “Play” verb, instructing Teler to play a pre-recorded welcome message, or it could be a “Gather” verb, telling Teler to play a greeting and then immediately start listening for the user’s response.
Step 3: Teler Listens and Streams
Following the command from your AgentKit, Teler starts its most critical task.
- Real-time streaming: As the user speaks, Teler captures the raw audio and begins streaming it in real-time to your AgentKit. More specifically, it streams it to the Speech-to-Text (STT) engine you have designated in your AgentKit.
Step 4: The AgentKit “Thinking” Loop
This is where your AI’s brain does its work.
- Transcription: Your STT engine transcribes the audio into text.
- Intelligence: This text is passed to your LLM, which processes the user’s intent, consults its business logic, and formulates a response.
- Voice Generation: The LLM’s text response is passed to your TTS engine, which synthesizes it into a new audio stream.
Also Read: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Voice-Enabled AI Agents Using Teler and OpenAI’s AgentKit
Step 5: AgentKit Commands Teler to Respond
Once your AgentKit has the audio response ready, it sends another API command back to Teler, instructing it to play this new audio stream to the user.
This “Listen -> Think -> Respond” loop repeats for every turn of the conversation, happening in a fraction of a second. Teler acts as the loyal and efficient “voice puppet,” perfectly executing the real-time commands sent by the AgentKit “brain.”
A recent industry report on AI in customer service found that 60% of businesses that use conversational AI report improved customer satisfaction, a direct result of this kind of fast and efficient interaction.
Here is a simplified table showing the division of labor:
| Responsibility | FreJun AI’s Teler Engine | Your AgentKit |
| Connecting the Call | YES | NO |
| Real-time Audio Streaming | YES | NO |
| Executing API Commands | YES | NO |
| Deciding What to Say | NO | YES |
| Understanding the User | NO | YES |
| Managing Business Logic | NO | YES |
Ready to give your AI brain a powerful voice? Sign up for FreJun AI and explore our APIs to start building.
Why is This Decoupled Architecture Superior?
Designing your system this way, with a clear separation between the “voice” and the “brain” is the key to building a production-grade application. It provides several critical advantages that are essential for any serious deployment.
The power of this approach is reflected in the market; a recent analysis projects that the global market for Communication Platform as a Service (CPaaS), which is built on this architectural principle, will grow to over $45 billion by 2027.
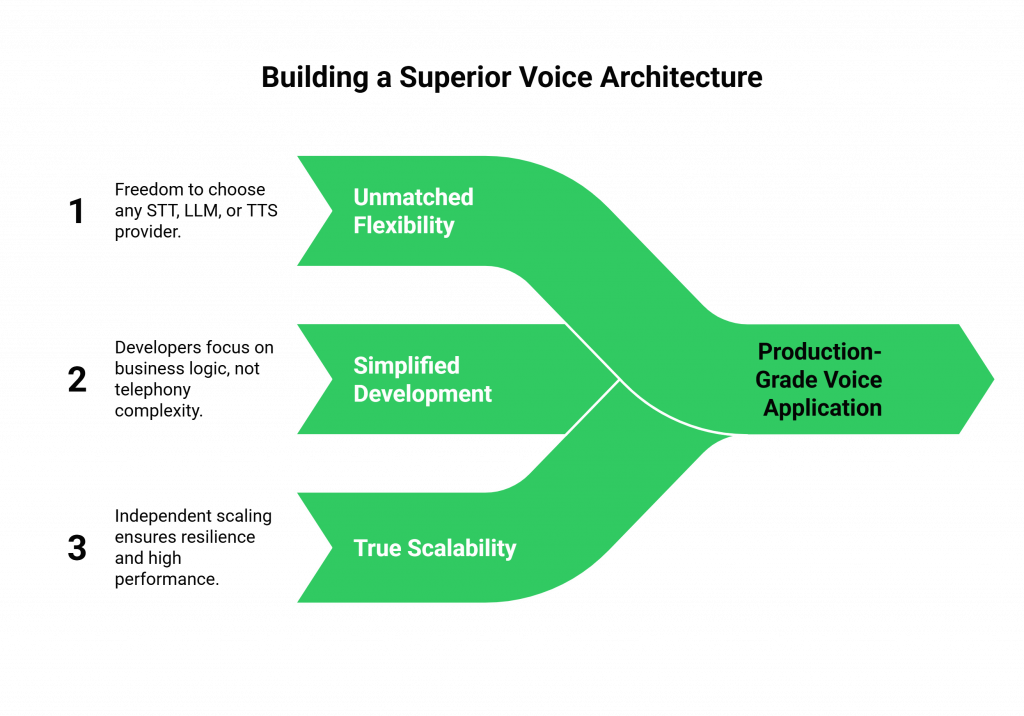
Unmatched Flexibility
Because your AgentKit operates separately, you have complete freedom. You are not locked into our AI and can use any STT, LLM, or TTS provider. You can host AgentKit on any cloud or on-premise. Teler simply connects AgentKit to real-time voice calls, no matter where it lives or how it is built.
