Intelligent Voice Agents are becoming essential for real-time, human-like communication. Yet, most AI systems still struggle to bridge the gap between text and natural voice conversations. This is where FreJun Teler transforms the game – enabling AgentKit-powered agents to interact over calls with seamless, low-latency audio and full conversational context.
In this blog, we explore how Teler’s global voice infrastructure enhances AgentKit’s Intelligent Agents with real-time streaming, context retention, and cross-LLM flexibility – making voice truly intelligent and scalable for founders, engineers, and product teams building next-generation AI communication.
Why Are Intelligent Voice Agents Becoming Essential for Modern AI Workflows?
Until recently, most AI assistants were text-based. They could write, search, or summarize-but they couldn’t speak naturally. Businesses soon realized that a text-only interface limited adoption because customers still prefer to talk when urgency or emotion is involved.
Today, Intelligent Voice Agents are closing that gap. These systems allow users to speak to an AI system just like they would to a human support agent. The result is faster interaction, improved trust, and less friction during tasks such as booking, complaint resolution, or sales qualification.
According to industry benchmarks, over 60 % of enterprises plan to implement voice intelligence in customer-facing workflows by 2026. Voice interfaces are no longer an experiment-they are now a competitive requirement.
However, behind every smooth, human-like conversation lies a complex engineering problem: transforming real-time human speech into structured, actionable AI input and sending back clear audio within milliseconds. This is the foundation that AgentKit and other AI orchestration frameworks aim to automate.
What Actually Powers an Intelligent Voice Agent?
To understand how AgentKit’s intelligent agents gain a “voice,” let’s break down the internal architecture. A production-grade voice system generally consists of the following layers:
| Component | Function | Common Technologies |
| Speech-to-Text (STT) | Converts the caller’s voice into text in real time. | Whisper, Deepgram, Google Speech, Azure Cognitive Services |
| Large Language Model (LLM) | Processes text, reasons about context, and decides what to say or do next. | OpenAI GPT series, Anthropic Claude, Mistral 7B |
| Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Supplies the LLM with factual or domain-specific data. | Vector DBs – Pinecone, FAISS |
| Tool Calling / Action Layer | Executes external operations such as CRM updates or scheduling. | REST APIs, webhooks |
| Text-to-Speech (TTS) | Turns the model’s text output back into audio. | Play.ht, ElevenLabs, Azure Neural Voices |
| Transport / Telephony | Connects real calls and media streams to the AI pipeline. | SIP, WebRTC, VoIP APIs |
All these components together create the voice intelligence loop:
User – Speech – STT – LLM – TTS – Response – User
Every millisecond matters. The quicker each hand-off occurs, the more natural the agent sounds.
While the OpenAI voice API and similar stacks are making this loop easier, building a reliable end-to-end system still requires tight control over latency, error handling, and audio streaming.
What Challenges Do Teams Face When Turning AI Agents into Real-Time Voice Systems?
Building an intelligent voice agent appears simple in theory but is complex in deployment. Below are the core technical challenges that product and engineering teams repeatedly encounter.
1. Latency and Conversation Flow
- Every time audio is recorded, transcribed, processed, and synthesized back, delay increases.
- Even a 700 ms pause feels unnatural to human listeners.
- Low-latency streaming and buffering strategies are essential for agent performance optimization.
2. Context Drift
- LLMs operate on text windows. When a call extends beyond their token limit, earlier context gets lost.
- Maintaining a rolling context store or an external state manager prevents repetitive answers.
3. Audio Quality and Noise
- In telephony environments, packet loss and background noise reduce transcription accuracy.
- Teams must use noise suppression and jitter buffering at the media layer.
4. Telephony Integration
- Different carriers and SIP gateways handle codecs and signaling differently.
- Engineers must normalize these differences so the voice stream remains consistent for the AI stack.
5. Security and Compliance
- Voice data often contains personally identifiable information.
- Encryption during transport (TLS/SRTP) and proper data retention policies are non-negotiable.
6. Scaling and Monitoring
- During peak hours, hundreds of concurrent calls can overload media servers.
- Without observability-latency metrics, dropped packets, or failed TTS events-it’s impossible to diagnose user-reported issues quickly.
Transitioning from a demo-level prototype to an enterprise-ready deployment requires solving all these layers simultaneously.
Where Does AgentKit Stand in the Voice Intelligence Ecosystem?
