The super fast adoption of real-time voice assistants has made VoIP networks more critical than ever. While these systems promise faster customer service and scalable automation, they also expand the attack surface, making VoIP network security a non-negotiable priority. From call hijacking to transcript leakage, the risks now extend beyond traditional telephony into AI-driven pipelines.
This blog explores how organizations can secure both the VoIP network and the AI layers that power modern voice applications. We’ll cover common threats, best practices, compliance requirements, and the importance of aligning infrastructure with enterprise expectations.
For teams ready to move fast, a secure voice infrastructure for AI applications provides the backbone to deploy real-time, enterprise-grade voice AI confidently.
What Is VoIP Network Security and Why Does It Matter for Voice AI?
VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, routes voice calls through the internet instead of copper lines. It is flexible and cost-efficient, which is why modern businesses use it. But unlike traditional telephony, VoIP runs on IP-based networks. That means it inherits the same vulnerabilities as other online systems: interception, unauthorized access, and denial of service.
When a voice AI assistant is added to a VoIP setup, the exposure increases further. Every conversation is not just transmitted but also processed, logged, and sometimes linked to other systems like CRMs or payment gateways. If any part of this chain is insecure, attackers can exploit it.
That is why VoIP network security is essential. It is not only about keeping calls private, but also about protecting the integrity of the AI-powered assistant that sits on top of the network.
Learn how to run secure, scalable voice agents across global VoIP networks while maintaining low latency and compliance everywhere.
What Are the Biggest Security Risks in VoIP Networks?
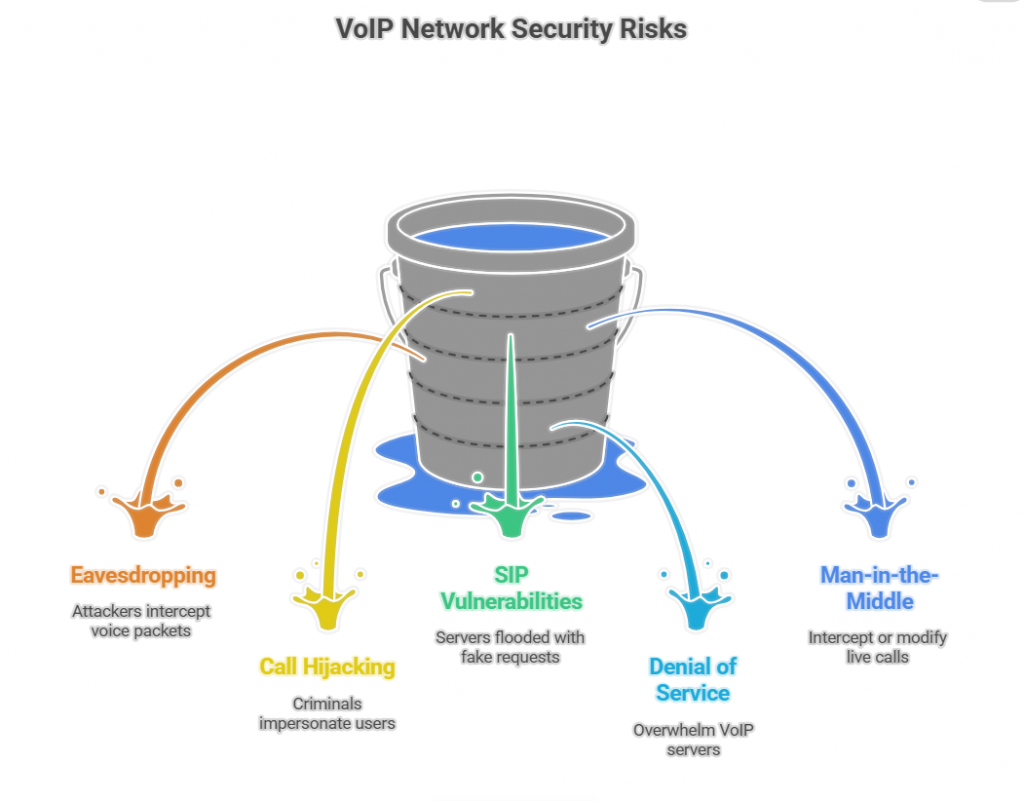
A VoIP network introduces several risks that need to be addressed before layering AI functionality. According to NIST SP 800-58, VoIP networks are highly exposed to DoS, eavesdropping, and traffic analysis if left unprotected.