Also Read: How MCP Servers Bridge AgentKit and Teler for AI Workflow Automation
Simplified Development
This architecture allows you to abstract away the immense complexity of telephony. Your developers do not need to become experts in SIP, RTP, or carrier networking. They can focus on what they do best: writing the business logic and conversational intelligence of your agent. They interact with the complex world of voice through a simple, clean, and well-documented set of API commands.
True Scalability and Reliability
Teler is a distributed, carrier-grade engine built for massive scale and high reliability. By offloading real-time media processing to Teler, you prevent your core application (AgentKit) from becoming burdened. Each component scales independently, creating a more resilient and high-performing system.
Conclusion
The process to connect AgentKit to realtime voice calls is the final and most important step in bringing your AI to life. It is a process that requires a powerful, reliable, and developer-friendly bridge between the world of AI logic and the world of real-time telephony. FreJun AI’s Teler engine is that bridge.
By acting as a programmable, real-time media server that is controlled by your AgentKit, Teler provides the robust and flexible foundation you need. This decoupled architecture simplifies development, ensures reliability at scale, and gives you the freedom to build the most intelligent and responsive voice agents imaginable.
Want a technical deep dive into our APIs and see how you can connect your specific AgentKit to Teler in minutes? Schedule a demo with our team.
Also Read: UK Phone Number Formats for UAE Businesses
Frequently Asked questions (FAQs)
Teler is our core voice infrastructure engine. Its primary job is to handle the low-level, real-time mechanics of a phone call, including connecting to the telephone network and streaming audio with very low latency. It acts as the “voice” that your AgentKit controls.
AgentKit is the logical environment where your AI’s intelligence lives. It is your application, containing your STT, LLM, and TTS models, along with your business logic and conversational state management.
They communicate through a system of APIs and webhooks. Teler notifies your AgentKit of call events (like a new inbound call) via webhooks. Your AgentKit then controls what Teler does on the live call (like playing audio or listening) by sending it commands via our Realtime API.
No. Our architecture is designed to be completely flexible. You can host your AgentKit anywhere you want—on AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, or even on your own on-premise servers. Teler can connect to it as long as it has a publicly accessible endpoint.
The first step is to purchase a phone number through the FreJun AI dashboard and configure it to send a webhook to your AgentKit’s main endpoint. When a call comes in to that number, Teler will automatically notify your application.
Yes. You can use our API to instruct Teler to make an outbound call to any phone number. Once you answer the call, Teler will send a webhook back to your AgentKit, and the same conversational loop begins.
Teler is a globally distributed, edge-based engine. It processes the call at a data center physically close to the end-user, which minimizes network latency. The real-time audio streaming is highly optimized for speed, ensuring a natural conversational flow.
Yes. All communication between Teler and your AgentKit, including webhook notifications and API commands, uses HTTPS for security. We also provide authentication methods to ensure only your application controls your calls.
