The evolution of the chatbot has been a journey from simple text-based scripts to intelligent, conversational partners. The latest and most powerful leap in this evolution is the ability to move from text to talk, creating a voice-based experience that is not only conversational but also actionable. By building a chatbot with API calls, you can create an AI agent that doesn’t just provide information, it performs tasks. It can check an account balance, book an appointment, or process an order, all through a natural, spoken dialogue.
Table of contents
- What is a Voice-Based Chatbot with API Calls?
- The Hidden Roadblock: Your Bot Can Talk to APIs, But Not on the Phone
- FreJun: The API That Connects Your Bot to the World
- In-App Bot vs. Omnichannel Bot: A Strategic Comparison
- How to Build a Complete Voice-Based Chatbot with API Calls?
- Best Practices for a Flawless, Action-Oriented Voice Experience
- Final Thoughts: From a Smart Assistant to a Powerful Agent
This fusion of voice and action is the new frontier of user experience. However, after successfully building the complex backend logic to orchestrate these API calls, many development teams hit a critical and often insurmountable roadblock. Their brilliant, action-oriented bot is trapped, unable to connect to the most important channel for business communication: the telephone.
What is a Voice-Based Chatbot with API Calls?
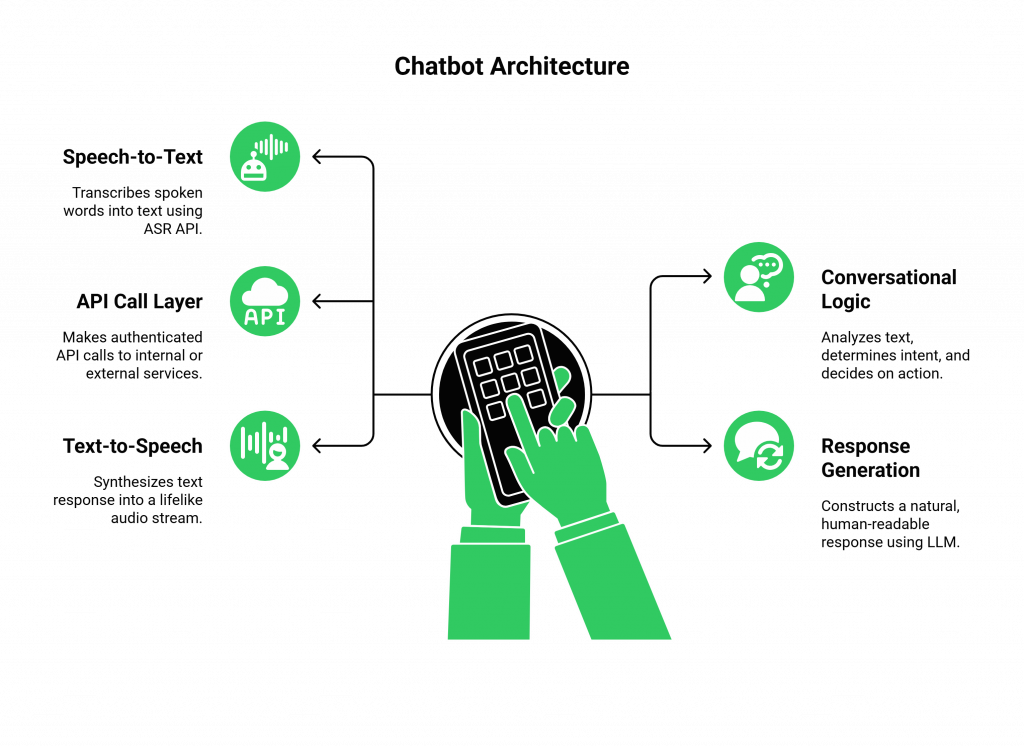
A voice-based chatbot with API calls is a sophisticated system that uses a real-time pipeline of technologies to simulate a helpful, human-like agent. The architecture is a symphony of API integrations:
- Speech-to-Text (ASR): A user speaks a command, and an ASR API (like OpenAI Realtime or Google Speech-to-Text) transcribes their words into text.
- Conversational Logic (LLM): The transcribed text is sent to the bot’s “brain”, a language model like GPT-4o. The AI analyzes the user’s intent and determines if it needs to perform an action.
- API Call Layer: If an action is required, the bot’s backend makes an authenticated API call to an internal or external service (e.g., a CRM, a booking system, or a database).
- Response Generation: The bot receives the result from the API call and uses the LLM to construct a natural, human-readable response.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): The bot’s text response is sent to a TTS API (such as one from ElevenLabs or Google) that synthesizes it into a lifelike audio stream.