Eavesdropping
If calls are not encrypted, attackers can intercept voice packets and listen in. Sensitive data like credit card numbers, medical details, or account passwords may be exposed.
Call Hijacking and Spoofing
Weak authentication allows criminals to impersonate users or reroute calls. Caller ID spoofing is especially dangerous because it can trick both humans and AI systems into trusting false identities.
SIP Vulnerabilities
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), used to set up and manage calls, is a frequent target. Attacks include flooding servers with fake requests or hijacking registrations to redirect calls.
Denial of Service
A surge of fake traffic can overwhelm VoIP servers. For AI assistants, this creates delays, dropped calls, and unusable service.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
If signaling or media streams are not properly secured, attackers can intercept or modify live call data.
What Are the Security Risks Unique to Voice AI Systems?
Voice AI systems extend the threat surface beyond traditional VoIP. Here are some risks specific to the AI layer:
- Prompt injection: Attackers use crafted phrases to override AI logic.
- Manipulated audio: Distorted or adversarial inputs can confuse speech recognition.
- Unauthorized tool access: If tokens or permissions are mismanaged, attackers could trigger unintended actions like payments or CRM updates.
- Transcript leakage: Conversations stored without encryption may reveal personal information.
- Replay attacks: Pre-recorded voices can trick AI into authenticating fake users.
The overlap of VoIP network risks and AI logic risks means businesses must adopt a two-pronged approach. Both layers must be secured together.
How Do You Secure a VoIP Network for AI-Powered Voice Assistants?
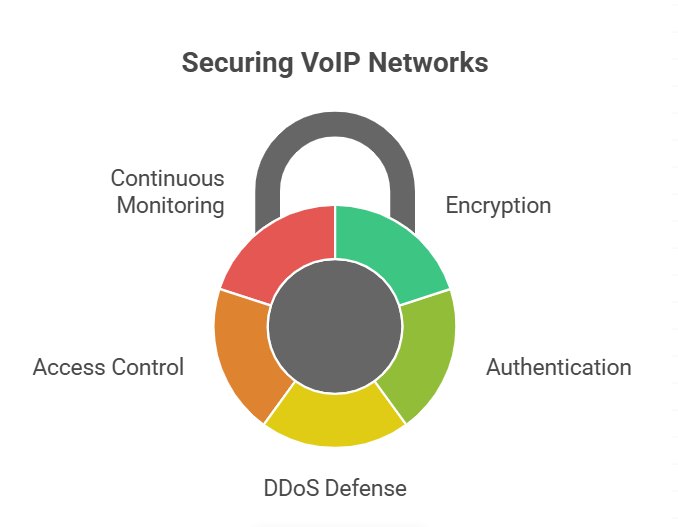
Before introducing AI, the VoIP layer must be hardened. The following measures form the foundation of VoIP network security:
- Encryption of voice data: Use SRTP (Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol) for audio streams and TLS for signaling. In sensitive environments, calls may also be routed through VPN tunnels.
- Strong caller and device authentication: Implement STIR/SHAKEN protocols to verify caller identity and use complex SIP credentials to prevent hijacking.
- Defense against DDoS: Deploy Session Border Controllers (SBCs) to filter traffic, use geo-blocking for high-risk regions, and maintain redundancy across data centers.
- Access control: Apply multi-factor authentication for all admin accounts and assign role-based access to reduce privilege abuse.
- Continuous monitoring: Track call patterns and network activity in real time. Irregular routing or abnormal call durations should trigger alerts.
With these controls in place, a VoIP network provides a secure foundation for adding voice AI.
How Do You Secure the AI Layer in Voice Communications?