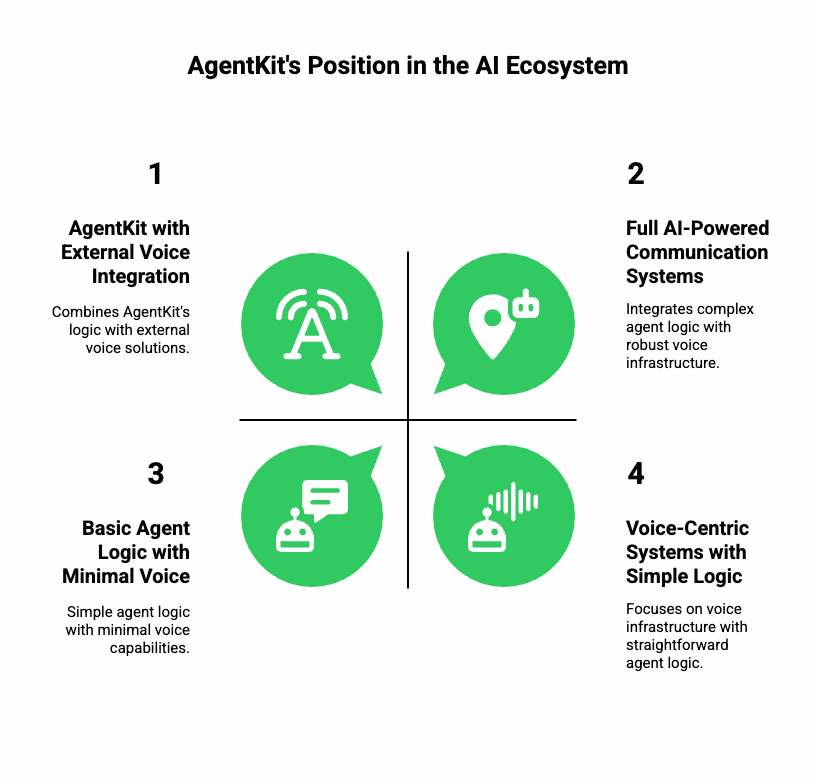
AgentKit simplifies how autonomous AI agents are created and managed. Instead of writing orchestration logic from scratch, teams can define agent behaviors, tools, and context flows through its unified API.
Here’s what makes AgentKit valuable to engineering teams:
- Declarative Agent Logic: Define goals and tool access instead of writing low-level prompt chains.
- Task Chaining and Memory: Retains state across sessions, ideal for multi-turn tasks like booking or troubleshooting.
- Event Hooks and Tool Calls: Connect any API endpoint-CRM, payment API, or analytics pipeline.
- Language-Model Flexibility: Works with any LLM (OpenAI, Anthropic, Claude, etc.).
Despite this flexibility, AgentKit focuses mainly on reasoning and decision-making. It does not provide a built-in voice infrastructure. For teams wanting full AI-powered communication-actual two-way spoken interaction-another layer must handle audio capture, encoding, streaming, and playback.
That missing piece is where a dedicated voice infrastructure layer becomes critical.
What Does a Typical Voice Agent Architecture Look Like Before Adding a Voice Infrastructure Layer?
To visualize the problem, let’s walk through a simplified version of how many teams currently integrate voice capabilities:
- User speaks into a phone call or browser microphone.
- STT engine transcribes audio chunks to text.
- AgentKit + LLM receives text and decides what to do.
- TTS engine converts the response into audio.
- Call provider API plays that audio back to the user.
While this approach works for prototypes, it introduces several inefficiencies:
| Pain Point | Impact on Voice Experience |
| Multiple APIs with no sync | Each network hop adds latency > 1 s |
| Unmanaged audio transport | Dropouts, packet loss, clipped speech |
| Lack of context persistence | Agent forgets prior interaction |
| Complex dev ops | Separate telephony, AI, and logging stacks |
| Limited scalability | Hard to handle thousands of concurrent calls |
For product managers and engineering leads, this means slower iteration cycles and rising infrastructure overhead. What’s missing is a unified, low-latency transport layer that can speak both “telephony” and “AI.”
How Does FreJun Teler Bridge the Gap Between Text-Based Agents and Real-Time Voice?
In the previous section, we saw that AgentKit is exceptional at orchestrating logic and tasks – but lacks an integrated voice infrastructure layer.
This is exactly where FreJun Teler steps in.
Teler is a programmable voice API and streaming layer built specifically for AI-native products.
It acts as a real-time transport bridge between LLMs, TTS/STT engines, and telephony networks, removing the need for teams to build custom audio pipelines from scratch.
