The inbound phone call is one of the richest and most sensitive data streams in any business. In a single conversation, a customer might share their name, their address, their credit card number, their account password, or their private health information.
For decades, this incredibly sensitive data was ephemeral, disappearing the moment the call ended. In the modern era of call recording, transcription, and AI-driven analytics, every spoken word has become a piece of data that must be rigorously protected.
For any business, a breach of this voice data is not just a technical failure; it’s a catastrophic event that can lead to devastating financial penalties, legal action, and a complete erosion of customer trust. This is why, for modern inbound call handling solutions, data security is not a feature; it is the absolute, non-negotiable foundation upon which the entire system must be built.
This guide is a security-first blueprint for business leaders and technical architects. We will explore the threat landscape for voice data, dissect the core architectural principles of a secure system, and provide a clear framework for building an inbound call handling operation that is not just efficient, but an impenetrable fortress for your customers’ most sensitive information.
Table of contents
Why is Voice Data a High-Value Target for Attackers?
To build a strong defense, you must first understand what you are protecting and why it is so valuable. Voice data is a unique and high-value target for malicious actors for several reasons.
- It’s a Treasure Trove of PII: A single call can contain a wealth of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) that can be used for identity theft and fraud.
- It Contains Financial Data: Customers often read their credit card numbers over the phone to make payments, making call recordings a prime target for financial criminals.
- It’s a Source of Business Intelligence: Call recordings can contain sensitive business information, such as details about upcoming projects or internal problems, which could be valuable to a competitor.
- It’s Biometric Data: A person’s voice is a unique biometric signature. As voice-based authentication becomes more common, voice recordings could be used to try and spoof these systems.
The financial consequences of failing to protect this data are staggering. The latest “Cost of a Data Breach” report from IBM found that the global average cost of a single data breach has climbed to a record high of $4.45 million.
What is the “Threat Model” for Inbound Call Handling?
A “threat model” is a way of thinking like an attacker to identify the potential vulnerabilities in your system. For inbound call handling solutions, the threats exist at every stage of the call’s lifecycle.
| Call Stage | Threat Vector | The Attacker’s Goal |
| In Transit | Eavesdropping / Man-in-the-Middle: | To intercept the unencrypted audio of the live call as it travels over the internet. |
| At the Endpoint | Webhook Spoofing / Unauthorized API Access: | To send fake data to your application’s API or to gain unauthorized access to your voice platform’s control panel. |
| At Rest | Storage System Breach: | To gain access to your database of call recordings and transcripts. |
| In Processing | Data Leakage in AI Models: | To exploit a vulnerability that causes an AI to reveal sensitive data it has processed. |
Also Read: How Developers Can Use Teler and AgentKit to Build Human-Like Voice Agents
What are the Architectural Pillars of a Secure System?
Building an impenetrable fortress for your voice data requires a multi-layered, “defense-in-depth” strategy. These are the non-negotiable architectural principles that every secure inbound call handling solutions must have.
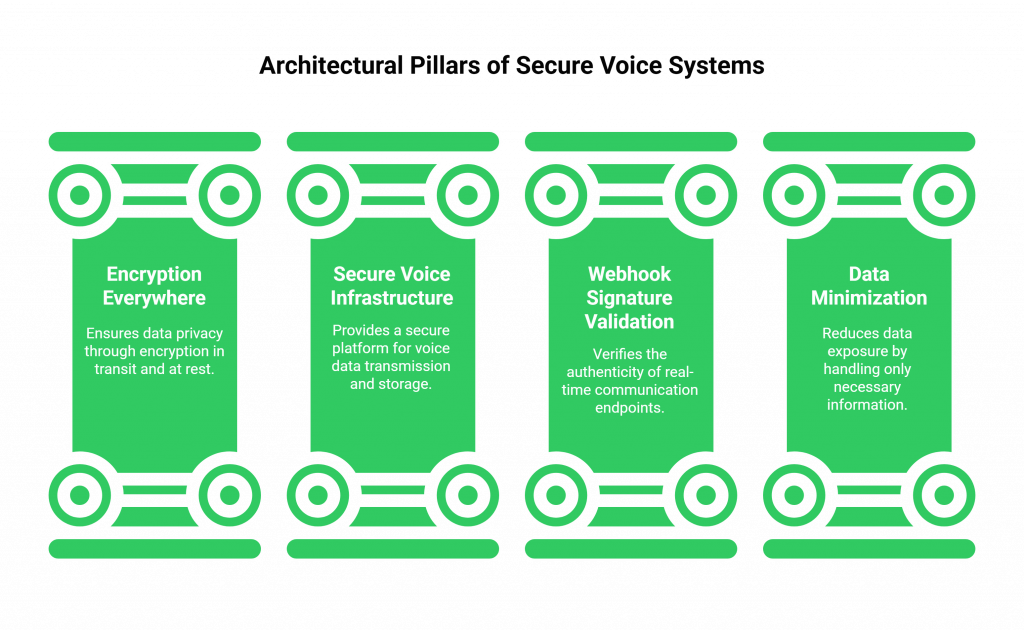
How Do You Ensure “Encryption Everywhere”?
Encryption is the fundamental building block of data privacy. It is the process of scrambling data so that only authorized parties can read it. For a voice system, you must encrypt everything.