This pipeline allows a user to say, “What’s the status of my recent order?” and get a real, spoken answer based on live data from your e-commerce platform.
The Hidden Roadblock: Your Bot Can Talk to APIs, But Not on the Phone
You have successfully built this pipeline. Your backend is a model of efficient API orchestration. Your bot can listen, think, and act. It works perfectly when a user interacts with it through your website or mobile app. Now, your business wants to deploy this powerful agent on its customer service hotline. This is where the project stalls.
The problem is that the entire ecosystem of technologies you’ve used, from the browser’s microphone APIs to the AI services, was not designed to interface with the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). To make your bot answer a phone call, you would have to build a highly specialized and complex voice infrastructure stack from the ground up. This involves solving a host of non-trivial engineering challenges:
- Telephony Protocols: Managing SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) trunks to connect to telecom carriers.
- Real-Time Media Servers: Building and maintaining dedicated servers to handle raw audio streams from thousands of concurrent calls.
- Call Control Signaling: Architecting a system to programmatically manage the entire lifecycle of every phone call.
Your brilliant bot, capable of making any API call you can imagine, is ironically unable to answer the most important call of all: a customer’s.
FreJun: The API That Connects Your Bot to the World
This is the exact problem FreJun AI solve. We are not another AI API. We are the specialized voice infrastructure platform that provides the missing API, the one that connects the voice-based chatbot with API calls you’ve already built to the telephone network.
FreJun handles all the complexities of telephony, allowing you to focus on what you do best: orchestrating APIs to create an intelligent and actionable bot.
- We are AI-Agnostic: You bring your own “brain.” FreJun integrates seamlessly with any backend built on any combination of STT, LLM, TTS, and business APIs.
- We Manage the Voice Transport: We handle the phone numbers, the SIP trunks, the global media servers, and the low-latency audio streaming.
- We Provide a Simple, Developer-First API: Our platform makes a live phone call look like just another WebSocket connection to your application.
With FreJun, you can finally unleash the full power of your action-oriented bot, making it accessible to all your customers, on any channel.
Key Takeaway
Building a voice-based chatbot with API calls is a two-part challenge. The first part is the AI and business logic orchestration, a familiar task for skilled backend developers. The second, much harder part is the voice infrastructure needed to connect that logic to the telephone network. FreJun provides the simple, powerful API that solves this second problem, enabling you to focus on your core competency while still delivering an enterprise-grade, omnichannel solution.
In-App Bot vs. Omnichannel Bot: A Strategic Comparison
| Feature | The In-App Chatbot with API Calls | The Omnichannel Chatbot with API Calls (Powered by FreJun) |
| Accessibility | Limited to users who are actively on your website or in your app. | Universally accessible to anyone with a phone, plus all digital channels. |
| Use Cases | In-app account management, on-site order tracking. | 24/7 call centers, automated phone orders, virtual receptionists, critical incident support. |
| Business Impact | A powerful feature for your digital-savvy users. | A transformative business tool that serves all customer segments. |
| Infrastructure Burden | Low for web deployment. Immense if you attempt to build your own telephony. | Zero telephony infrastructure to build. FreJun manages the entire voice stack. |
| Customer Journey | Fragmented. A user may have to switch from a call to your app to get automated help. | Unified. A user can interact with the same intelligent agent across all channels. |
How to Build a Complete Voice-Based Chatbot with API Calls?
This step-by-step guide outlines the modern architecture for creating a single AI agent that works across your website, mobile app, and the phone.
