When you are building a real-time AI agent, the temptation is to compare vendors head-to-head. Should you use AssemblyAI or Pipecat? For developers, the answer is clear once you look under the hood: they’re not substitutes but complements.
AssemblyAI provides transcription and audio intelligence APIs, while Pipecat is the open-source framework that orchestrates those services into a low-latency pipeline. Understanding how they fit together is the difference between hacking a demo and architecting a production-ready system.
Table of contents
- The Misleading Showdown in Voice AI Development
- The Anatomy of a Modern AI Voice Agent
- What is AssemblyAI.com? The Master of Audio Intelligence
- What is Pipecat.ai? The Real-Time Conversation Orchestrator
- The Missing Link: The Voice Transport Layer That Powers It All
- Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai: A Comparison of Roles, Not Rivals
- How a Production-Grade Voice Agent Works? A Step-by-Step Guide
- Final Thoughts: Building Your AI Stack with an Architect’s Mindset
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The Misleading Showdown in Voice AI Development
In the rapidly expanding universe of AI voice technology, development teams often find themselves evaluating tools by pitting them against each other. This leads to questions that, on the surface, seem logical: “Which platform is better for our AI agent? Should we use AssemblyAI or Pipecat?” This framing creates a false dilemma, a showdown between two platforms that are not actually in competition. The debate over Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai is one of the most common yet fundamentally misunderstood comparisons in the space.
Asking to choose between them is like asking a chef to choose between their finest ingredients and their fully equipped kitchen. You need both to prepare a meal. AssemblyAI is a premier ingredient, a specialized service for understanding audio with incredible precision. Pipecat is the kitchen, the open-source framework that orchestrates all the ingredients and processes to create the final conversational dish.
This guide will dismantle the flawed Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai comparison. We will explore their distinct and complementary roles, clarify how they work together to create a powerful voice agent, and highlight the critical, often-overlooked infrastructure layer that neither provides, but which is essential for any real-world application.
Also Read: Assemblyai.com vs Elevenlabs.io: Feature by Feature Comparison for AI Voice Agents
The Anatomy of a Modern AI Voice Agent
To grasp why this comparison is misleading, you must first understand the modern voice AI stack. A real-time conversational agent is not a single piece of software but an ecosystem of specialized services working in perfect harmony.
- The Ears (Speech-to-Text): This layer listens to the incoming audio from a user and transcribes it into text with speed and accuracy. Its performance dictates whether your agent understands the user correctly.
- The Brain (LLM & Logic): This is the core intelligence. It takes the transcribed text, comprehends the user’s intent, queries any necessary data, and formulates a response in text form.
- The Voice (Text-to-Speech): This layer takes the text response from the brain and synthesizes it into natural-sounding, human-like speech.
- The Orchestrator (Framework): This is the conductor of the entire process. It manages the real-time flow of data between the ears, brain, and voice, ensuring the conversation happens with minimal latency and no awkward pauses.
- The Transport Layer (Telephony Infrastructure): This is the foundational plumbing. It connects the entire AI stack to the outside world via a phone number, managing the call itself and streaming audio back and forth reliably.
With this framework in mind, the roles of AssemblyAI and Pipecat become crystal clear.
What is AssemblyAI.com? The Master of Audio Intelligence
AssemblyAI is a leading AI company that specializes in a single, complex domain: understanding and processing audio data. Through a suite of powerful APIs, it provides developers with the tools to transcribe and analyze spoken content with exceptionally high accuracy. It serves as the hyper-intelligent “ears” of your voice AI stack.
Its models are trained on a massive dataset, allowing them to deliver precise transcriptions in real time, even in challenging audio environments.
Key Features and Strengths of AssemblyAI
- High-Precision Transcription: At its core, AssemblyAI offers state-of-the-art speech-to-text (ASR) capabilities, forming the reliable foundation for any voice application.
- Rich Audio Intelligence: It goes far beyond simple transcription, offering a deep understanding of the audio content through features like:
- Speaker Diarization: Identifying and labeling different speakers in a single audio stream.
- Summarization: Automatically generating concise summaries of long conversations or recordings.
- Keyword Spotting: Detecting specific keywords or phrases mentioned by the user.
- Content Moderation: Flagging sensitive or inappropriate content within a conversation.
- Intelligent Turn-Detection: AssemblyAI uses a sophisticated hybrid approach called “semantic endpointing.” It analyzes both the audio context (pauses, intonation) and the transcribed text to determine when a user has naturally finished speaking, which is crucial for preventing awkward interruptions.
Ideal Use Cases for AssemblyAI
AssemblyAI is the perfect tool for any backend process that requires deep insights from audio. This includes call center analytics, compliance monitoring, generating captions for media, and, most importantly, providing the clean, accurate transcription that a conversational agent needs to function.