Once the VoIP foundation is secured, focus shifts to the AI side. Voice assistants add real-time processing, external integrations, and data storage – all of which must be secured.
Encrypting AI Pipelines
Every connection between speech recognition, the AI engine, and text-to-speech must be encrypted. Using TLS ensures that data is not intercepted in transit.
Input Validation
AI should not process raw inputs blindly. Filters can detect malicious attempts, such as phrases designed to override instructions or unusual acoustic patterns that may indicate adversarial audio.
Access Control for AI Configuration
Not everyone should be able to adjust prompts or retrain the model. Applying role-based access control prevents accidental or malicious changes to system behavior.
Data Protection in Transcripts
Transcripts are valuable but sensitive. They should be anonymized to remove identifiers, encrypted when stored, and only retained as long as business requirements demand.
Monitoring and Auditing
Every action taken by the AI should be logged. This includes responses, tool calls, and data retrieval. Continuous auditing ensures traceability and helps detect suspicious activity quickly.
Putting It Together: A Secure Workflow
When combined, these controls create a layered security workflow for Voice AI over VoIP:
- A caller connects over an encrypted VoIP channel.
- The VoIP network verifies identity and filters malicious traffic.
- The speech-to-text engine converts audio into encrypted text streams.
- The AI engine processes the request, applying access rules and input validation.
- The text-to-speech system delivers the response, again over an encrypted channel.
- Logs are stored with anonymization and audit trails.
By addressing both VoIP network security and AI security, organizations can deploy real-time voice assistants without exposing themselves to unnecessary risk.
How Do You Secure Real-Time Integration Between AI and VoIP?
Even if the VoIP network and the AI pipelines are individually protected, the point where they meet is the most sensitive. This is where real-time audio streams are captured, passed into the AI, and returned as a synthesized voice. Any weakness here can expose the entire system.
One of the main challenges is balancing encryption with latency. Voice assistants must operate in milliseconds. If security adds too much delay, the conversation feels broken. The right approach is to use lightweight but robust encryption standards. For example, SRTP (Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol) protects the audio itself, while TLS 1.3 secures the signaling layer without adding noticeable overhead. Research shows improper SRTP key handling allows SIP proxies to intercept encryption keys, undermining confidentiality of media streams.
Another integration risk is tool access. Modern AI agents rarely operate in isolation. They book meetings, check accounts, or initiate payments. If external APIs are not properly restricted, attackers can exploit them. Best practice here is to use token-based authentication with very limited scope – a token meant for “calendar read-only” should never be able to authorize a payment.
Finally, observability ties it all together. Teams need to monitor both call traffic and AI actions in real time. A sudden surge in outbound requests, unusual API calls, or increased call setup failures should trigger automatic flags. Without monitoring, even well-secured systems may fail silently when an attack happens.
Explore the step-by-step process for deploying real-time voice assistants on VoIP networks with robust security, stability, and developer-first integration.
How Does Frejun Teler Help Secure Voice AI on VoIP Networks?
Traditional VoIP providers were never built with AI pipelines in mind. They focus on call routing and uptime, leaving engineering teams to handle encryption, real-time media streaming, and integration with speech recognition or text-to-speech engines. This creates added complexity and risk when deploying AI-powered voice assistants.
Frejun Teler is designed differently. It provides the secure backbone for AI-first voice applications, with end-to-end encryption using SRTP and TLS to keep every stream protected by default. Instead of treating audio as a simple data flow, Teler acts as a reliable transport layer purpose-built for real-time voice AI.
Each connection is stable and session-specific, preventing data overlap across calls. For developers, Teler offers comprehensive SDKs that make it easy to embed secure voice features directly into web or mobile applications and manage call logic safely from the backend.
Another key advantage is AI pipeline flexibility. Teler is model-agnostic, meaning teams can connect any STT, TTS, or LLM service without being locked into a vendor. This allows product leaders to keep full control of their AI logic, while relying on Teler to manage the demanding voice infrastructure.