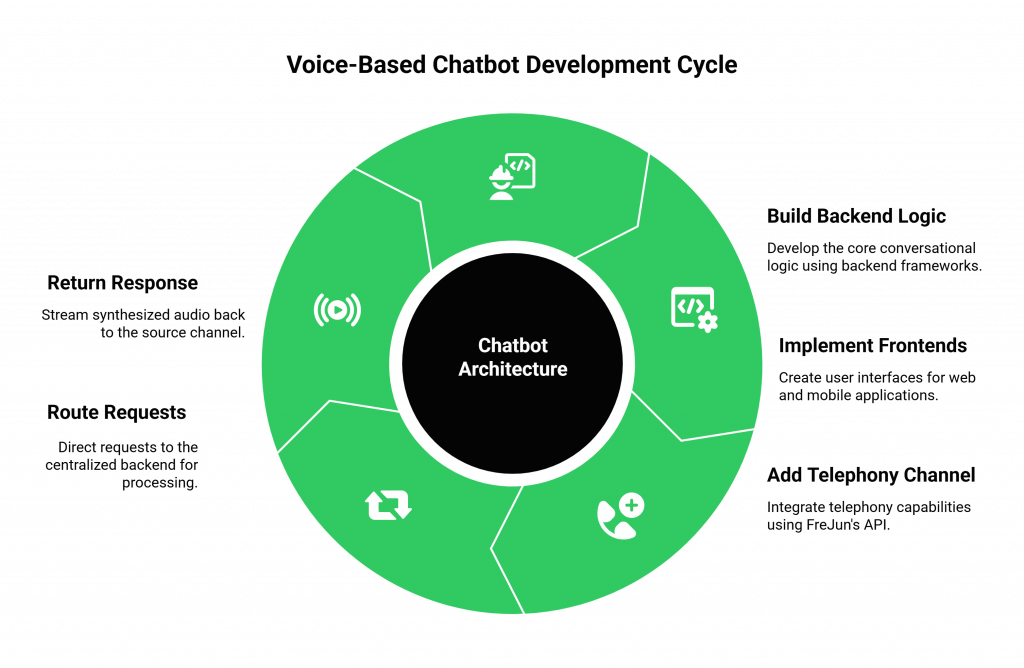
Step 1: Architect Your Backend for Orchestration
First, build your core conversational logic. Using your preferred backend framework (like FastAPI or Express.js), write the code that orchestrates the entire pipeline: STT, LLM, your internal/external business APIs, and TTS. This backend is the heart of your chatbot with API calls.
Step 2: Implement Your Digital Frontends
Build the user interfaces for your web and mobile applications. Use client-side libraries to capture microphone audio and stream it to your backend.
Step 3: Add the Telephony Channel with FreJun’s API
This is the critical step that makes your bot truly omnichannel.
- Sign up for FreJun and instantly provision a virtual phone number.
- Use FreJun’s server-side SDK in your backend to handle incoming WebSocket connections from our platform.
- In the FreJun dashboard, configure your number’s webhook to point to your backend’s API endpoint.
Step 4: Route All Requests to Your Centralized Backend
Your backend will now receive requests from multiple channels. You can easily identify the source and then route the data to the same core logic you built in Step 1. Your bot’s intelligence and its ability to make API calls remain consistent across all platforms.
Step 5: Return the Response to the Correct Channel
Once your bot has made its API calls and generated a response, your backend streams the synthesized audio back to the source it came from, either to the web/mobile client or to the FreJun API, which plays it to the caller.
Best Practices for a Flawless, Action-Oriented Voice Experience
- Use Persistent, Low-Latency Connections: For real-time voice and fast API responses, use WebSockets to manage the bi-directional flow of data.
- Handle Asynchronous API Calls: Design your backend to handle API calls that may take a few moments to respond. Your bot can provide an interim response like, “One moment while I check that for you,” to create a more natural experience.
- Secure All Your Endpoints: Never expose your API keys on the client side. Manage all credentials securely on your backend and ensure all communication is encrypted.
- Design for Failure: Your bot’s logic should gracefully handle failed API calls, providing a helpful error message to the user or offering to escalate the conversation to a human agent.
Final Thoughts: From a Smart Assistant to a Powerful Agent
The ability to build a voice-based chatbot with API calls is a game-changer. It elevates your bot from a passive information source to an active agent that can get things done on behalf of your users. But this power is only fully realized when it is not confined to a single channel.
By adopting a true omnichannel strategy, you can transform your bot into a powerful, 24/7 workhorse for your entire business. The path to this transformation doesn’t require you to become a telecom company. It requires a smart integration strategy that combines the best AI and business APIs with a robust voice infrastructure partner.
Let FreJun handle the phone lines, so you can focus on building a bot that can truly talk the talk and walk the walk.
Further Reading – Conversational Voice AI for SaaS Developers: A How-To
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No, it integrates with it. You use an LLM API to provide the “brain” for your bot. FreJun provides the “body”, the ability for that brain to listen, speak, and interact over a real phone call.
Yes. Because your own backend is orchestrating the process, it can securely make authenticated API calls to any of your internal microservices, databases, or legacy systems.
We offer developer-first SDKs and a simple API. If your team can work with a standard backend framework and a WebSocket connection, you have all the skills needed to integrate FreJun.
Your backend is responsible for managing the session state. FreJun provides a unique session ID for each call, which you can use as a key to store and retrieve the entire conversation history, including the results of previous API calls, from a database or cache.
Absolutely. FreJun’s API provides full call control, including initiating outbound calls. You could, for example, have your bot proactively call a customer to inform them about their order status, a workflow that an API call to your shipping provider would trigger.