Here’s how it fits into the full stack:
| Layer | Traditional Voice Agent Stack | With FreJun Teler |
| Audio Transport | Multiple fragmented APIs | Unified voice streaming layer |
| Latency | 700–1200 ms | <300 ms end-to-end |
| Context Retention | External memory required | Built-in conversational session management |
| Scaling | Requires custom infrastructure | Natively scalable via Teler cloud |
| Reliability | Call drops and jitter | Optimized SIP/WebRTC bridge with QoS control |
By connecting Teler to AgentKit, an intelligent agent that once relied solely on text I/O can now speak, listen, and respond like a human – all while maintaining ultra-low latency and contextual accuracy.
How Does Teler Technically Integrate with AgentKit?
The Teler + AgentKit integration follows a modular design pattern.
Let’s look at how each component communicates step-by-step:
- Incoming Audio Stream
- A user initiates a voice call via phone, browser, or app.
- Teler captures audio packets through its SIP or WebRTC endpoint.
- The audio is instantly routed to a Speech-to-Text engine such as OpenAI Whisper or Deepgram.
- A user initiates a voice call via phone, browser, or app.
- Text-to-AgentKit
- The transcribed text is sent to AgentKit’s agent runtime, where the LLM (OpenAI GPT or Claude, etc.) interprets the intent, uses RAG if needed, and decides the next response or tool action.
- The transcribed text is sent to AgentKit’s agent runtime, where the LLM (OpenAI GPT or Claude, etc.) interprets the intent, uses RAG if needed, and decides the next response or tool action.
- Agent Response to TTS
- The generated text output is routed back to Teler.
- Teler then pushes this to a Text-to-Speech (TTS) provider (e.g., ElevenLabs, Azure Neural Voices) for audio generation.
- The generated text output is routed back to Teler.
- Real-Time Audio Playback
- The synthesized audio is streamed back to the user within milliseconds.
- This maintains a continuous, fluid dialogue flow-without noticeable pauses or robotic cadence.
- The synthesized audio is streamed back to the user within milliseconds.
- Session Persistence & Monitoring
- Every call session is logged and monitored.
- Developers can visualize latency, API performance, and call duration metrics directly from Teler’s dashboard or integrate them into internal observability tools via APIs.
- Every call session is logged and monitored.
This pipeline design ensures developers focus on conversation logic rather than audio plumbing.
What Makes Teler’s Voice Infrastructure Technically Superior?
Teler is not just another telephony API. It’s purpose-built for AI-powered communication.
Its advantage comes from a combination of engineering optimizations tailored for real-time LLM interactions.
1. True Real-Time Streaming
Teler uses bidirectional streaming over WebRTC and SIP with adaptive jitter control.
This ensures:
- Audio delay below 300 ms, even under unstable network conditions.
- Immediate transmission of partial STT results for faster response start times.
2. LLM-Aware Media Handling
Unlike traditional telephony systems, Teler is optimized for AI backends.
It supports:
- Chunk-based transcription handoff (so LLMs can process mid-sentence).
- Interrupt handling, allowing agents to “barge in” or change response dynamically.
3. Scalable, Multi-Agent Infrastructure
With microservices-based routing, thousands of concurrent sessions can be handled without media bottlenecks.
Load balancing automatically scales horizontally, allowing agent performance optimization at scale.
4. Multi-Engine Flexibility
Teler is LLM-agnostic and TTS/STT-agnostic:
- Works with OpenAI voice API, Anthropic Claude, Mistral, or custom RAG setups.
- Developers can swap audio engines without refactoring core logic.
5. Built-In Session Intelligence
Each call session has contextual state memory.
This allows continuous conversations where agents can remember previous details-name, issue type, or order ID-improving user satisfaction.
How Does Teler Improve the AgentKit Experience for Developers?
From a developer’s perspective, integrating voice should not require weeks of telephony setup.
Teler simplifies this into a few declarative steps.
Simplified Integration Flow
POST /api/teler/session
{
“agentkit_agent_id”: “agent_123”,
“stt_engine”: “openai-whisper”,
“tts_engine”: “elevenlabs”,
“llm_provider”: “openai”,
“call_type”: “inbound”
}
Once configured, AgentKit’s agent automatically receives text input and returns responses via Teler’s media relay – all abstracted through a single API endpoint.
Developer Benefits
- Unified Control Plane: One interface for managing telephony, LLM logic, and media.
- Reduced DevOps Overhead: No separate STT/TTS socket handling.
- Comprehensive Logging: Real-time metrics for latency, call drops, and audio quality.
- Extensibility: Connects easily with CRMs, scheduling tools, or analytics systems.
This saves weeks of backend engineering time and makes it feasible for lean AI teams to deploy fully functional Intelligent Voice Agents without specialized telecom knowledge.
Get Signed Up to FreJun Teler Today!
How Does Voice Intelligence Improve Overall Agent Performance?