Also Read: Elevenlabs.io vs Vapi.ai: A Feature-by-Feature Comparison for AI Voice Agents
What is Pipecat.ai? The Real-Time Conversation Orchestrator
Pipecat.ai, an open-source Python framework from the creators of Daily.co, is designed to solve a different problem entirely. It doesn’t transcribe audio itself; instead, it serves as the high-speed “orchestrator” for the entire real-time conversation. It is the framework that manages the flow of data between all the other components, the ears, brain, and voice.
If AssemblyAI is a specialized component, Pipecat is the modular chassis you build your agent upon, allowing you to plug in your choice of services.
Key Features and Strengths of Pipecat.ai
- Ultra-Low Latency Orchestration: Pipecat is built for speed. It manages the entire conversational pipeline—from receiving user audio to generating a spoken response—with a focus on minimizing latency to create fluid, natural interactions.
- Open-Source and Modular: As a Python framework, it offers developers complete control and flexibility. You can easily plug in various AI services, meaning you can use AssemblyAI for transcription today and switch to another provider tomorrow if needed. It supports a wide range of STT, LLM, and TTS integrations.
- Real-Time Media Management: Pipecat is designed to handle live, streaming media, including both voice and video. This makes it ideal for building interactive front-end applications.
- Audio-Centric Turn Detection: Pipecat also includes its own turn-detection models, which analyze audio features like prosody and intonation to determine when a user has finished their thought.
Ideal Use Cases for Pipecat.ai
Pipecat is suited for building the interactive agent itself. Use cases include AI avatars, virtual customer support agents, NPCs in games, and any application where real-time, back-and-forth conversation is the core feature.
The Missing Link: The Voice Transport Layer That Powers It All
So, you have AssemblyAI as your ears and Pipecat as your orchestrator. Your agent can theoretically listen and respond. But a critical question remains: How does a customer on a phone actually talk to it?
- How do you get a phone number for your agent?
- What infrastructure handles the actual call connection?
- What system captures the audio from the phone network and streams it to your Pipecat agent with minimal latency?
- What system takes the final audio from Pipecat and plays it back to the customer with crystal clarity?
This is the role of the voice transport layer. Neither AssemblyAI nor Pipecat is a telephony company. They require a foundational platform to manage the real-world communication plumbing.
This is the exact problem FreJun solves. FreJun provides the robust, developer-first voice infrastructure that acts as the bridge between your entire AI stack and the global telephone network. We handle the complex, low-level streaming and call management, ensuring your brilliantly orchestrated agent has a reliable, carrier-grade connection to your users.
Also Read: Retellai.com vs Synthflow.ai: Feature by Feature Comparison for AI Voice Agents
Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai: A Comparison of Roles, Not Rivals
To put the Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai discussion to rest, let’s compare their fundamental roles within a voice AI architecture. This is not a list of competing features but a clarification of their distinct and symbiotic functions.
| Aspect | AssemblyAI.com | Pipecat.ai |
| Primary Role | Component (The ‘Ears’) | Framework (The ‘Orchestrator’) |
| Core Function | Understands & analyzes incoming audio. | Manages & generates outgoing responses. |
| Core Technology | Speech-to-Text (ASR) & Audio Intelligence | Real-Time Media Orchestration |
| Place in Stack | A specialized service you plug into a framework. | The framework that you plug services into. |
| Relationship | Collaborative. AssemblyAI is a premier STT provider for Pipecat. | Collaborative. Pipecat is a framework that leverages services like AssemblyAI. |
| Key Focus | Accuracy of transcription and audio insights. | Latency of the end-to-end conversational loop. |
| Open Source | No, it is a proprietary API-based service. | Yes, it is an open-source Python framework. |
How a Production-Grade Voice Agent Works? A Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s walk through a real-world scenario to see how FreJun, Pipecat, and AssemblyAI work together to handle a live customer call.