By combining encrypted transport, stable session management, developer-first tooling, and expert integration support, Teler removes the infrastructure burden from teams. Founders, product managers, and engineering leads can focus on creating intelligent voice experiences, knowing that the underlying VoIP network security and AI integration are already taken care of.
What Compliance Standards Apply to Voice AI and VoIP Security?
Security controls are only part of the story. For enterprise deployments, compliance with regulations is equally important. The FBI’s IC3 report logged over 859,000 cybercrime complaints in 2024, totaling $16.6 billion in losses. Different industries impose different obligations depending on the type of data processed during a call.
- GDPR: In Europe, any voice transcript containing personal data must follow GDPR rules. This includes obtaining consent, anonymizing stored data, and allowing users to request deletion.
- HIPAA: In the US, healthcare providers must follow HIPAA requirements. Calls that involve patient information must be encrypted end to end, with audit logs to track access.
- PCI DSS: If voice assistants process payments, PCI DSS rules apply. Sensitive cardholder data cannot be stored unencrypted, and access must be tightly restricted.
- SOC 2: For technology vendors, SOC 2 demonstrates a mature security posture. Many enterprise buyers demand it as part of their vendor evaluation.
Table: Compliance Standards by Scenario
| Use Case | Standard to Follow | Key Requirements |
| Customer support in EU | GDPR | Consent, anonymization, right to erasure |
| Healthcare interactions | HIPAA | Encryption, audit logs, access control |
| Payment transactions | PCI DSS | Data encryption, restricted storage |
| Enterprise SaaS providers | SOC 2 | Controls for security, availability, privacy |
Building with compliance in mind from the start prevents costly redesigns later and makes enterprise adoption smoother.
Discover how secure outbound voice campaigns use AI-driven personalization over VoIP networks to improve engagement, trust, and customer satisfaction.
What Is the Future of Securing Voice AI and VoIP?
The landscape of security is constantly evolving. As attackers become more sophisticated, defenses must anticipate rather than just react. Several trends are shaping the future of VoIP network security and voice AI protection.
The first is the rise of zero-trust architectures. Traditional systems often assume that once someone is inside the network, they can be trusted. Zero trust removes this assumption. Every call, every request, every action is verified, regardless of origin.
The second is AI-driven anomaly detection. Just as attackers are automating their methods, defenders are applying machine learning to detect unusual call patterns or AI behaviors. For example, if an agent suddenly receives hundreds of near-identical requests, anomaly detection can pause activity before damage is done.
A third trend is preparation for quantum-resistant encryption. Current encryption methods like RSA may eventually be broken by quantum computing. Forward-looking organizations are already testing post-quantum algorithms to ensure their voice systems remain secure for decades to come.
Finally, there is growing momentum behind privacy-preserving AI techniques such as federated learning and differential privacy. These allow models to improve using distributed data without directly exposing sensitive transcripts or recordings. This makes the AI smarter while keeping personal information protected.
Conclusion
Real-time voice assistants on VoIP are already transforming customer interactions, but their success depends on trust. That trust is built by securing every layer: encrypting the VoIP transport, protecting AI pipelines, safeguarding integrations, and aligning with compliance frameworks. For founders, product managers, and engineering leads, the challenge is doing all this without delaying innovation.
Frejun Teler solves this by providing a secure, enterprise-grade backbone for AI voice deployments. It delivers encrypted transport, stable session management, and developer-first SDKs, so teams can focus on building intelligent voice experiences instead of managing infrastructure risk.
Ready to secure your voice AI journey?
Schedule a demo for Teler and see how quickly you can launch safely.
FAQs –
1: What is the secure protocol for VoIP?
The most secure protocols are SRTP for media streams and TLS for signaling.
2: What is secure VoIP?
Secure VoIP encrypts calls, protects signaling, and prevents unauthorized access to voice data.
3: How secure is VoIP phone service?
With SRTP, TLS, MFA, and monitoring, VoIP phone service can be highly secure.
4: How do you secure Voice AI on VoIP networks?
Combine VoIP encryption, AI input validation, strict access control, and compliance-driven data protection.