When Intelligent Voice Agents gain access to a stable, low-latency audio layer like Teler, their measurable performance improves across multiple KPIs.
| Performance Metric | Without Teler | With Teler Integration |
| First Response Latency | ~1.2 s | <0.3 s |
| Conversation Continuity | Interrupted | Seamless |
| Context Retention | Limited to text | Voice + Context-aware |
| Agent Interrupt Handling | None | Real-time adaptive |
| Customer Experience Score | Moderate | Significantly higher |
Key Impacts
- Faster Interactions: No waiting for full transcription before response.
- Natural Flow: Human-like rhythm with controlled pacing and pauses.
- Reduced Drop-offs: Lower latency = higher customer engagement.
- Operational Efficiency: Agents can handle more concurrent sessions per CPU unit.
These improvements directly translate to cost savings and better user retention – crucial metrics for any startup or enterprise scaling conversational AI.
Can Teams Combine Teler with the OpenAI Voice API or Custom LLM Models?
Absolutely.
Teler’s architecture is intentionally open – it’s designed to plug into any voice or reasoning engine.
Example combinations that teams often implement:
- Teler + OpenAI Voice API + AgentKit:
For real-time reasoning and human-like speech synthesis. - Teler + Local LLM (Mistral / Llama) + Custom STT/TTS:
For on-premise, privacy-first deployments. - Teler + Multilingual STT/TTS Engines:
For multilingual contact centers or global customer bases.
This flexibility ensures your voice intelligence stack stays future-proof even as LLM providers evolve.
What Are the Practical Use Cases of Teler + AgentKit Integration?
The combined stack unlocks several high-value business applications:
- Customer Support Automation: Handle inbound voice queries 24×7 with contextual recall.
- Sales and Lead Qualification: Real-time engagement, data capture, and CRM updates.
- HR and Recruitment Calls: Schedule or pre-screen candidates automatically.
- Post-Service Feedback Calls: Generate structured survey data from natural conversations.
- Internal IT or Ops Assistants: Voice-enabled bots for quick troubleshooting or knowledge retrieval.
Each use case benefits from faster response cycles, improved accuracy, and reduced manual load on human teams.
What’s Next for AI-Powered Voice Communication?
As more businesses shift to multimodal AI, the next phase will involve:
- Voice-native interfaces across SaaS and enterprise tools,
- Real-time reasoning with low-latency LLMs, and
- Autonomous decision-making agents that can act, not just talk.
FreJun Teler is engineered for this direction – to help AI developers build, deploy, and scale reliable voice intelligence pipelines without telecom complexity.
Final Take: Why Teler Is the Voice Layer AgentKit Needed
To summarize the Teler AgentKit enhancement:
- AgentKit brings intelligence; Teler brings voice infrastructure.
- Together, they form a unified stack for AI-powered communication.
- The integration delivers natural conversation flow, real-time reasoning, and production-grade scalability.
For product teams building the next generation of Intelligent Voice Agents, this combination reduces friction, accelerates deployment, and improves the end-user experience dramatically.
Ready to Build Your Own Intelligent Voice Agent?
Whether you’re a founder, a product manager, or an engineering lead exploring next-gen communication, the time to experiment with Teler + AgentKit is now.
Experience the difference of real-time, intelligent voice without building infrastructure from scratch.
Schedule a Demo with FreJun Teler and see how your AI agent can finally speak intelligently.
FAQs –
- Can I use Teler with any LLM?
Yes, Teler supports all major LLMs like OpenAI, Claude, and Mistral for seamless voice integration. - Does Teler handle speech recognition?
Teler integrates with STT engines like Whisper or Deepgram to convert voice input into text for your AI. - What latency can I expect with Teler?
End-to-end latency stays under 300 milliseconds, ensuring smooth, human-like real-time voice interactions. - Do I need telephony expertise to use Teler?
No, Teler abstracts complex SIP and VoIP layers, making it easy for AI developers to deploy voice agents. - How does Teler improve AgentKit’s performance?
It adds real-time voice intelligence, reducing lag and improving conversational accuracy for every AgentKit-driven AI agent. - Is Teler compatible with OpenAI Voice API?
Yes, it connects easily with OpenAI Voice API, enhancing audio quality and conversational responsiveness. - Can I scale multiple voice agents simultaneously?
Absolutely, Teler’s distributed architecture supports thousands of concurrent calls with automatic load balancing. - Does Teler store user audio data?
Teler follows strict security protocols; you control data storage and retention based on compliance needs. - What are common Teler + AgentKit use cases?
Customer support, lead qualification, appointment scheduling, feedback collection, and HR voice screening. - How quickly can I deploy a voice agent?
With Teler’s SDKs, most teams launch production-ready voice agents in under a week.