- Encryption in Transit: This protects data as it travels. You must use SRTP (Secure Real-time Transport Protocol) to encrypt the raw audio of the call itself and TLS 1.2+ to encrypt all API calls and webhook notifications.
- Encryption at Rest: This protects data when it is stored. Any call recordings or transcripts must be stored in an encrypted format using a strong algorithm like AES-256.
Why is a Secure Voice Infrastructure the Essential Foundation?
As a business, you should not be responsible for managing the deep, complex world of carrier-level security and encryption protocols. This is the specialized role of your voice infrastructure provider. A high-quality voice API platform acts as your secure “armored transport” layer.
A platform like FreJun AI is built with a security-first mindset, securely ingesting audio from the global telephone network and delivering it to your application through a fully encrypted, authenticated channel.
How Do You Secure Your Application’s “Front Door”?
The webhook endpoint on your backend server is the “front door” for all real-time communication. You must secure it. The industry-standard method is webhook signature validation. Your voice provider will use a secret key to create a unique cryptographic signature for every webhook. Your application’s first step must be to verify this signature. This guarantees that you are only listening to authentic messages from your trusted provider.
What is the “Principle of Data Minimization”?
The most secure data is the data you never have in the first place. Your system should be designed to only handle and store the absolute minimum amount of information necessary.
- Automated Redaction: Your application logic should be programmed to automatically redact or scrub sensitive PII from any logs or transcripts before they are stored.
- Secure DTMF for Payments: For handling payment information, you should never have a user speak their credit card number. Instead, use a secure DTMF (keypad tone) capture feature. A secure voice infrastructure platform like FreJun AI can capture these tones as data and send them directly to a payment processor, ensuring the sensitive numbers never touch your call recordings or AI models.
Ready to build an inbound call solution on a foundation of enterprise-grade security? Sign up for FreJun AI!
Also Read: Why Are Businesses Shifting to AI Voice Agents?
What Role Does Compliance Play in Data Security?
For many industries, data security is not just a best practice; it is the law. Your inbound call handling solutions must be designed to meet the strict requirements of regulations like:
- PCI DSS: The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, which governs the handling of credit card information.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, which protects sensitive patient health information in the US.
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation, which gives citizens of the EU strong rights over their personal data.
Achieving compliance requires a partnership with your voice infrastructure provider. They must be able to provide the necessary technical controls (like encryption and secure DTMF) and, in some cases, be willing to sign legal agreements (like a Business Associate Agreement for HIPAA).
The importance of this is growing, as a recent report from PwC found that 85% of consumers say they will not do business with a company if they have concerns about its security practices.
Also Read: 346 Country Code: Location, Region, and Dialing Guide
Conclusion
In the modern digital economy, data is your most valuable asset, and voice data is your most sensitive. The security of your inbound call handling solutions is not an IT issue; it is a fundamental business issue that has a direct impact on your brand’s reputation and your customers’ trust.
By embracing a security-first mindset, architecting a multi-layered defense, and partnering with a voice infrastructure provider that shares your uncompromising commitment to data privacy, you can build a system that is not just intelligent and efficient but also a trusted and impenetrable guardian of your customers’ most private information.
Want to discuss how our security architecture can help you meet your specific compliance needs? Schedule a demo for FreJun Teler.
Also Read: How to Choose the Best Click to Call Software for Your Business?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The biggest risk is a “man-in-the-middle” attack, where an attacker intercepts unencrypted audio data as it travels over the internet. This is why end-to-end encryption is non-negotiable.
SRTP (Secure Real-time Transport Protocol) is the standard for providing encryption for the actual audio packets of a VoIP call. TLS (Transport Layer Security) is the standard for encrypting the data in other types of connections, like your API calls and WebSocket streams.
A webhook signature is a cryptographic hash that your voice provider includes with every webhook. It’s important because it allows your application to mathematically prove that the webhook is authentic and came from your trusted provider, protecting your system from forged or malicious requests.
A secure voice system helps by providing a DTMF capture feature. This allows a user to enter their credit card number with their keypad. The API captures these tones as data and sends them directly to a payment processor, ensuring it never speaks or stores the sensitive numbers in a call recording.
Data redaction is the process of automatically identifying and removing or masking sensitive information (like a Social Security number or a password) from a stored transcript or call recording.
Yes, provided you choose an enterprise-grade provider that has a strong security posture. Look for providers that are compliant with standards like SOC 2 and ISO 27001, offer end-to-end encryption, and are willing to sign legal agreements like a BAA for healthcare compliance.
A secret manager (like AWS Secrets Manager or HashiCorp Vault) is a secure service for storing and managing your sensitive API keys. It’s a best practice to use a secret manager instead of storing keys in configuration files or your source code.
A model-agnostic platform, like FreJun AI, is not tied to a specific AI provider. This can be a security advantage, as it allows you to choose AI models that meet your specific privacy requirements (e.g., using a self-hosted open-source model).
FreJun AI secures the stream in multiple layers. We use SRTP to encrypt the call leg, TLS to encrypt the WebSocket connection to your server, and provide robust features like webhook signature validation. We act as the secure “armored transport” for your voice data.