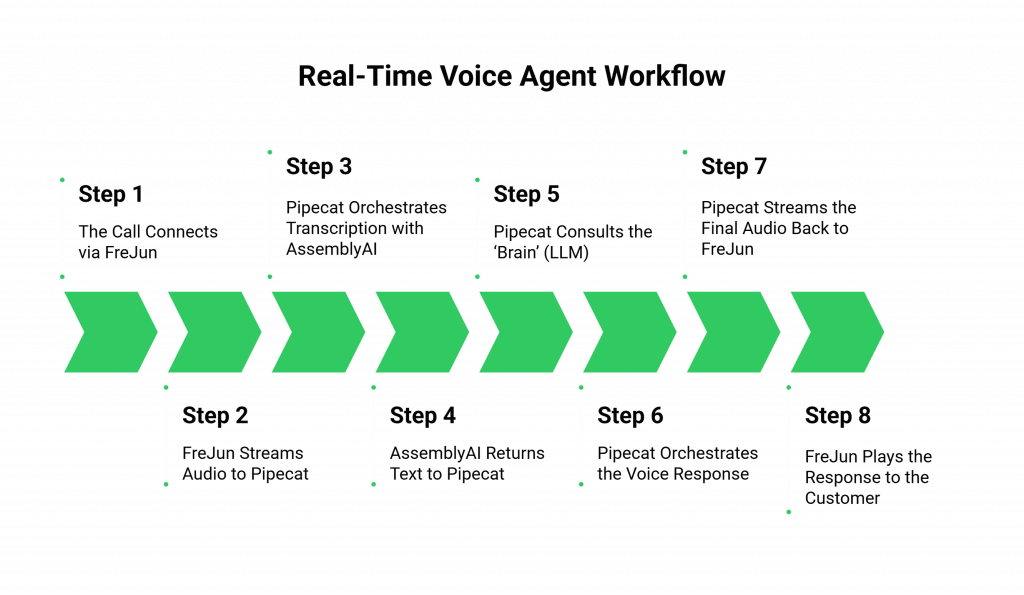
- Step 1: The Call Connects via FreJun: A customer dials the phone number you’ve provisioned through FreJun. Our platform answers the call and establishes a stable, low-latency media stream.
- Step 2: FreJun Streams Audio to Pipecat: As the customer speaks, FreJun captures their voice from the telephone network and streams the raw audio data in real time to your Pipecat agent.
- Step 3: Pipecat Orchestrates Transcription with AssemblyAI: Your Pipecat application, acting as the orchestrator, immediately forwards this incoming audio stream to the AssemblyAI API for transcription.
- Step 4: AssemblyAI Returns Text to Pipecat: AssemblyAI processes the audio with incredible speed, transcribes it into accurate text, and sends this text data back to your Pipecat framework.
- Step 5: Pipecat Consults the ‘Brain’ (LLM): Pipecat takes the transcribed text and passes it to your chosen Large Language Model (e.g., GPT-4). The LLM analyzes the user’s intent and generates a text-based response.
- Step 6: Pipecat Orchestrates the Voice Response: The LLM’s text response is sent back to Pipecat. Pipecat then forwards this text to your chosen Text-to-Speech (TTS) service (e.g., ElevenLabs, PlayHT).
- Step 7: Pipecat Streams the Final Audio Back to FreJun: The TTS service generates the audio for the response and streams it back to Pipecat. Pipecat then pipes this final audio output into the FreJun media stream.
- Step 8: FreJun Plays the Response to the Customer: FreJun takes the audio from your agent and plays it back to the customer over the phone, completing the conversational loop with minimal perceptible delay.
Also Read: Deepgram.com vs Play.ai: A Feature-by-Feature Comparison for AI Voice Agents
Final Thoughts: Building Your AI Stack with an Architect’s Mindset
To build a truly exceptional AI voice agent, you must think like an architect, not just a shopper. An architect doesn’t ask if bricks are better than plumbing; they understand that a functional building requires both, working in harmony. Similarly, in the world of voice AI, AssemblyAI provides the robust bricks of audio understanding, while Pipecat offers the sophisticated plumbing to manage the flow of conversation.
The flawed Assemblyai.com vs Pipecat.ai comparison dissolves when you see them as powerful allies in your development stack. By leveraging AssemblyAI’s world-class transcription accuracy within Pipecat’s flexible, low-latency orchestration framework, you can build a voice agent that is both incredibly intelligent and remarkably responsive.
However, even the most perfectly designed building is useless without a solid foundation. In voice AI, that foundation is the transport layer. FreJun provides the carrier-grade infrastructure to ensure that your meticulously architected agent can communicate with the outside world reliably, clearly, and at scale.
Also Read: Saudi Arabia’s Financial Institutions: How to Use WhatsApp Approved Templates Effectively
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To build a high-quality agent, you need a transcription service (like AssemblyAI) and an orchestration framework (like Pipecat). Pipecat is open-source and modular, so while AssemblyAI is a top choice for transcription, you could plug in other providers. But you always need both functions.
Pipecat’s main benefit is managing the complex, real-time flow of data between multiple AI services (STT, LLM, TTS) with a focus on minimizing latency. This is crucial for creating natural, fluid conversations without awkward delays.
While you could for a non-real-time task (like analyzing a recording), for a live conversation, you need a framework like Pipecat to handle the continuous, bidirectional streaming of audio and data between all the necessary services and the end-user.
No, they do not perform the same function. Pipecat is a free, open-source framework for building agents. AssemblyAI is a paid, proprietary service for transcribing audio. You would typically pay for AssemblyAI’s service and use the free Pipecat framework to manage it.
